Abstract
As part of a research programme focused on flavonoid biosynthesis in the seed coat of Brassica napus L. (oilseed rape), orthologs of the BANYULS gene that encoded anthocyanidin reductase were cloned in B. napus as well as in the related species Brassica rapa and Brassica oleracea. B. napus genome contained four functional copies of BAN, two originating from each diploid progenitor. Amino acid sequences were highly conserved between the Brassicaceae including B. napus, B. rapa, B. oleracea as well as the model plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Along the 200 bp in 5′ of the ATG codon, Bna.BAN promoters (ProBna.BAN) were conserved with AtANR promoter and contained putative cis-acting elements. In addition, transgenic Arabidopsis and oilseed rape plants carrying the first 230 bp of ProBna.BAN fused to the UidA reporter gene were generated. In the two Brassicaceae backgrounds, ProBna.BAN activity was restricted to the seed coat. In B. napus seed, ProBna.BAN was activated in procyanidin-accumulating cells, namely the innermost layer of the inner integument and the micropyle-chalaza area. At the transcriptional level, the four Bna.BAN genes were expressed in the seed. Laser microdissection assays of the seed integuments showed that Bna.BAN expression was restricted to the inner integument, which was consistent with the activation profile of ProBna.BAN. Finally, Bna.BAN genes were mapped onto oilseed rape genetic maps and potential co-localisations with seed colour quantitative trait loci are discussed.
Keywords: Anthocyanidin reductase, BANYULS genes, Brassica, Flavonoid metabolism, Seed coat-specific promoter
Introduction
Oilseed rape (Brassica napus L., AACC 2n = 38) is a worldwide major oil crop that also supplies oil-free meal with a high-protein content (38–40%) and a well-balanced amino acid composition. However, the use of oilseed rape meal as a source of proteins for livestock is still limited due to undesirable compounds, such as glucosinolates, phytic acid and phenolics. For instance, the concentration of phenolics in Brassica spp. is at least 30 times higher than the one of soybean (Shahidi and Naczk 1992). Major phenolics in B. napus seed are phenolic acids and procyanidins (Naczk et al. 1998). Procyanidins are flavonoid end-products (Fig. 1a) that accumulate as colourless compounds in the seed coat during seed development (Nesi et al. 2009) and turn to brown to dark colour upon oxidations during seed desiccation. Despite their numerous biological effects, seed phenolics and more particularly procyanidins are often considered as anti-nutritionals in oilseed rape, because they impact negatively animal production (especially for non-ruminant livestock) by altering feed intake and/or by lowering live weight gains. Indeed, these compounds contribute to oilseed rape meal dark colour, bitter taste and astringency (Shahidi and Naczk 1992). In addition, phenolics are able to form complexes with proteins, polysaccharides and other macromolecules, thus, reducing their bioavailability and/or their in vivo digestibility (Naczk et al. 1998). They can also bind enzymes of the digestive system, thus inhibiting their activities (Fenwick et al. 1984). On the opposite, in other crops such as legumes, proanthocyanidins have a recognised role in the prevention of pasture bloat for ruminants (reviewed in Marles et al. 2003b).
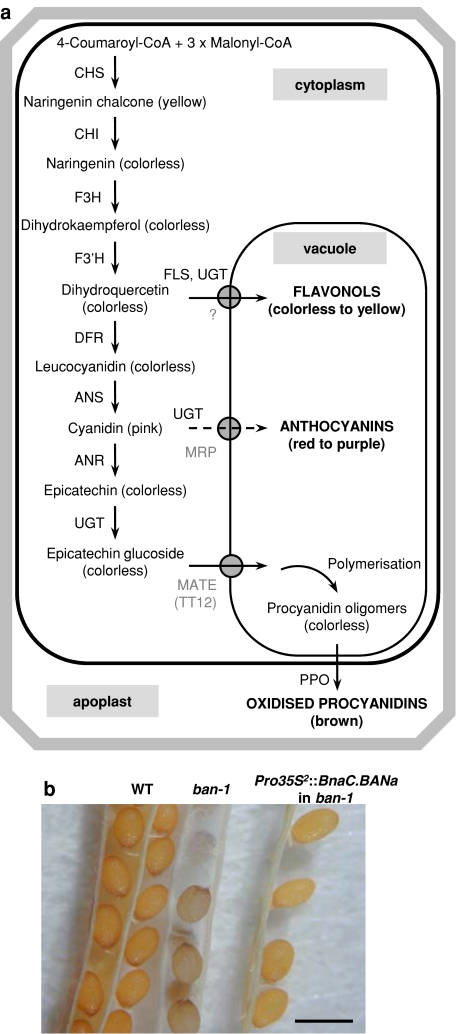
Fig. 1.
Flavonoid metabolism in seeds: the importance of ANR encoded by BAN. a Flavonoid biosynthetic pathway in the seed coat from Brassicaceae. Transporters are indicated in grey. Dashed line indicates the anthocyanin sub-branch that was not identified in the seed coat. ANR anthocyanidin reductase, ANS anthocyanidin synthase, CHI chalcone isomerase, CHS chalcone synthase, DFR dihydroflavonol 4-reductase, F3H flavanone 3-hydroxylase, F3′H flavonoid 3′-hydroxylase, FLS flavonol synthase, MATE multidrug and toxic compound extrusion transporter, MRP multidrug resistance-associated protein, PPO polyphenol oxidase, UGT uridine diphosphate glycosyltransferase. b Complementation of Arabidopsis ban phenotype by oilseed rape BAN genes. Seeds are from the wild-type genotype (WT, left), the Arabidopsis ban-1 null mutant (middle) and the T2 progeny of ban-1 carrying the Pro35S 2::BnaC.BANa construct (right). All the genotypes were from the Wassilewskija-2 ecotype. Plants were grown at the same time to avoid subtle colour variations inherent to plant culture conditions and seed age. Bar 500 μm
Yellow seediness, which is associated with a reduction in procyanidin content, represents a major agronomic trait for Brassica crop improvement and has concentrated important research efforts over the last two decades. Indeed, yellow-seeded Brassica lines offer advantages over their black-seeded counterparts in that they display higher levels in oil and proteins as well as a lower dietary fibre content associated with a thinner seed coat (Simbaya et al. 1995; Slominski et al. 1999). Therefore, the resulting meal has an improved energy value. Yellow-seeded lines naturally exist for several Brassica spp. including B. rapa (AA 2n = 20), B. juncea (AABB 2n = 36) or B. carinata (BBCC 2n = 34), whereas all B. napus genotypes produce brown to black seeds.
Several studies reported the use of interspecific crosses to transfer yellow seediness from Brassica spp. to B. napus (reviewed in Rahman 2001). However, this approach has proven to be difficult and rather inefficient. Indeed, the resulting oilseed rape germplasms still display brown pigments and the phenotype is highly variable depending on the environmental growth conditions (Van Deynze et al. 1993). In addition, yellow-seeded Brassica forms often show precocious germination (Ren and Bewley 1998) and a low agronomic value (Rakow et al. 1999). One could hypothesise that the entire flavonoid pathway is more or less altered in this yellow-seeded plant material, thus, reducing the whole plant vigour. Indeed, seed flavonoids are involved in defence against biotic stresses and contribute to physiological processes such as seed maturation or dormancy (reviewed in Shirley 1998). Reverse genetic approaches based on the target genes specifically involved in the procyanidin branch of flavonoid metabolism (see Fig. 1a) could open promising way to develop stable yellow-seeded B. napus lines impaired in seed coat pigmentation with no or few collateral effects on the whole plant pigmentation or on other seed flavonoids. To date, only one Chinese group reported the existence of yellow-seeded B. napus lines available commercially. Indeed, two yellow-seeded B. napus hybrid cultivars were registered in China in 2003 and 2004 and are planted over to one million ha area (Li et al. 2007).
Molecular bases of seed pigmentation in Brassica spp. remain largely unknown despite the identification of numerous molecular markers linked to seed colour trait (Somers et al. 2001; Liu et al. 2005). The dihydroflavonol reductase (DFR) gene is assumed to act as a control point in seed pigmentation of B. carinata (Marles et al. 2003a) and B. juncea (E. Lionneton, INRA Dijon, France, personal communication). In contrast, flavonoid metabolism has been largely elucidated in the model crucifer Arabidopsis thaliana in which at least 23 loci are required for normal seed pigmentation (reviewed in Lepiniec et al. 2006). These genes are collectively named TRANSPARENT TESTA (TT)-like, since they confer a pale-brown to yellow seed phenotype when mutated. Nine of the 18 Arabidopsis TT-like genes that have been cloned and functionally characterised are restricted to procyanidin metabolism (reviewed in Lepiniec et al. 2006) and thus they stand for good candidate genes to investigate the procyanidin-related molecular mechanisms in B. napus.
Amongst these candidates, BANYULS (BAN) encodes an anthocyanidin reductase (AtANR; Devic et al. 1999; Xie et al. 2003), which plays a critical role in procyanidin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis seed coat. Indeed, AtANR catalyses the formation of the (−)-epicatechin from cyanidin (Xie et al. 2003; Fig. 1a) and appears to be the only procyanidin-unit producing enzyme, since no leucoanthocyanidin reductase (conversion of leucocyanidin to (+)-catechin) was found in Arabidopsis. This is consistent with the fact that only (−)-epicatechin was detected in Arabidopsis seed (Routaboul et al. 2006). In addition, the ban mutant phenotype is of particular interest, since cyanidin is rechanneled to the anthocyanin pathway in the seed coat, leading to greyish seeds (Albert et al. 1997; Devic et al. 1999). We previously provided evidence that epicatechin rather than catechin was produced in B. napus seed coats suggesting that orthologous BAN genes were functional in oilseed rape (Nesi et al. 2009).
Previous studies reported the feasibility to identify TT orthologous genes in Brassica. For instance, TT2, TT7 and TT12 orthologs have been identified in oilseed rape (Wei et al. 2007; Xu et al. 2007; Chai et al. 2009) and expressed sequences were found for TT8, TT16 and TTG1 (Nesi et al. 2009). In addition, we recently demonstrated that the Arabidopsis ANR (ProAtANR) promoter could be activated in B. napus (Nesi et al. 2009) suggesting that the regulatory mechanisms are conserved between the two Brassicaceae.
The aim of the present study was to characterise the BAN locus in B. napus (Bna.BAN) in terms of genomic and functional analyses. Our results led to the cloning of four BAN orthologs in the oilseed rape genome, which were able to functionally complement Arabidopsis ban null mutations. We also demonstrated that these genes were specifically expressed in the seed and that their promoters were activated into the seed coat of A. thaliana and B. napus. These results suggested that the Bna.BAN genes could be potential candidates for the production of low-procyanidin oilseed rape genotypes. Finally, the Bna.BAN genes were mapped onto the oilseed rape genetic map. The results are discussed with respect to comparative genomics between Brassicaceae.
