Abstract
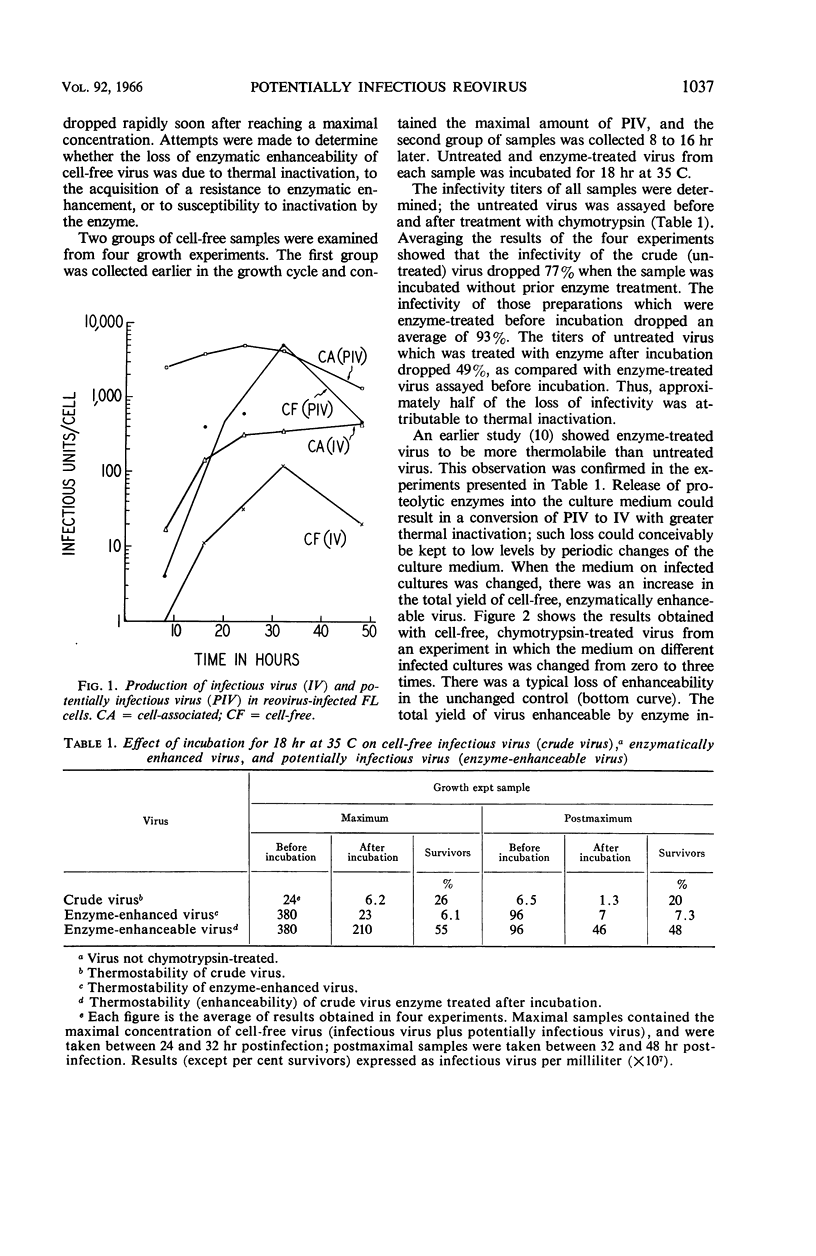
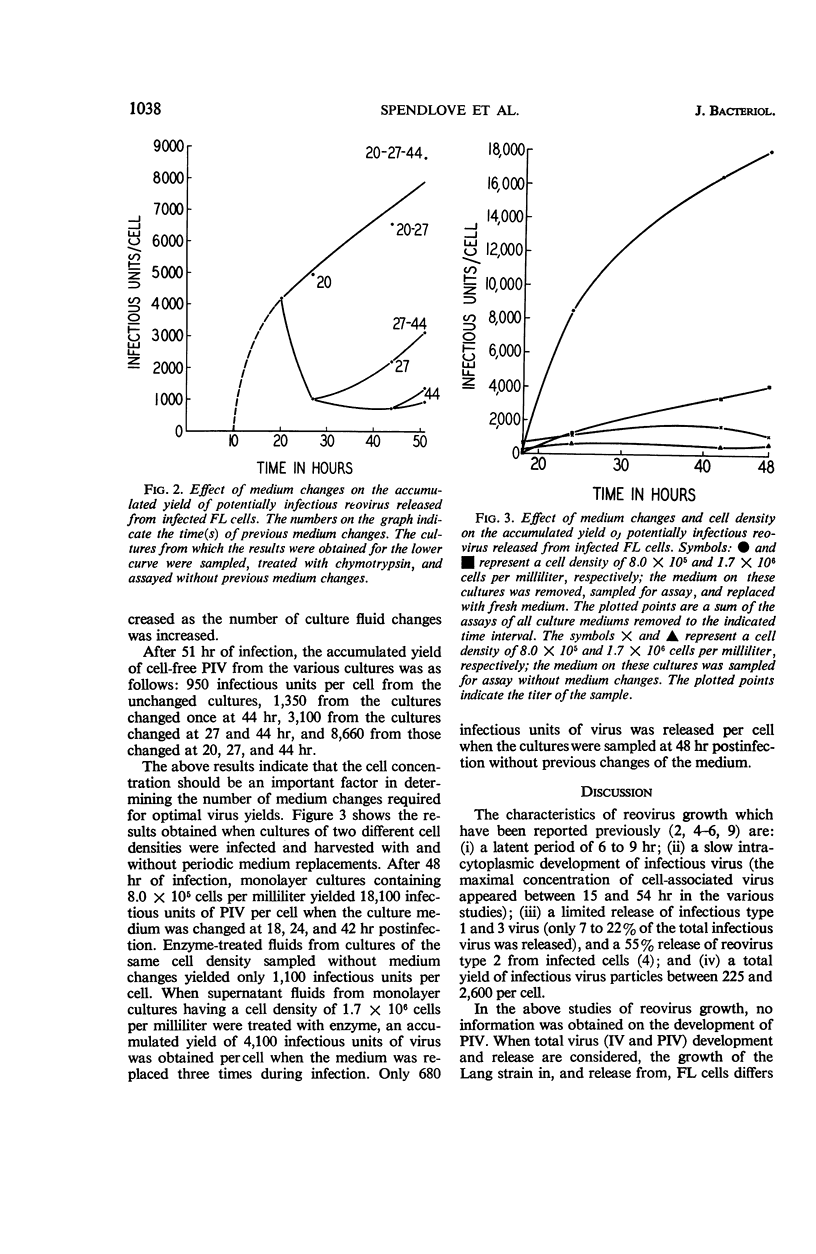
Spendlove, Rex S. (California State Department of Public Health, Berkeley), Edwin H. Lennette, Charles O. Knight, and Jean N. Chin. Production in FL cells of infectious and potentially infectious reovirus. J. Bacteriol. 92:1036–1040. 1966.—A comparative study was made of the development in, and release from, FL cells of infectious and potentially infectious (chymotrypsin-activatable) reovirus (Lang strain). The latent period was shorter, the rate of synthesis was more rapid, and the total yield was more than 10-fold greater in potentially infectious virus as compared with infectious virus. Almost all of the potentially infectious virus, but only approximately one-third of the infectious virus, was released from the infected cells.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DALES S. ASSOCIATION BETWEEN THE SPINDLE APPARATUS AND REOVIRUS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Aug;50:268–275. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.2.268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOMATOS P. J., TAMM I., DALES S., FRANKLIN R. M. Reovirus type 3: physical characteristics and interaction with L cells. Virology. 1962 Jul;17:441–454. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90139-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oie H., Loh P. C., Soergel M. Growth characteristics and immunocytochemical studies of reovirus type 2 in a line of human amnion cells. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1966;18(1):16–24. doi: 10.1007/BF01241697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RHIM J. S., JORDAN L. E., MAYOR H. D. Cytochemical, fluorescent-antibody and electron microscopic studies on the growth of reovirus (ECHO 10) in tissue culture. Virology. 