Abstract
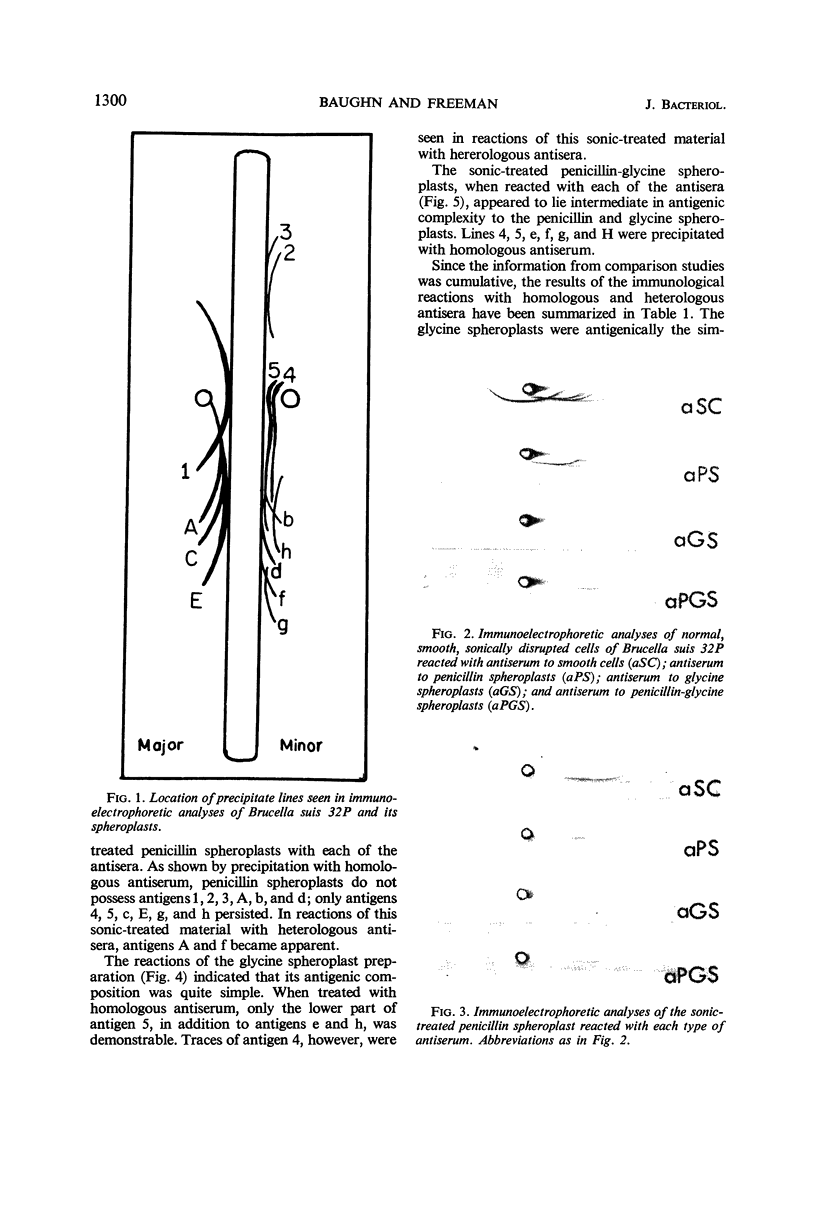
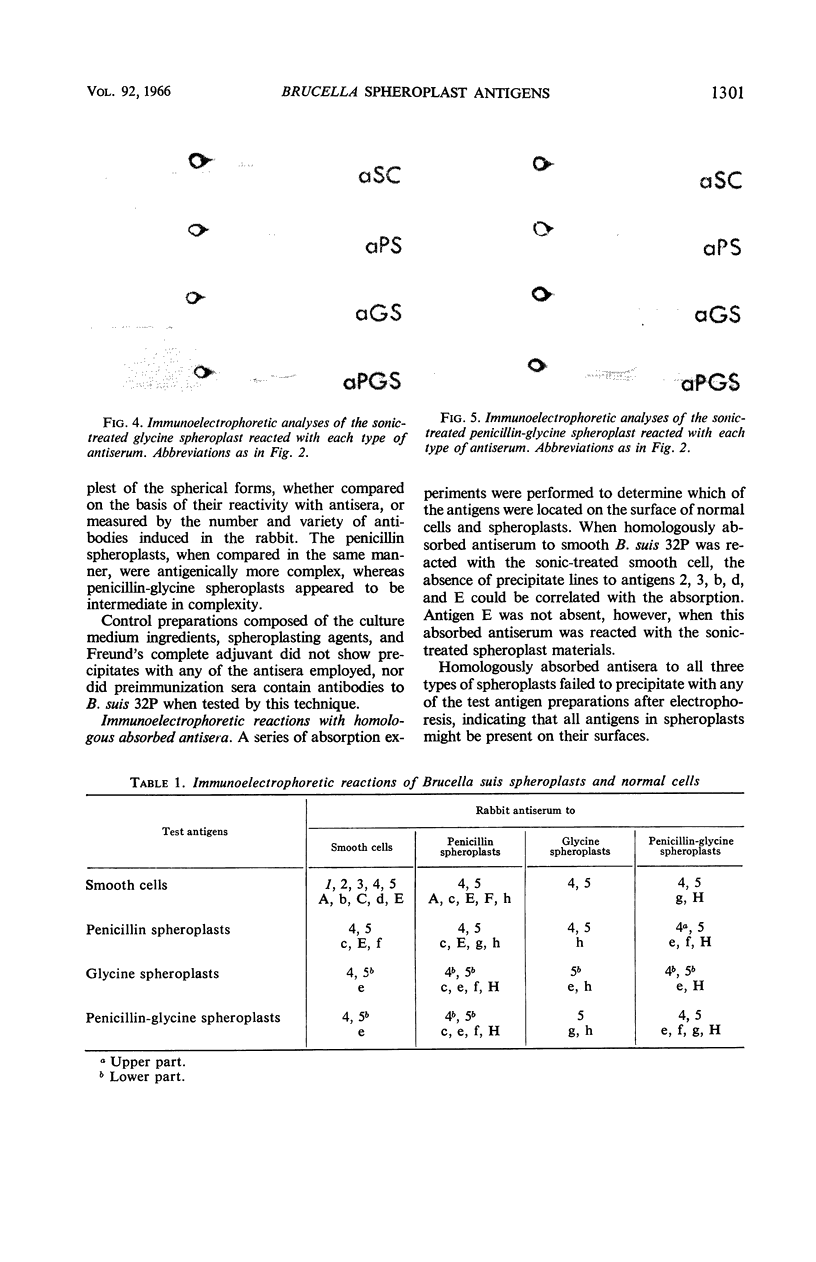
Baughn, Robert E. (University of Tennessee, Memphis), and Bob A. Freeman. Antigenic structure of Brucella suis spheroplasts. J. Bacteriol. 92:1298–1303. 1966.—Immunoelectrophoresis was used to differentiate between the antigenic mosaics of normal cells of Brucella suis and of spheroplasts prepared by treatment with penicillin, glycine, and a combination of these agents. Smooth cells possessed at least 13 antigens, 10 of which were precipitated with homologous antiserum. Three additional antigens were visualized by reaction with spheroplast antisera. Spheroplasts induced with glycine were the least complex, with only six antigens. Penicillin-glycine spheroplasts were similar, but possessed one additional antigen. Penicillin spheroplasts were the most complex, with eight antigens. Although there appeared to be quantitative differences between the antigens of spheroplasts and normal cells, no completely new antigens were detected in spheroplasts. Serum absorption studies indicated that four antigens were associated with the surface of normal B. suis, none of which occurred in spheroplasts.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BAUMANN-GRACE J. B., TOMCSIK J. The surface structure and serological typing of Bacillus megaterium. J Gen Microbiol. 1957 Aug;17(1):227–237. doi: 10.1099/00221287-17-1-227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREEMAN B. A., KROSS D. J., CIRCO R. Host-parasite relationships in brucellosis. II. Destruction of macrophage cultures by Brucella of different virulence. J. J Infect Dis. 1961 May-Jun;108:333–338. doi: 10.1093/infdis/108.3.333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREEMAN B. A., RUMACK B. H. CYTOPATHOGENIC EFFECT OF BRUCELLA SPHEROPLASTS ON MONOCYTES IN TISSUE CULTURE. J Bacteriol. 1964 Nov;88:1310–1315. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.5.1310-1315.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GERHARDT P., VENNES J. W. Immunologic comparison of isolated surface membranes of bacillus megaterium. Science. 1956 Sep 21;124(3221):535–536. doi: 10.1126/science.124.3221.535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLENCHUR H., SEAL U. S., ZINNEMAN H. H., HALL W. H. Antigenicity of some Brucella melitensis cell fractions. J Bacteriol. 1963 Feb;85:363–368. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.2.363-368.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HINES W. D., FREEMAN B. A., PEARSON G. R. PRODUCTION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF BRUCELLA SPHEROPLASTS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Feb;87:438–445. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.2.438-445.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OLITZKI A. L., SULITZEANU D. Studies on the antigenic structure of Brucella suis with the aid of the agar gel precipitation technique. I. The resistance of antigens to physical, chemical and enzymatic treatments. Br J Exp Pathol. 1958 Jun;39(3):219–227. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STINEBRING W. R. Characteristics of intracellularly grown Brucella abortus. J Infect Dis. 1962 Jul-Aug;111:17–24. doi: 10.1093/infdis/111.1.17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]