Materials and methods
Plant material and growth conditions
Brassica napus L. Westar (spring double low cv., INRA Rennes, France) was chosen for oilseed rape genetic transformation assays and B. napus L. Jet Neuf (winter single low cv., INRA Rennes, France) was used for gene expression analyses as well as for microdissection assays. Details for oilseed rape growth conditions in greenhouse or under controlled conditions were reported previously (Nesi et al. 2009). For gene expression analysis and histochemical staining, tagged siliques were collected from individual plants at different stages of seed development from 5 to 60 days after pollination (dap) and seeds were carefully removed from siliques.
Arabidopsis thaliana L. wild-type plants from the Wassilevskija-2 ecotype (INRA Versailles, France) were used in this study as well as ban-1 (ABW1; Albert et al. 1997) and ban-4 (CUS2; Lepiniec et al., unpublished data) mutant lines. These two null mutants originated from the INRA Versailles Arabidopsis T-DNA lines collection. They were kindly provided by INRA Versailles and multiplied at INRA Rennes. Arabidopsis plants were routinely grown in a greenhouse (16-h photoperiod, 10–15°C night/20–25°C day temperature) on Traysubstrat 092 (Klasmann-Deilmann, Bourgoin Jallieu, France). For genetic transformation, 20–30 plants were grown together in 15 cm ∅ pots until flowering. For histochemical analyses, developing siliques of Arabidopsis transgenic plants were harvested at several days after flowering (1–10 daf) and carefully opened to allow seed staining and observations. For aseptic growth, seeds were surface sterilized and plated on MS medium. Petri dishes were incubated 48 h at 4°C to break seed dormancy and then placed into a growth room (22 ± 2°C; 16 h/8 h light/dark; 70 μmol m−2 s−1 light intensity) to allow germination.
Nucleic acid manipulations
Genomic DNA was isolated from young plant leaves using a cetyltrimethylammonium bromide method (Doyle and Doyle 1990) and treated with RNaseA (0.1 mg/mL). To check the presence of transgenes in the genome of transformed plants, we used a simplified genomic DNA extraction procedure as described by Klimyuk et al. (1993). Plasmid DNA was purified from bacterial overnight culture using the Qiagen Plasmid Maxi Kit (Qiagen, Chatsworth, CA, USA), following the recommendations of the supplier.
Total RNA from plant organs was extracted with the SV Total RNA Isolation System (Promega, Madison, WI, USA) according to the instructions of the manufacturer. The Absolutely RNA® FFPE Kit (Stratagene, Amsterdam, The Netherlands) was used to recover total RNA from paraffin-embedded tissues. All the extracts were treated with RNase-free DNase I (Promega) and RNA quality and quantity was estimated as described previously (Nesi et al. 2009). DNA-free RNA extract was converted into first-strand cDNA using the SuperScriptII pre-amplification system for first-strand synthesis kit (Invitrogen, Glasgow, UK) and oligo(dT)12–18, following the manufacturer’s recommendations.
Polymerase chain reactions (PCR) were conducted in a 20 μL mix containing 10 ng of DNA, 0.25 mM of dNTPs (Promega), 0.5 μM of each primers (Eurogentec, Angers, France) and 0.5 U of Taq DNA polymerase (Promega) in the appropriate buffer (1×) supplemented with 2.5 mM MgCl2. The amplification programme was run on a PTC-225 thermocycler (MJ Research, Waltham, MA, USA) with the following conditions: 35 cycles of denaturation at 94°C for 30 s (3 min for the first cycle), annealing at 55–60°C for 30 s and elongation at 72°C for 1 min 30 s (10 min for the last cycle). Sequences of primers used during the course of this work are given in Table 1. Enzymatic restriction of PCR products was conducted in a 10 μL mixture containing 5 μL of PCR sample and 5 U of enzyme (Promega), in the appropriate buffer (1×) supplemented with 1% BSA. PCR samples and enzymatic restriction products were migrated onto a 2.5% (w/v) agarose electrophoresis gel.
Table 1.
List of primers used in this study
| Primer names | Sequencesa (5′ → 3′) |
|---|---|
| AtANR-UP | GTCATTGGTGGCACGGGAAACTTAGCCT |
| AtANR-RP | GATCGGAGTTGCGACATGGAAGATGTA |
| BnBAN-UP1 | TACAAGGAGTGATCAACGTGTTG |
| BnBAN-UP2 | GATTTTCTCACAAAGGAGAAGC |
| BnBAN-UP3 | CGGTGGCACAGGAAACTTAGC |
| BnBAN-UP4 | CAAGGAAATGCAGAAGCTATC |
| BnBAN-UP5 | GGAGATGTATGATCAGATGG |
| BnBAN-UP6 | CTTCTTCTGATTCTTAGGTGAG |
| BnBAN-UP7 | ATCAAGTAAAAAGATCAAAATC |
| BnBAN-RP1 | ATAGCTTCTGCATTTCCTTGAG |
| BnBAN-RP2 | GAATAGAGGCTAAGTTTCCTGTGC |
| BnBAN-RP3 | AACTAACTTGTTTACCTTCTTC |
| BnBAN-RP4 | TAAAATCGACCAACATATTAT |
| BnaABANa-RP | TTACATACATTATGTAAAAATG |
| BnaCBANa-RP | TTCCATGATCTAAAAACACTG |
| BnaCBANb-RP | ATCTAACTCAAGTATCAAGC |
| BnBANa-ATG | ATGACAAGCACTGATCAGACCAC |
| BnBANa-Stop | GATTCTTTAGGCCCATCGGTTTGTC |
| BnBANb-ATG | ATGGCAACCGTTGATCAGACCG |
| BnBANb-Stop | TTAAGGTTTGATCAATCCTTTTGACTC |
| pBnBAN-UP | attB1-CTTCTTCTGATTCTTAGGTG |
| pBnBANa-RP | attB2-ATATATTATAAATTCTTAAC |
| pBnBANb-RP | attB2-ATTAAATTCTTAAGACACAG |
| BnEF1-UP | TCGAGACCACCAAGTACTACTGCAC |
| BnEF1-RP | GATCCTTGACAGCAACATTCTTAAC |
| AP1 | GGATCCTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGC |
| AP2 | CTATAGGGCTCGAGCGGC |
| T7 | GTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGC |
aattB1 and attB2 refer to the Gateway® recombination sequences
Isolation of Bna.BAN genes
To recover the genomic clones carrying Bna.BAN sequences, we used the B. napus BAC “DarmorBZH” library (also named Bna-B-DarmorBZH) generated by Genoplante. The complete library consists of 73,728 clones of 200–250 kb genomic DNA each, thus, representing around 12 genome equivalents of B. napus L. Darmor-bzh (winter double low cv.). Bna-B-DarmorBZH is maintained at CNRGV (INRA Toulouse) and available upon order (http://cnrgv.toulouse.inra.fr/en/library/genomic_resource/Bna-B-DarmorBZH). Only 232 amplification reactions are needed to recover a clone coordinate in plate–row–column format (192 plate pools, 16 row pools per plate and 24 individual columns per line). Primer combinations used for screening the Bna-B-DarmorBZH library during the course of this study were AtANR-UP/AtANR-RP and BnBAN-UP1/BnBAN-RP1 (Table 1). Individual BACs were obtained from the CNRGV with the following coordinates in plate–row–column format: 7O16, 8G5, 9A6, 42O14, 44M20, 48G5, 48M22, 49N16, 60P24, 79G17, 88G15, 89H8, 96L14, 101P20, 127L14, 127P11, 174I21 and 185N20. Selected BACs were sequenced by BnBAN-UP1, BnBAN-UP2, BnBAN-UP3 and BnBAN-UP4 primers (Table 1).
5′- and 3′-genomic sequences of Bna.BAN genes were isolated using a PCR walking approach on BAC clones 8G5, 89H8 and 127P11. The procedure was essentially performed as described by Devic et al. (1997). BAC DNA preparations (~500 ng) were submitted to a blunt-end enzymatic restriction using DraI or EcoRV before ligation to an adapter duplex to produce two independent walk libraries per BAC. 5′- and 3′-genomic regions were amplified using a pair of nested primers specific to the Bna.BAN-coding sequences in combination with a pair of nested primers specific to the adapter (AP1 and AP2; Table 1). The amplified fragments were cloned into the pGEM®-T plasmid according to the recommendations of the supplier (Promega) and sequenced. Primers used were as following (see Table 1): BnBAN-RP2 to clone the 5′ region of 89H8, BnBAN-RP2 followed by BnBAN-RP3 to clone the 5′ regions of 8G5 and 127P11 and BnBAN-UP5 to clone the 3′ regions of 8G5 and 127P11.
Constructs and plant transformation
All PCR products used for construction of transgenic plants were generated by using Pfu (Stratagene, La Jolla, CA, USA) or KOD Hot Start DNA polymerase (Novagene, Madison, WI, USA) as robust and high-fidelity DNA polymerases. Molecular cloning was conducted in Escherichia coli DH10B that showed total sensitiveness to the ccdB gene product inserted into Gateway® cassettes. The integrity of the constructs was checked both by sequencing and through enzymatic restrictions. The resulting binary vectors were electroporated into Agrobacterium tumefaciens C58C1pMP90 strain (Koncz et al. 1984).
For complementation assays, the coding regions (CDS) of the targeted genes were amplified from cDNA preparation using primer sets BnBANa-ATG/BnBANa-Stop for BnaA.BANa and BnaC.BANa CDS and BnBANb-ATG/BnBANb-Stop for BnaA.BANb and BnaC.BANb CDS (Table 1). PCR products were blunt-end ligated into the polylinker of the pMagic binary vector (Nesi et al. 2002) which carries the expression cassette Pro35S 2::Term (i.e., double-enhanced 35S promoter of cauliflower mosaic virus [CaMV]::CaMV polyadenylation signals). The orientation of the clones was checked by restriction enzyme, PCR amplification and sequence analyses.
For generation of promoter-UidA transcriptional fusions, a region upstream of the ATG start codon (including promoter and 5′-untranslated region) was cloned into the entry vector pDONR™ 207 using the Gateway® BP clonase® II enzyme mix (Invitrogen), sequenced and transferred into the binary vector pBIB101GUS (F. Divol, B. Dubreucq and J.C. Palauqui, INRA Versailles, unpublished data) by an LR recombination reaction (Gateway® LR clonase® II enzyme mix, Invitrogen). Primer sets used for the generation of the promoter fragments were as following: pBnBAN-UP/pBnBANa-RP and pBnBAN-UP/pBnBANb-RP to generate 230-bp fragments of ProBnaC.BANa and ProBnaC.BANb, respectively.