1962 Jun;17:342–355. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90125-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RHIM J. S., SMITH K. O., MELNICK J. L. Complete and coreless forms of reovirus (ECHO 10). Ratio of number of virus particles to infective units in the one-step growth cycle. Virology. 1961 Dec;15:428–435. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90110-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPENDLOVE R. S., LENNETTE E. H., CHIN J. N., KNIGHT C. O. EFFECT OF ANTIMITOTIC AGENTS ON INTRACELLULAR REOVIRUS ANTIGEN. Cancer Res. 1964 Nov;24:1826–1833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPENDLOVE R. S., LENNETTE E. H., JOHN A. C. THE ROLE OF THE MITOTIC APPARATUS IN THE INTRACELLULAR LOCATION OF REOVIRUS ANTIGEN. J Immunol. 1963 Apr;90:554–560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPENDLOVE R. S., LENNETTE E. H., KNIGHT C. O., CHIN J. N. DEVELOPMENT OF VIRAL ANTIGEN AND INFECTIOUS VIRUS IN HELA CELLS INFECTED WITH REOVIRUS. J Immunol. 1963 Apr;90:548–553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPENDLOVE R. S., SCHAFFER F. L. ENZYMATIC ENHANCEMENT OF INFECTIVITY OF REOVIRUS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Mar;89:597–602. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.3.597-602.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALLIS C., SMITH K. O., MELNICH J. L. REOVIRUS ACTIVATION BY HEATING AND INACTIVATION BY COOLING IN MGC12 SOLUTIONS. Virology. 1964 Apr;22:608–619. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90083-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