Genetic transformation of oilseed rape was carried out according to Sparrow et al. (2004, 2006). Seeds were sown on full strength MS at a density of 20 seeds per 90-mm ∅ Petri dish. The plates were maintained 72 h at 4°C before being transferred in the growth room for seed germination. Cotyledonary petioles were excised from 7-day-old seedlings, dipped into an overnight suspension of Agrobacterium (adjusted to OD650nm = 0.1) and placed on co-cultivation medium (MS medium with 30 g L−1 sucrose, 8 g L−1 plant agar, 2 mg L−1 BAP, pH = 5.7) in the growth room for 72 h. The explants were then transferred to selection medium (co-cultivation medium supplemented with 400 mg L−1 timentin and 25 mg L−1 kanamycin as selective agent). Controls (explants that had or had not been inoculated with Agrobacterium) were established on a kanamycin-free medium. All explants were transferred to fresh selection medium after 3 weeks. The first green shoots appeared 5–6 weeks after inoculation, usually via a callus phase. Elongated shoots were excised from calli and transferred on rooting medium consisting of half-strength MS salts, MS vitamins, 10 mg L−1 sucrose, 5 mg L−1 IBA, 1 g L−1 gelrite and 4.1 g L−1 plant agar, supplemented with 400 mg L−1 timentin and 50 mg L−1 kanamycin. Shoots were maintained on this medium until rooting. Further sub-culturing was done to ensure that a main stem was isolated. Rooted shoots were then transferred to the greenhouse where they were maintained under propagator during the first 2 weeks to ensure correct acclimatisation. For each construct, oilseed rape transformation was conducted as two independent replicates with 300 cotyledonary explants inoculated per replicate as well as a further 10 inoculated and 10 non-inoculated explants established on selection-free medium as controls. Positive transgenics were identified by PCR analysis for green shoots rooting on kanamycin. All plant growth regulators and antibiotics were from Duchefa Biochemie (Haarlem, The Netherlands).
Arabidopsis plants were transformed by floral dipping (Clough and Bent 1998) using 0.05% of Silwet L-77 (Lehle seeds, Round Rock, TX, USA). Primary transformants were selected on Murashige and Skoog medium supplemented with hygromycin (75 mg L−1) or kanamycin (50 mg L−1) and then transferred in soil for further characterisation.
GUS staining and observations of organs from transgenic plants carrying promoter-UidA transcriptional fusions were carried out as described by Nesi et al. (2009). Samples for seed sections were treated as described elsewhere (Nesi et al. 2009) and resin-embedded using the Technovit 7100 resin kit (Heraeus Kulzer Histo-Technik, Wehrheim, Germany) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The embedded samples were sectioned to a thickness of 18 μm using a semiautomatic microtome (HM335E, Microm, Microtech, Francheville, France) equipped with metallic blades (Heraeus Kulzer). Sections were observed with a microscope (Axioskop2 Plus, Zeiss, Jena, Germany) under bright-field optics.
Sample preparation and laser microdissection of B. napus seeds
Immature seeds were collected at 15 dap and immersed immediately into 5 mL of freshly prepared fixative (1/0.8 [v/v] ethanol/RCL2; Delfour et al. 2006; Alphelys, Plaisir, France) maintained on ice. Seeds in fixative were subjected to 4 h of vacuum (15, 15, 30 min and 3 h) at 4°C to assist sinking of tissue and infiltration, and stored in fixative at 4°C for 24 h. Fixed samples were dehydrated at room temperature through a graded series of ethanol (2 h each [v/v] 75, 80, 90, 100, 100 and 100%), followed by three toluene baths (100% 2 h each). Toluene was replaced by two liquid paraffin baths (Paraplast Normal Bulk, Labonord, France) 2 and 3 h at 65°C and the samples were then embedded in paraffin. Ten micrometers thick sections were cut with a microtome, floated in water on microscope slides (Superfrost Plus), dried at 42°C for 15 min, deparaffinised in xylene for 10 min and stored under vacuum for maximal 1 h before microdissection.
Laser microdissection was performed using the Veritas™ instrument (Arcturus Biosystems, Mountain View, CA, USA). Laser cutting method was used to cut and remove tissue fragments. Cells encircled on the computer screen using a mouse were then cut by UV laser (349 nm wavelength) and captured onto PEN membrane glass slide (Molecular Devices, Sunnyvale, CA, USA). Care was taken to preserve the integrity of the cells of interest. Capture conditions with IR laser (810 nm wavelength) were optimised to obtain a clean, narrow excision of the selected cells: 20 XT objective, power 90 and pulse 3500.
Genetic mapping
For mapping of Bna.BAN genes, we used the Stellar × Drakkar (SD) doubled haploid (DH) population and the Darmor-bzh × Yudal (DY) DH population that consist of 94 and 445 genotyped DH lines, respectively (Lombard and Delourme 2001; Delourme et al. 2006). Primer sets used for genetic mapping were as following: BnBAN-UP6/BnaABANa-RP for BnaA.BANa and BnBAN-UP7/BnaCBANa-RP for BnaC.BANa. Linkage analyses were performed using MAPMAKER/EXP version 3.0b (Lincoln et al. 1993). Framework map used in this study was constructed in Lombard and Delourme (2001) for SD and updated in Delourme et al. (2006) for DY. Bna.BAN genes were assigned to a linkage group using the ASSIGN command (LOD threshold = 4.0) and then placed in the most confident interval with the PLACE command (LOD threshold = 2.0). Segregation data for single loci flanked by double crossovers were re-examined. Recombination frequencies were converted into centimorgans with the Kosambi function (Kosambi 1944).
Monosomic and polysomic addition lines carrying one or several additional C chromosomes from either B. napus or B. oleracea were established in our group (A.M. Chèvre and F. Eber, INRA Rennes, unpublished results). These lines were used to assign monomorphic markers corresponding to a specific C chromosome.
Sequence analyses
Sequence similarity searches were performed using the BLAST algorithm according to Altschul et al. (1990) through the NCBI server where 458,264 B. napus expressed hits have been released (last update 11 July 2008) and assembled into 26,733 clusters (UniGene Bna Build #17). BLASTN option was used to recover oilseed rape ESTs starting from Arabidopsis sequences. The cDNA clones BN15019B21 (GenBank CD813283), BN25045I20 (GenBank CD822528) and BN25045M17 (GenBank CD822594) were obtained from Genoplante oilseed rape cDNA libraries BN15 (ID = Lib. 13977) and BN25 (ID = Lib. 13979), and were sequenced by T7, BnBAN-UP1 and BnBAN-UP4 primers (Table 1). All DNA sequences were performed by Cogenics (Grenoble, France).
Sequence alignments were inferred by ClustalW and drawn with Boxshade (http://www.ch.embnet.org/software/Box_form.html). Restriction patterns were generated with RESTRICT (http://mobyle.pasteur.fr/cgi-bin/MobylePortal/portal.py?form=restrict). PLACE database (http://www.dna.affrc.go.jp/PLACE/signalup.html) was used to look for cis-acting regulatory DNA elements in promoter sequences. Amino acid sequences were submitted to SCANPROSITE (http://www.expasy.ch/tools/scanprosite/) to retrieve protein domains and functional sites and to the 2ZIP server (http://2zip.molgen.mpg.de/index.html; Bornberg-Bauer et al. 1998) to predict leucine zippers.
For distance analysis, an alignment of the most conserved region amongst plant ANR amino acid sequences was generated with ClustalW. The corresponding distance matrix was calculated and submitted to a neighbour-joining analysis using the Treecon algorithm (Van de Peer and De Wachter 1994) to infer a branching pattern. For statistical analysis, 1,000 bootstraps replications were performed. The consensus tree was drawn with the Treecon package. The sequences mentioned in this study were as following with their GenBank accession numbers given into parentheses. For A. thaliana, AtANR (At1g61720; Devic et al. 1999) and AtDFR (At5g42800; Shirley et al. 1992); for B. napus, BnaC.BANa (FJ938333), BnaC.BANb (FJ938334), BnaA.BANa (FJ938335) and BnaA.BANb (FJ938336) (this study); for B. oleracea BolC.BANa (FJ938337) and BolC.BANb (FJ938338) (this study); for B. rapa BraA.BANa (FJ938339) and BraA.BANb (FJ938340) (this study); for Diospyros kaki, DkANR (BAF56654; Ikegami et al. 2007); for strawberry Fragaria × ananassa, FraANR-a (ABG76843), FraANR-b (ABG76842) and FraANR-c (ABD95362) (Almeida et al. 2007); for Ginkgo biloba, GbANR (AAU95082; Shen et al. 2006); for Gossypium hirsutum, GhANR (ABM64802; Xiao et al. 2007); for Lotus corniculus, LcANR1 (ABC71337), LcANR2 (ABC71336), LcANR1-1 (ABC71332), LcANR1-2 (ABC71333), LcANR1-3 (ABC71334) and LcANR1-4 (ABC71335) (Paolocci et al. 2007); for Lotus uliginosus, LuANR (ABM90632; direct submission); for apple Malus × domestica, MdANR-a (AAZ79363; Pfeiffer et al. 2006), MdANR-b (AAX12184; Takos et al. 2006) and MdANR-c (AAZ17408; direct submission); for Medicago truncatula, MtANR (AAN77735; Xie et al. 2003); for Populus trichocarpa, PtANR-BAN1 (EEE86150) an PtANR-BAN2 (EEE97882) (direct submission); for Pyrus communis, PcANR (ABB77695; Fischer et al. 2007); and for Vitis vinifera, VvANR-a (BAD89742; Fujita et al. 2005) and VvANR-b (AAZ82409; Pfeiffer et al. 2006).
Results
Four BAN genes were retrieved into the B. napus genome
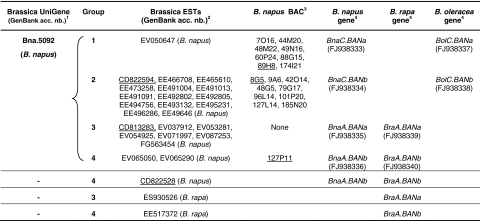
A total of 25 oilseed rape ESTs that showed high similarities with Arabidopsis ANR cDNA were identified within the public databases, amongst which 24 belong to the same cluster (Bna.5092; Table 2). Sequence alignment of these 25 ESTs (data not shown) displayed four distinct groups of transcripts (Table 2). Three cDNA clones, namely CD822594 (group 2), CD813283 (group 3) and CD822528 (group 4), were obtained from Genoplante and subsequently sequenced. CD822594 and CD822528 were full-length cDNAs of 1,202 and 1,217 bp respectively, including coding sequences of 1,026 bp each (data not shown). In contrast, CD813283 consisted of a partial cDNA of 1,132 bp with a truncated coding sequence of 966 bp. In addition, two ESTs from B. rapa were also found that belong to groups 3 and 4, respectively (Table 2), suggesting that there were at least two BAN orthologs in the genome of both oilseed rape ancestors.
Table 2.
BAN sequences in Brassica genomes
1When available cluster ID is given as defined by the UniGene Bna Build #17 that includes 458,264 rapeseed ESTs
2ESTs that correspond to cDNA clones obtained from Genoplante and used for further sequencing are underlined. CD813283 correspond to cDNA clone BN15019B21; CD822528 to cDNA clone BN25045I20 and CD822594 to cDNA clone BN25045M17
3BAC clones were identified within the Bna-B-DarmorBZH library and are given with coordinates in the plate-row-column format. Selected BACs for genomic DNA sequencing are underlined
4 Corresponding genomic sequences that were submitted to GenBank with accession numbers given into parentheses
To recover genomic clones of Bna.BAN genes, we screened the Bna-B-DarmorBZH BAC library with primer pairs derived from Arabidopsis (AtANR-UP/AtANR-RP) or from oilseed rape ESTs (BnBAN-UP1/BnBAN-RP1). A total of 18 BACs were identified of which eight belong to sequence group nb.1, nine to group nb.2 and one to group nb.4 (Table 2). No BAC from the group nb.3 was isolated. BACs 89H8, 8G5 and 127P11 were selected as representative genomic sequences from groups 1, 2 and 4, respectively. Sequences of Bna.BAN genes carried by the three selected BACs were established using successively primers BnBAN-UP3, BnBAN-UP1, BnBAN-UP2 and BnBAN-UP4 (Table 1) that were designed from cDNA sequences. In addition, 5′- and 3′-genomic sequences of Bna.BAN genes were obtained by PCR walking on selected BAC clones (see “Materials and methods”). The three Bna.BAN genomic sequences were as following: Bna.BAN group 1 consisted of a 340-bp 5′ sequence followed by a 1,505-bp coding sequence and was deposited to GenBank as FJ938333 (Table 2), Bna.BAN group 2 consisted of a 1,400-bp coding sequence surrounded by 835- and 620-bp sequences in 5′- and 3′-ends, respectively and was deposited to GenBank as FJ938334 (Table 2), and Bna.BAN group 4 was 2,417-bp long, including 639 bp in 5′, 1,428 bp of coding sequence and 350 bp in 3′ and was deposited to GenBank as FJ938336 (Table 2). A fourth DNA sequence was directly amplified and cloned from genomic DNA of B. napus cv. Darmor-bzh using primer pair BnBAN-UP6/BnBAN-RP4 (Table 1). This sequence of 1,787 bp corresponded to group nb. 3 for which no BAC was found. It contained a coding region of 1,466 bp surrounded by 220 bp in 5′ and 101 bp in 3′, it was deposited to GenBank as FJ938335 (Table 2).
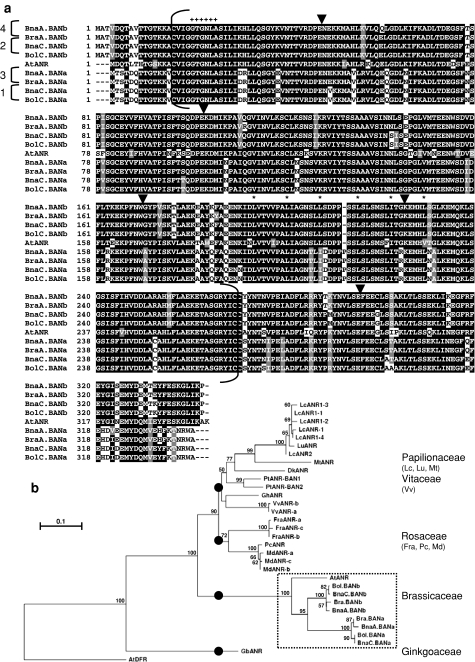
To build up the origin of the four Bna.BAN, we amplified and sequenced BAN genes from both oilseed rape progenitors using genomic DNA preparations from B. rapa var. Chiffu (genome AA) and B. oleracea var. C10 (genome CC, 2n = 18). Two orthologs were identified in each progenitor genome that belong to two groups of homeology (hereafter called “a” and “b”) and were named BraA.BANa (FJ938339), BraA.BANb (FJ938340), BolC.BANa (FJ938337) and BolC.BANb (FJ938338), according to Østergaard and King (2008) (Table 2). Alignment of BAN deduced amino acid sequences from Brassica spp. revealed that Bna.BAN sequences fell into the two groups of homeology (Fig. 2a) and displayed similarities with either A- or C-homologs. Therefore, Bna.BAN genes from groups 1–4 were, respectively, renamed BnaC.BANa (FJ938333), BnaC.BANb (FJ938334), BnaA.BANa (FJ938335) and BnaA.BANb (FJ938336). Brassica BAN coding sequences consisted of six exons and the positions of the five introns were conserved with those from AtANR (Fig. 2a). When compared with Arabidopsis ANR sequence, Brassica BAN deduced proteins from the “b” homeology group displayed up to 83% of residue identity, whereas those from the “a” homeology family showed only 76% of identity. In addition, Brassica BAN proteins from a given homeology family (either “a” or “b”) showed up to 97–99% residue identity, whereas this score only reached 79–81% of identity between proteins from the two homeology families. A classical Rossmann NAD(P)H/NAD(P) + binding domain, which is conserved amongst oxidoreductase proteins, was found at the N-terminus from Brassica BAN amino acid sequences (Fig. 2a). Finally, a perfect leucine repeat that did not correspond to a leucine zipper was predicted by the 2-ZIP Server within BAN protein sequences from the “b” group (residues +194, 201, 208, 215, 222 and 229). This region was also present in AtANR protein, but was not retrieved in Bna.BAN proteins from the “a” group due to the insertion of a proline residue at position +213 (Fig. 2a). Analysis of distance relationships between plant ANR-like sequences revealed that Brassica BAN sequences were closer to Arabidopsis ANR than to any other ANR-related sequence (Fig. 2b). In addition, the group formed by the Brassicaceae ANR/BAN seemed to have evolved independently from the other ANR from dicotyledonous plants (Fig. 2b).
Fig. 2.
Relationships between Bna.BAN and plant ANR-like amino acid sequences. a Alignment of complete deduced amino acid sequences from Brassica BAN with AtANR. Residues are numbered from the putative translation initiation start codon. Identical residues are boxed in black and similar residues are shaded in grey. Dashes indicate gaps introduced in the sequences to allow maximal alignment. Numbers on the left side of the alignment refer to the four sequence groups identified for Bna.BAN genes (see Table 2). Positions of introns are indicated by the arrowheads above the alignment. The Rossmann NADB-binding domain consisting of the conserved motif GXGXXA is indicated (+). The six invariable residues of the leucine repeat predicted in BAN protein sequences are indicated by the stars. Brackets delimit the region (around 253 amino acid positions) used to build the distance tree shown in b. b Dendrogram of relationships between deduced amino acid sequences from Brassica Bna.BAN and plant ANR-like enzymes. A multiple alignment of protein sequences covering around 253 residues (a) was generated. The consensus tree was obtained by neighbour-joining analysis using Treecon, bootstrapped with 1,000 iterations and rooted using the AtDFR sequence. Bootstrap values are indicated before nodes when score was over 50%. Accession numbers of the different sequences used to build the dendogram are given in “Materials and methods”
To prove that Bna.BAN genes were functional orthologs of AtANR, a phenotypic complementation assay was conducted on homozygous ban mutants with B. napus BAN genes. Bna.BAN coding sequences were amplified and cloned into the pMagic binary vector to establish Pro35S 2::Bna.BAN constructs. Homozygous ban-1 or -4 Arabidopsis plants were independently transfected with each one of the four Pro35S 2::Bna.BAN constructs. For each transformation assay, from 10 to 50 independent primary transformants (T1) were obtained that all gave wild-type brown-seeded T2 progenies (Fig. 1b). Therefore, these results provided evidence that Bna.BAN genes were able to complement Arabidopsis ban mutations and that they could be considered as functional orthologs of AtANR.
Genetic localisation of Bna.BAN loci
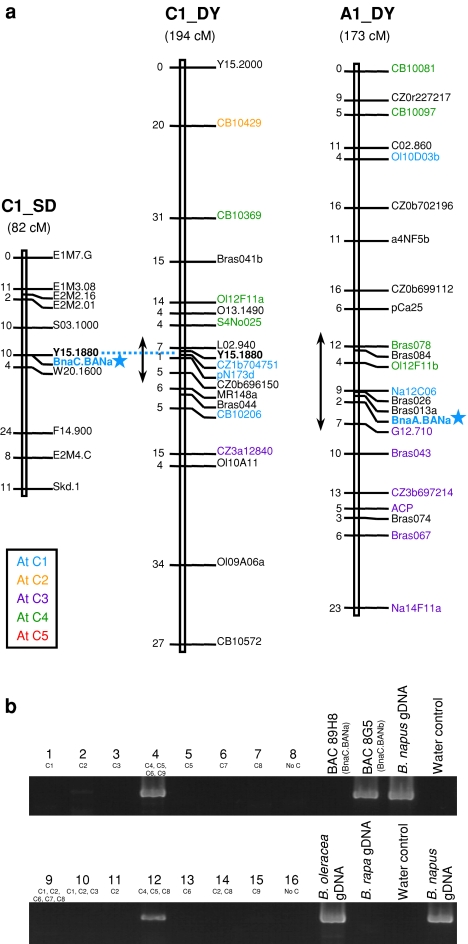
Locus-specific primer pairs were designed to map the Bna.BAN genes. The primer pair BnBAN-UP6/BnaABANa-RP (Table 1) was specific of the BnaA.BANa locus. A polymorphic amplicon of ~1,300 bp in Darmor-bzh and of ~1,600 bp in Yudal was obtained (data not shown). Out of the 445 DY DH lines, 209 showed the Darmor-bzh phenotype and 195 the Yudal phenotype, which fitted to the expected 1:1 segregation ratio (χ2 = 0.48 < α0.05 = 3.84). The BnaA.BANa locus was located on chromosome A1 (LOD = 84.7) that corresponded to the former DY1b linkage group (Lombard and Delourme 2001), in distances of 2.3 and 7 cM of the markers Bras013a (SSR) and G12.710 (RAPD), respectively (Fig. 3a).
Fig. 3.
Map positions of Bna.BAN genes in oilseed rape. a BnaA.BANa and BnaC.BANa mapped to chromosomes A1 and C1, respectively (shown by the stars). Numbers on the left side of the chromosomes are given in cM. Centromeric positions on the DY map are indicated by double arrows according to Pouilly et al. (2008). Markers are coloured according to the identified homologous regions in Arabidopsis (refer to colour legend in a). b Amplification of a specific BnaC.BANb fragment using mono- and polysomic lines carrying additional C chromosomes from either B. napus (plants 1–8) or B. oleracea (plants 9–16). Additional chromosomes present in each line are indicated below the corresponding plant number. gDNA genomic DNA
Primer combination BnBAN-UP7/BnaCBANa-RP (Table 1) was designed to amplify a ~1,400-bp fragment specific of the BnaC.BANa gene. The amplicon displayed one SspI restriction site in the Stellar sequence, resulting in restriction fragments of 800 and 600 bp (data not shown). Out of the 94 SD DH lines, 38 showed the Stellar phenotype and 46 the Drakkar phenotype consistent to the expected 1:1 segregation ratio (χ2 = 0.76 < α0.05 = 3.84). The BnaC.BANa locus mapped to C1 (LOD = 17.9) and co-localised with Y15.1880 (RAPD) (Fig. 3a) which also mapped on the DY C1 linkage group in the vicinity of L02.940 (RAPD) and CZ1b704751 (PCR-specific marker).
No polymorphism was identified for BnaA.BANb and BnaC.BANb after sequencing the full genomic DNA on several oilseed rape accessions. We used plants that carried one or several additional C chromosomes to assign a fragment of ~600 bp specific to the BnaC.BANb gene (amplification with primers BnBAN-UP4/BnaCBANb-RP; Table 1). Our results clearly demonstrated that BnaC.BANb was located onto the C4 linkage group, since the amplicon was detected in plant nb. 4 (additional C4, C5, C6 and C9 chromosomes) as well as in plant nb. 12 (C4, C5 and C8) but not in plant nb. 5 (C5) (Fig. 3b).
Expression pattern of Bna.BAN genes
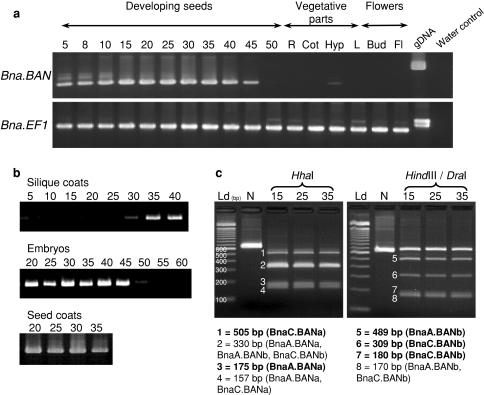
Primer pair BnBAN-UP3/BnBAN-RP1 (Table 1) was chosen to monitor global expression of the Bna.BAN genes, since these primers amplify the four corresponding sequences, resulting in the production of a 662-bp amplicon for BnaA.BANa or BnaC.BANa and a 659-bp amplicon for BnaA.BANb or BnaC.BANb. Bna.BAN transcripts accumulated in developing seeds from 5 to 45 dap, but not in vegetative parts (with the exception of a faint signal in hypocotyls) nor in reproductive organs (buds and flowers) (Fig. 4a). In addition, Bna.BAN transcripts were detected in seed coats as well as in silique coats and embryos during seed development (Fig. 4b).
Fig. 4.
Accumulation of Bna.BAN transcripts. a Global expression of Bna.BAN genes was monitored by 35 PCR cycles using primers that amplify the four Bna.BAN transcripts on Jet Neuf cDNA preparations from developing seeds (collected at 5–50 dap), vegetative parts (R roots, Cot cotyledons, Hyp hypocotyls, L leaves), and reproductive organs (Bud floral buds, Fl flowers). Jet Neuf genomic DNA (gDNA) was used as a positive control. PCR products were visualised on a 2% (w/v) agarose gel stained with ethidium bromide. Bna.EF1 was amplified as an internal control (refer to Nesi et al. 2009), using primers BnEF1-UP and BnEF1-RP (Table 1). b Accumulation of Bna.BAN transcripts in silique coats (5–40 dap), embryos (20–60 dap) and seed coats (20–35 dap). c Expression pattern of individual Bna.BAN genes was investigated using polymorphic restriction sites. HhaI restriction produced two bands of 505 and 175 bp specific to BnaC.BANa (fragment 1) and BnaA.BANa (fragment 3), respectively. HindIII/DraI restriction generated fragments specific to BnaA.BANb (fragment 5, 489 bp) and to BnaC.BANb (fragment 6, 309 bp and fragment 7, 180 bp). Specific bands are indicated in boldface below the pictures. Ld 100 bp DNA ladder (Invitrogen), N native PCR product, 15, 25, 35 dap of seed developmental stages. The products were resolved in a 3% (w/v) agarose gel stained with ethidium bromide
To investigate the expression pattern of specific Bna.BAN genes, we used the presence of polymorphic enzymatic restriction sites on the corresponding BnBAN-UP3/BnBAN-RP1 amplicon sequences. For instance, one and two HhaI restriction sites were identified on BnaC.BANa (position +505) and BnaA.BANa (+303 and +505), respectively, that differ from the HhaI restriction site found in both BnaA.BANb and BnaC.BANb (+330 each). On the same line, a HindIII restriction site (position +489) was found in Bna.BANb fragments, but not in Bna.BANa ones and a DraI restriction site was specific to BnaC.BANb (+309). Enzymatic restriction assays were performed on amplification products (Fig. 4c) and allowed to distinguish two HhaI bands of 505 and 175 bp specific to BnaC.BANa and BnaA.BANa, respectively, one HindIII fragment of 498 bp specific to BnaA.BANb, one DraI fragment of 309 bp as well as one HindIII/DraI fragment of 180 bp both specific to BnaC.BANb. Taken together, these data provided evidence that the four Bna.BAN transcripts accumulated in B. napus seed. In addition, this result was confirmed at any seed developmental stage (Fig. 4c) as well as in all organs tested (data not shown), and there were no obvious differences in transcript level between the four copies.
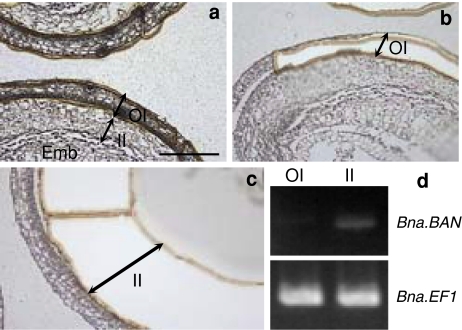
Tissular localisation of Bna.BAN transcripts in seeds was analysed. For this purpose, fragments from the outer (OI, Fig. 5b) or the inner integument (II, Fig. 5c) were collected via laser microdissection of immature seeds at 15 dap, which corresponded to a developmental stage when the integuments were easily distinguishable (Fig. 5a). Total RNAs were extracted from these samples and first-strand cDNAs were synthesised that were used to monitor expression of Bna.BAN genes with BnBAN-UP3 and BnBAN-RP1 primers (Table 1). Our results showed that Bna.BAN transcripts specifically accumulated into the inner integument (Fig. 5d).
Fig. 5.
Laser microdissection of integuments from B. napus immature seeds. Sections (10 μm) of immature seeds (15 dap) from Jet Neuf before (a) and after (b, c) UV laser microdissection. Laser cutting method was used to cut and remove tissue fragments. Cells encircled on the computer screen using a mouse were then cut by UV laser and captured onto a slide. Bna.BAN transcripts were detected after 35 cycles of amplification (d) on RT products obtained from outer or inner integument samples collected in b and c, respectively. Expression profile of Bna.EF1 was used as an internal control. Emb embryo, II inner integument, OI outer integument. Bar 400 μm
Activation patterns of Bna.BAN promoters
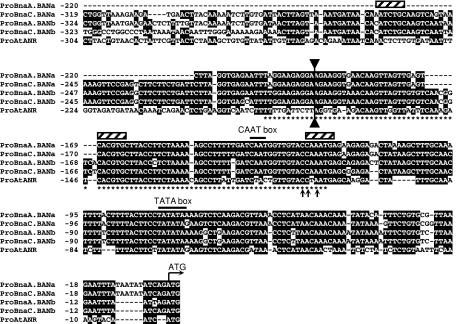
The four sequences of the Bna.BAN promoters (see above for cloning details) were compared together and with the ProAtANR one. ProBna.BAN were highly conserved (Fig. 6) with identity rates that reached 96–97% within the “a” or “b” homeology families and around 82% between the two groups. ProBna.BAN and ProAtANR were highly conserved along the 200 bp in 5′ of the ATG codon with an average identity rate of 66% (Fig. 6), whereas it decreased down to 35–40% beyond this region. This suggested that most of the cis-acting motifs potentially crucial for BAN activation in Brassicaceae should be present in this conserved region of 200 bp. For instance, this region includes the 86-bp sequence defined as the procyanidin enhancer by Debeaujon et al. (2003) that was shown to be necessary and sufficient for reporter gene expression in pigmented cells of the Arabidopsis seed coat. In addition, the three bases (CC-A, Fig. 6) which were thought to play crucial roles for ProAtANR activation, since they belong to a putative high-affinity P-binding site shared by several flavonoid gene promoter sequences, were also retrieved in ProBna.BAN sequences. Finally, using PLACE database, we could identify basic region helix–loop–helix/leucine zipper (bHLH/ZIP)-binding sites (CANNTG; Weisshaar and Jenkins 1998) within this region as well as putative CAAT- and TATA-boxes (Fig. 6).
Fig. 6.
Sequences of BAN promoters. Bna.BAN and AtANR promoter sequences were aligned over 300- to 325-bp long. The ATG start codon and the putative CAAT and TATA boxes are indicated above the alignment. Stars below the ProAtANR sequence indicate nucleotides included into the 86-bp procyanidin enhancer previously defined by Debeaujon et al. (2003). bHLH/ZIP consensus binding sites (CANNTG) were found (hatched box). Arrows below the alignment point out the three bases conserved amongst several flavonoid gene promoters and that belong to a putative high-affinity P-binding site. The double arrow delimits the region where Bna.BAN and AtANR promoter sequences share most of sequence identities
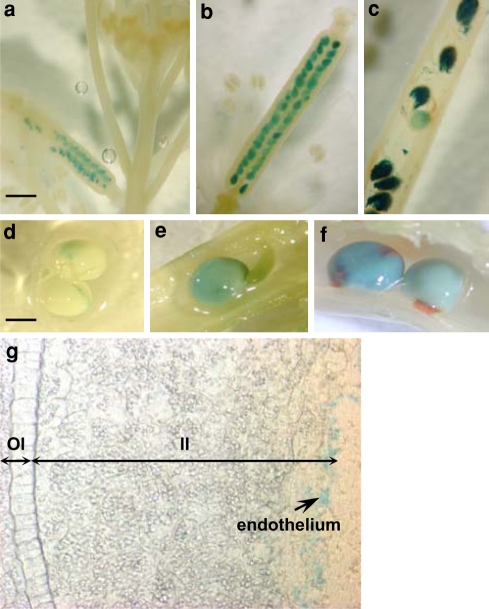
To monitor the activation pattern of Bna.BAN promoters in planta, transcriptional fusions were generated between portions of ProBna.BAN and UidA gene. A fragment of 230 bp including the conserved region of 200 bp from ProBna.BAN was chosen. Fusions were established for ProBnaC.BANa and ProBnaC.BANb only and introduced into Arabidopsis or oilseed rape. Primary transformants of Arabidopsis carrying the ProBnaC.BANa:UidA fusion displayed GUS staining only in seeds (Fig. 7a–c). No visible GUS staining was detectable in buds and flowers (Fig. 7a). Activation of ProBnaC.BANa in Arabidopsis seed started from very early seed developmental stages at around 2 daf (Fig. 7a, four cell embryo stage) became more intense at 4–5 daf (Fig. 7b, globular embryo stage) and persisted in late embryo developmental stages (Fig. 7c, U-shaped embryo stage). GUS staining was also restricted to seeds in transgenic oilseed rape plants (Fig. 7d–f). A faint blue staining was detectable in the micropyle-chalaza area from 10 dap seeds (Fig. 7d). This stain spread the whole seed body in seeds at 15 dap (Fig. 7e) and became more intense at 25 dap (Fig. 7f). Seed sections revealed that the GUS staining was restricted to the endothelium of the inner integument (Fig. 7g) and more generally to the procyanidin-accumulating cell layer, since GUS was also detected into the micropyle-chalaza area (data not shown). Similar results were obtained with the ProBnaC.BANb:UidA fusion when introduced into Arabidopsis or oilseed rape (data not shown). Taken together, all these results indicated that the 230 first nucleotides of ProBnaC.BAN were sufficient for the spatio-temporal activation profile of both BnaC.BAN genes in Arabidopsis and oilseed rape.
Fig. 7.
Localisation of ProBna.BAN activity in A. thaliana and in B. napus. Transgenic plants of Arabidopsis or B. napus carrying the ProBnaC.BANa _230bp:UidA transcriptional fusion were GUS stained to localise the ProBnaC.BANa activation pattern. Siliques from Arabidopsis primary transformants were harvested at 2 daf (a), at 4–5 daf (b) and at 9 daf (c). Developing seeds from B. napus primary transformants were harvested at 10 dap (d), 15 dap (e) and 25 dap (f). Seeds in e were resin-embedded to perform 18-μm thick section (g). The expression of ProBnaC.BANa is restricted to the endothelium layer as shown by the arrow (g). II inner integument, OI outer integument. Bars 250 μm (a), 300 μm (b), 400 μm (c, g) and 1 mm (d, e, f)
Discussion
Comparative genomics between Brassicaceae for genes encoding ANR-related proteins
The BAN gene encodes ANR, a key enzyme of procyanidin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis seed (Devic et al. 1999; Xie et al. 2003). In this study, we described the cloning of the BAN loci in the close relative species of B. napus, B. oleracea and B. rapa. For this purpose, we undertook a molecular approach based on the high-sequence conservation between the Brassicaceae genomes (Paterson et al. 2001; Parkin et al. 2002, 2005) and using the Brassica genomic resources available. This strategy has proven to be efficient for the cloning of several flavonoid genes in the Brassica genomes in previous studies (Xu et al. 2007; Wei et al. 2007; Yan et al. 2007, 2008; Lee et al. 2008; Chai et al. 2009).
Here, four BAN genes were identified into the B. napus genome that belong to two distinct groups of homeology (named group “a” and group “b” respectively) and that could stand for paralogous sequences, since two BAN genes, one from group “a” and the other from group “b”, were isolated from each of the two oilseed rape ancestors, B. oleracea and B. rapa. Deduced amino acid sequences of Brassica BAN displayed around 97–99% of identity within a given homeology group and paralogous sequences showed only around 80% of identity between each others. Identity level with Arabidopsis ANR varied from 76 to 83% depending on the paralogs (group “a” and group “b” respectively). Phylogenetic analysis demonstrated that Brassica BAN sequences were closest to Arabidopsis ANR than to any other plant ANR like, which suggested that the true orthologs from AtANR were identified.
Comparative genomic studies hypothesised that each Arabidopsis locus should correspond to six orthologs in oilseed rape due to Brassica genome triplication after divergence from the ancestor of Arabidopsis genus and subsequent allopolyploidization (Lysak et al. 2005; Parkin et al. 2005). However, the genome of the hexaploid Brassica ancestor should have undergone a great number of gene losses during diploidization events that occurred to form the B. oleracea and B. rapa genomes (Lysak et al. 2006; Town et al. 2006). This could explain why only four and not six BAN loci were retrieved into the oilseed rape genome. Similar results were obtained with orthologs of flavonoid-related genes cloned elsewhere. For instance, Wei et al. (2007) described the cloning of three BnTT2 orthologs and Chai et al. (2009) reported that only two TT12 homologs were present in oilseed rape.
AtANR gene was located on Arabidopsis chromosome 1 (AtC1), with the AGI number At1g61720. The two homeologous genes BnaA.BANa and BnaC.BANa were mapped onto the A1 and C1 chromosomes respectively, close to the centromeric regions. These two homeologous linkage groups were primarily syntenic to portions of AtC4 (top arm) and AtC3 (bottom arm), but a small area within the vicinity of the centromeric region displayed synteny with a portion of AtC1 (Fig. 3a, Parkin et al. 2005). For instance, the corresponding region on C1 DY carried the markers CZ1b704751, pN173d and CB10206 (Fig. 3a) that matched to the Arabidopsis genes At1g54710, At1g57680 and At1g60160, respectively (Parkin et al. 2005; Delourme et al. 2006). This demonstrated that BnaC.BANa was mapped within an oilseed rape segment that showed synteny with AtC1. On the same line, BnaA.BANa was mapped onto A1 DY at 2 cM from Na12C06 that matched to At1g60500. In addition, Parkin et al. (2005) showed that pN173a (At1g57680) was also located in the centromeric region of A1. These results proved that BnaA.BANa also mapped within an oilseed rape segment that showed synteny with AtC1. BnaC.BANb was assigned to the C4 chromosome. Interestingly, Parkin et al. (2005) reported that marker pN173b (At1g57680) was also mapped on C4, within a region syntenic to the AtC1 segment that comprises AtBAN. Therefore, we could hypothesise that BnaC.BANb is likely to map to this region. No polymorphism was found to date for the fourth gene, BnaC.BANa. Finally, it is worthwhile to note that the RFLP marker pN173, which matched to At1g57680, was located on chromosomes A1, C1 and C4 (Parkin et al. 2005) in regions carrying the Bna.BAN genes (this study) and was also found on chromosomes C8, A9 and C9 (Parkin et al. 2005). This demonstrated that the region around AtANR was retrieved at six different locations into the oilseed rape genome, although only four Bna.BAN genes were identified, providing evidence that at least two Bna.BAN genes were lost during genome evolution.
Bna.BAN genes encode functional orthologs from AtANR and are expressed in procyanidin-accumulating cells
Bna.BAN displayed high-sequence conservation with AtANR (see above), although differences induced loss of putative functional domains in some of the protein sequences. For instance, a leucine repeat was found in AtANR and Bna.BAN group “b” but not in Bna.BAN group “a” due to a proline insertion in protein sequences from the latest group (Fig. 2a). To answer the question whether the changes in protein structure were accompanied by a modification of the protein function in planta or not, we performed complementation assays with Bna.BAN coding sequences. When expressed in Arabidopsis ban mutant backgrounds, Bna.BAN genes were all able to restore the Arabidopsis wild-type seed phenotype. In addition, the four Bna.BAN paralogs were expressed in oilseed rape and displayed similar expression pattern within the different organs. Taken together, these results demonstrated that the cloned Bna.BAN genes were the functional orthologs from AtANR and that there was no neo-/sub-functionalisation nor pseudogenes amongst the four oilseed rape paralogs. Several previous studies have proposed that changes in expression profile between homeologs were one clue into the evolution of allopolyploid genomes (reviewed in Flagel and Wendel 2009).
Bna.BAN transcripts were restricted to the seeds from the very early developmental stages (5 dap) until the end of maturation (45 dap). No signal was detected in buds or flowers, suggesting that Bna.BAN genes were not expressed in ovules. Within the seed, Bna.BAN transcripts accumulated in the seed coat and more particularly into the inner integument as revealed by laser microdissection assays, a result which was confirmed by ProBna.BAN:UidA transcriptional fusions. This spatio-temporal expression pattern fitted with the accumulation of procyanidins in B. napus seeds (Nesi et al. 2009 and data not shown) and seemed to be conserved with AtANR expression profile. However, in our experiments Bna.BAN expression was also detected into developing embryos and silique coats by RT-PCR, but one could assume that the expression in these tissues was fainter compared with expression into the seed coat, since no GUS activity was reported in embryos nor in siliques. On the opposite, Debeaujon et al. (2003) suggested that AtANR expression was restricted to the procyanidin-accumulating cell layer within the seed coat based on the expression results and promoter-GUS fusions analyses. However, recent data published from the Arabidopsis eFP Browser (bar.utoronto.ca) revealed that AtANR transcripts also accumulated to a lesser extent in apical part of globular embryo collected by laser capture microdissection. Taken together our data suggested that Bna.BAN genes expression profile was correlated with procyanidin accumulation in B. napus seed coat.
BAN regulatory network is active in B. napus inner integument
Analysis of Bna.BAN promoters showed that 200 bp in 5′ of the putative start codon were highly conserved between the four paralogs and also with ProAtANR sequence. In addition, this region carried most of the putative cis-acting motifs (bHLH/ZIP-binding site, CAAT- and TATA-boxes, procyanidin enhancer), thus leading to the hypothesis that this conserved sequence likely stood for the BAN promoter in Brassicaceae.
In a previous study, we reported that ProAtANR was active in procyanidin-accumulating cells of B. napus seed coat (Nesi et al. 2009) suggesting that the AtANR regulatory network was conserved between Arabidopsis and oilseed rape. Here, we presented complementary results based on the analysis of Arabidopsis and oilseed rape transgenic plants carrying ProBna.BAN _230bp:UidA fusions. All transgenic plants displayed GUS activity restricted to the seed and more precisely to the inner integument demonstrating that this 230-bp promoter was sufficient to induce Bna.BAN. In addition, ProBna.BAN:UidA activity matched very well to the procyanidin accumulation pattern both in Arabidopsis and in oilseed rape. The fact that ProBna.BAN:UidA was active into Arabidopsis seed strengthened the hypothesis that a common regulatory network controlled BAN in Brassicaceae. Nesi et al. (2009) reported the identification of cDNA for TT8, TT16 and TTG1 homologs in oilseed rape and homologs from TT1 and TT2 were identified elsewhere (Wei et al. 2007). Taken together, these results suggested that the regulatory complex that govern ANR expression in Arabidopsis was functional in the oilseed rape inner integument and should interact with the first 230 bp of ProBna.BAN.
Bna.BAN genes represent candidate markers for seed colour QTLs
A number of previous studies reported the identification and the localisation of genomic regions controlling seed pigmentation. Comparison of mapping data from seed colour QTLs with those from Bna.BAN genes could highlight putative co-localisations. For instance, Badani et al. (2006) identified eight QTLs involved in seed pigmentation, one of which was located on A1 at 12 cM from the SSR Na14-D07. On the same line, Liu et al. (2006) found two seed colour QTLs, one of which was also located at the level of Na14-D07. Interestingly, BnaA.BANa was located on A1 and could be a candidate gene for these QTLs. Fu et al. (2007) found 12 seed colour QTLs, one of which mapped close to the SSR Bras072. This marker was located on the homeolog linkage groups C4 and A5 in our DY mapping population. Interestingly, BnaC.BANb was assigned to C4. All these findings remained to be confirmed by mapping the Bna.BAN genes in the populations used for the detection of seed colour QTLs.
To conclude, prospects of this work will include the identification and the functional characterisation of other flavonoid-related genes in oilseed rape to find accurate candidate genes for yellow-seeded genotypes breeding programmes.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Isabelle Debeaujon (INRA Versailles) for critically reading the present manuscript, Jean-Marc Routaboul and Loïc Lepiniec (INRA Versailles) for enthusiastic discussions during the progress of this work, Fanchon Divol, Bertrand Dubreucq and Jean-Christophe Palauqui (INRA Versailles) for the kind gift of the pBIB101-GUS vector and Maria Manzanares-Dauleux (INRA Rennes) for the gift of DNA from B. oleracea C10, Genoplante for providing the cDNA clones (BN15019B21, BN25045I20 and BN25045M17), INRA Versailles for sending seeds from ban-1 and ban-4 Arabidopsis mutant lines, Anne-Marie Chèvre and Frédérique Eber (INRA Rennes) for providing unpublished monosomic and polysomic addition lines from B. napus, Harry Belcram and Sandra Moreau (INRA Evry, France) for technical assistance for BAC library management and screenings, Pascale Bellaud (INSERM Rennes, France) for sample preparation and contribution to laser microdissection assays and Penny Sparrow (John Innes Centre, Norwich, UK) for excellent advice on oilseed rape transformation. Part of this work was funded through a GABI-Genoplante collaborative project (CompGen: “Comparative genomics between Arabidopsis and Brassica for genes directing seed-specific flavonoid biosynthesis”). B.A. is supported by the Région de Bretagne through a 3 years PhD grant (nb. 06007978).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Open Access
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial License which permits any noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and source are credited.
Abbreviations
- ANR
Anthocyanidin reductase
- BAC
Bacterial artificial chromosome
- BAN
Banyuls
- daf
Day after flowering
- dap
Day after pollination
- DH
Doubled haploid
- DY
Darmor-bzh × Yudal
- EST
Expressed sequence tag
- ha
Hectare
- QTL
Quantitative trait loci
- TT
Transparent Testa
- SD
Stellar × Drakkar
References
- Albert S, Delseny M, Devic M. BANYULS, a novel negative regulator of flavonoid biosynthesis in the Arabidopsis seed coat. Plant J. 1997;11:289–299. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313X.1997.11020289.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almeida JR, D’Amico E, Preuss A, Carbone F, de Vos CH, Deiml B, Mourgues F, Perrotta G, Fischer TC, Bovy AG, Martens S, Rosati C. Characterization of major enzymes and genes involved in flavonoid and proanthocyanidin biosynthesis during fruit development in strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa) Arch Biochem Biophys. 2007;465:61–71. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2007.04.040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990;215:403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badani AG, Snowdon RJ, Wittkop B, Lipsa FD, Baetzel R, Horn R, De Haro A, Font R, Lühs W, Friedt W. Colocalization of a partially dominant gene for yellow seed colour with a major QTL influencing acid detergent fibre (ADF) content in different crosses of oilseed rape (Brassica napus) Genome. 2006;49:1499–1509. doi: 10.1139/G06-091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornberg-Bauer E, Rivals E, Vingron M. Computational approaches to identify leucine zippers. Nucl Acids Res. 1998;26:2740–2746. doi: 10.1093/nar/26.11.2740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chai YR, Lei B, Huang HL, Li JN, Yin JM, Tang ZL, Wang R, Chen L. TRANSPARENT TESTA 12 genes from Brassica napus and parental species: cloning, evolution, and differential involvement in yellow seed trait. Mol Genet Genomics. 2009;81:109–123. doi: 10.1007/s00438-008-0399-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clough SJ, Bent AF. Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 1998;16:735–743. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.1998.00343.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debeaujon I, Nesi N, Perez P, Devic M, Grandjean O, Caboche M, Lepiniec L. Proanthocyanidin-accumulating cells in Arabidopsis testa: regulation of differentiation and role in seed development. Plant Cell. 2003;15:2514–2531. doi: 10.1105/tpc.014043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delfour C, Roger P, Bret C, Berthe ML, Rochaix P, Kalfa N, Raynaud P, Bibeau F, Maudelonde T, Boulle N. RCL2, a new fixative, preserves morphology and nucleic acid integrity in paraffin-embedded breast carcinoma and microdissected breast tumor cells. J Mol Diagn. 2006;8:157–169. doi: 10.2353/jmoldx.2006.050105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delourme R, Falentin C, Huteau V, Clouet V, Horvais R, Gandon B, Specel S, Hanneton L, Dheu J-E, Deschamps M, Margale E, Vincourt P, Renard M. Genetic control of oil content in oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.) Theor Appl Genet. 2006;113:1331–1345. doi: 10.1007/s00122-006-0386-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devic M, Albert S, Delseny M, Roscoe TJ. Efficient PCR walking on plant genomic DNA. Plant Physiol Biochem. 1997;35:331–339. [Google Scholar]
- Devic M, Guilleminot J, Debeaujon I, Bechtold N, Bensaude E, Koornneef M, Pelletier G, Delseny M. The BANYULS gene encodes a DFR-like protein and is a marker of early seed coat development. Plant J. 1999;19:387–398. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313X.1999.00529.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle JJ, Doyle JL. Isolation of plant DNA from fresh tissues. Focus. 1990;12:13–15. [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick G, Curl C, Butler N, Greenwood N, Pearson A. Rapeseed meal and egg taint: effects of low glucosinolate Brassica napus meal, dehulled meal and hulls and of neomycin. J Sci Food Agric. 1984;35:749–757. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.2740350710. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer TC, Gosch C, Pfeiffer J, Halbwirth H, Halle C, Stich K, Forkmann G. Flavonoid genes of pear (Pyrus communis) Trees. 2007;21:521–529. doi: 10.1007/s00468-007-0145-z. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Flagel LE, Wendel JF. Gene duplication and evolutionary novelty in plants. New Phytol. 2009;183:557–564. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2009.02923.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu FY, Liu LZ, Chai YR, Chen L, Yang T, Jin MY, Ma AF, Yan XY, Zhang ZS, Li JN. Localization of QTLs for seed color using recombinant inbred lines of Brassica napus in different environments. Genome. 2007;50:840–854. doi: 10.1139/G07-068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita A, Soma N, Goto-Yamamoto N, Shindo H, Kakuta T, Koizumi T, Hashizume K. Anthocyanidin reductase gene expression and accumulation of flavan-3-ols in grape berry. Am J Enol Vitic. 2005;56:336–342. [Google Scholar]
- Ikegami A, Eguchi S, Kitajima A, Inoue K, Yonemori K. Identification of genes involved in proanthocyanidin biosynthesis of persimmon (Diospyros kaki) fruit. Plant Sci. 2007;172:1037–1047. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2007.02.010. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Klimyuk VI, Carroll BJ, Thomas CM, Jones JD. Alkali treatment for rapid preparation of plant material for reliable PCR analysis. Plant J. 1993;3:493–494. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313X.1993.t01-26-00999.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koncz C, Kreuzaler F, Kalman Z, Schell J. A simple method to transfer, integrate and study expression of foreign genes, such as chicken ovalbumin and α-actin in plant tumors. EMBO J. 1984;3:1029–1037. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01923.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosambi DD. The estimation of map distance from recombination values. Ann Eugen. 1944;12:172–175. [Google Scholar]
- Lee WS, You JA, Chung H, Lee YH, Baek NI, Yoo JS, Park YD. Molecular cloning and biochemical analysis of dihydroflavonol 4-reductase (DFR) from Brassica rapa ssp pekinesis (Chinese cabbage) using a heterologous system. J Plant Biol. 2008;51:42–47. doi: 10.1007/BF03030739. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Lepiniec L, Debeaujon I, Routaboul J-M, Baudry A, Pourcel L, Nesi N, Caboche M. Genetics and biochemistry of seed flavonoids. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2006;57:405–430. doi: 10.1146/annurev.arplant.57.032905.105252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J, Chen L, Wang R, Duan Y (2007) A strategy for breeding of the yellow-seeded hybrid in Brassica napus L. In: Proceedings of 12th international rapeseed congress, Science Press USA Inc., Genetics and Breeding, pp 11–13
- Lincoln S, Daly M, Lander E (1993) Constructing genetic linkage maps with Mapmaker/Exp 3.0: a tutorial and reference manual, 3rd edn. Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research, Technical Report
- Liu ZW, Fu TD, Tu JX, Chen BY. Inheritance of seed colour and identification of RAPD and AFLP markers linked to the seed colour gene in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) Theor Appl Genet. 2005;110:303–310. doi: 10.1007/s00122-004-1835-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu LZ, Meng JL, Lin N, Chen L, Tang ZL, Zhang XK, Li JN. QTL mapping of seed coat color for yellow seeded Brassica napus. Acta Genet Sin. 2006;33:181–187. doi: 10.1016/S0379-4172(06)60037-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lombard V, Delourme R. A consensus linkage map for rapeseed (Brassica napus L.): construction and integration of three individual maps from DH populations. Theor Appl Genet. 2001;103:491–507. doi: 10.1007/s001220100560. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Lysak MA, Koch MA, Pecinka A, Schubert I. Chromosome triplication found across the tribe Brassiceae. Genome Res. 2005;15:516–525. doi: 10.1101/gr.3531105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lysak MA, Berr A, Pecinka A, Schmidt R, McBreen K, Schubert I. Mechanisms of chromosome number reduction in Arabidopsis thaliana and related Brassicaceae species. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103:5224–5229. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0510791103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marles MAS, Gruber MY, Scoles GJ, Muir AD. Pigmentation in the developing seed coat and seedling leaves of Brassica carinata is controlled at the dihydroflavonol reductase locus. Phytochemistry. 2003;62:663–672. doi: 10.1016/S0031-9422(02)00488-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marles MAS, Ray H, Gruber MY. New perspectives on proanthocyanidin biochemistry and molecular regulation. Phytochemistry. 2003;64:367–383. doi: 10.1016/S0031-9422(03)00377-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naczk M, Amarowicz R, Sullivan A, Shahidi F. Current research developments on polyphenolics of rapeseed/canola: a review. Food Chem. 1998;62:489–502. doi: 10.1016/S0308-8146(97)00198-2. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Nesi N, Debeaujon I, Jond C, Stewart AJ, Jenkins GI, Caboche M, Lepiniec L. The TRANSPARENT TESTA16 locus encodes the ARABIDOPSIS BSISTER MADS domain protein and is required for proper development and pigmentation of the seed coat. Plant Cell. 2002;14:2463–2479. doi: 10.1105/tpc.004127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesi N, Lucas MO, Auger B, Lécureuil A, Guerche P, Kronenberger J, Lepiniec L, Debeaujon I, Renard M. The promoter of the Arabidopsis thaliana BAN gene is active in tannin-accumulating cells of the Brassica napus seed coat. Plant Cell Rep. 2009;28:601–617. doi: 10.1007/s00299-008-0667-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Østergaard L, King GJ. Standardized gene nomenclature for the Brassica genus. Plant Methods. 2008;4:10–13. doi: 10.1186/1746-4811-4-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paolocci F, Robbins MP, Madeo L, Arcioni S, Martens S, Damiani F. Ectopic expression of a basic Helix–Loop–Helix gene transactivates parallel pathways of proanthocyanidin biosynthesis. Structure, expression analysis, and genetic control of leucoanthocyanidin 4-reductase and anthocyanidin reductase genes in Lotus corniculatus. Plant Physiol. 2007;143:504–516. doi: 10.1104/pp.106.090886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkin IAP, Lydiate DJ, Trick M. Assessing the level of collinearity between Arabidopsis thaliana and Brassica napus for A. thaliana chromosome 5. Genome. 2002;45:356–366. doi: 10.1139/g01-160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkin IAP, Gulden SM, Sharpe AG, Lukens L, Trick M, Osborn TC, Lydiate DJ. Segmental structure of the Brassica napus genome based on comparative analysis with Arabidopsis thaliana. Genetics. 2005;171:765–781. doi: 10.1534/genetics.105.042093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson AH, Lan TH, Amasino R, Osborn TC, Quiros C. Brassica genomics: a complement to, and early beneficiary of, the Arabidopsis sequence. Genome Biol. 2001;2:1011.1–1011.4. doi: 10.1186/gb-2001-2-3-reviews1011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeiffer J, Kuhnel C, Brandt J, Duy D, Punyasiri PA, Forkmann G, Fischer TC. Biosynthesis of flavan 3-ols by leucoanthocyanidin 4-reductases and anthocyanidin reductases in leaves of grape (Vitis vinifera L.), apple (Malus × domestica Borkh.) and other crops. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2006;44:323–334. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2006.06.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pouilly N, Delourme R, Alix K, Jenczewski E. Repetitive sequence-derived markers tag centromeres and telomeres and provide insights into chromosome evolution in Brassica napus. Chromosome Res. 2008;16:683–700. doi: 10.1007/s10577-008-1219-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahman MH. Production of yellow-seeded Brassica napus through interspecific crosses. Plant Breed. 2001;120:463–472. doi: 10.1046/j.1439-0523.2001.00640.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Rakow G, Raney JP, Relf-Eckstein J (1999) Agronomic performance and seed quality of a new source of yellow seeded Brassica napus. In: Proceedings of 10th international rapeseed congress. Canberra, Australia
- Ren C, Bewley JD. Seed development, testa structure and precocious germination of Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa subsp. pekinensis) Seed Sci Res. 1998;8:385–398. doi: 10.1017/S0960258500004311. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Routaboul JM, Kerhoas L, Debeaujon I, Pourcel L, Caboche M, Einhorn J, Lepiniec L. Flavonoid diversity and biosynthesis in seed of Arabidopsis thaliana. Planta. 2006;224:96–107. doi: 10.1007/s00425-005-0197-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shahidi F, Naczk M. An overview of the phenolics of canola and rapeseed: chemical, sensory and nutritional significance. J Am Oil Chem Soc. 1992;69:917–924. doi: 10.1007/BF02636344. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Shen GA, Pang Y, Wu W, Liu X, Zhao L, Sun X, Tang K. Isolation and characterization of a putative anthocyanidin reductase gene from Ginkgo biloba. J Plant Physiol. 2006;163:224–227. doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2005.06.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirley BW. Flavonoids in seeds and grains: physiological function, agronomic importance and the genetics of biosynthesis. Seed Sci Res. 1998;8:415–422. doi: 10.1017/S0960258500004372. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Shirley BW, Hanley S, Goodman HM. Effects of ionizing radiation on a plant genome: analysis of two Arabidopsis transparent testa mutations. Plant Cell. 1992;4:333–347. doi: 10.1105/tpc.4.3.333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simbaya J, Slominski BA, Rakow G, Campbell LD, Downey RK, Bello JM. Quality characteristics of yellow-seeded Brassica seed meals: protein, carbohydrates, and dietary fiber components. J Agric Food Chem. 1995;43:2062–2066. doi: 10.1021/jf00056a020. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Slominski BA, Simbaya J, Campbell LD, Rakow G, Guenter W. Nutritive value for broilers of meals derived from newly developed varieties of yellow-seeded canola. Anim Feed Sci Tech. 1999;78:249–262. doi: 10.1016/S0377-8401(99)00003-6. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Somers DJ, Rakow G, Prabhu VK, Friesen KRD. Identification of a major gene and RAPD markers for yellow seed coat colour in Brassica napus. Genome. 2001;44:1077–1082. doi: 10.1139/gen-44-6-1077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparrow PAC, Dale PJ, Irwin JA. The use of phenotypic markers to identify Brassica oleracea genotypes for routine high-throughput Agrobacterium-mediated transformation. Plant Cell Rep. 2004;23:64–70. doi: 10.1007/s00299-004-0818-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparrow PAC, Snape JW, Dale PJ, Irwin JA. The rapid identification of B. napus genotypes, for high-throughput transformation, using phenotypic tissue culture markers. Acta Horticult. 2006;706:239–246. [Google Scholar]
- Takos AM, Ubi BE, Robinson SP, Walker AR. Condensed tannin biosynthesis genes are regulated separately from other flavonoid biosynthesis genes in apple fruit skin. Plant Sci. 2006;170:487–499. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2005.10.001. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Town CD, Cheung F, Maiti R, Crabtree J, Haas BJ, Wortman JR, Hine EE, Althoff R, Arbogast TS, Tallon LJ, Vigouroux M, Trick M, Bancroft I. Comparative genomics of Brassica oleracea and Arabidopsis thaliana reveal gene loss, fragmentation, and dispersal after polyploidy. Plant Cell. 2006;18:1348–1359. doi: 10.1105/tpc.106.041665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van de Peer Y, De Wachter R. TREECON for Windows: a software package for the construction and drawing of evolutionary trees for the Microsoft Windows environment. Comput Appl Biosci. 1994;10:569–570. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/10.5.569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Deynze AE, Beversdorf WD, Pauls KP. Temperature effects on seed colour in black- and yellow-seeded rapeseed. Can J Plant Sci. 1993;73:383–387. [Google Scholar]
- Wei YL, Li JN, Lu J, Tang ZL, Pu DC, Chai YR. Molecular cloning of Brassica napus TRANSPARENT TESTA 2 gene family encoding potential MYB regulatory proteins of proanthocyanidin biosynthesis. Mol Biol Rep. 2007;34:105–120. doi: 10.1007/s11033-006-9024-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisshaar B, Jenkins GI. Phenylpropanoid biosynthesis and its regulation. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 1998;1:251–257. doi: 10.1016/S1369-5266(98)80113-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao YH, Zhang ZS, Yin MH, Luo M, Li XB, Hou L, Pei Y. Cotton flavonoid structural genes related to the pigmentation in brown fibers. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007;358:73–78. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.04.084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie D-Y, Sharma SB, Paiva NL, Ferreira D, Dixon RA. Role of anthocyanidin reductase, encoded by BANYULS in plant flavonoid biosynthesis. Science. 2003;299:396–399. doi: 10.1126/science.1078540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu BB, Li JN, Zhang XK, Wang R, Xie LL, Chai YR. Cloning and molecular characterization of a functional flavonoid 3′-hydroxylase gene from Brassica napus. J Plant Physiol. 2007;164:350–363. doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2006.03.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan ML, Liu Z, Guan CY, Chen SY, Liu XJ, Yuan MZ. Cloning and sequence analysis of flavonoid biosynthesis genes in Brassica juncea. Sci Agric Sin. 2007;40:2688–2695. [Google Scholar]
- Yan ML, Liu XJ, Liu ZS, Guan CY, Yuan MZ, Xiong XH. Cloning and expression analysis of dihydroflavonol 4-reductase gene in Brassica juncea. Acta Agron Sin. 2008;34:1–7. [Google Scholar]