Abstract
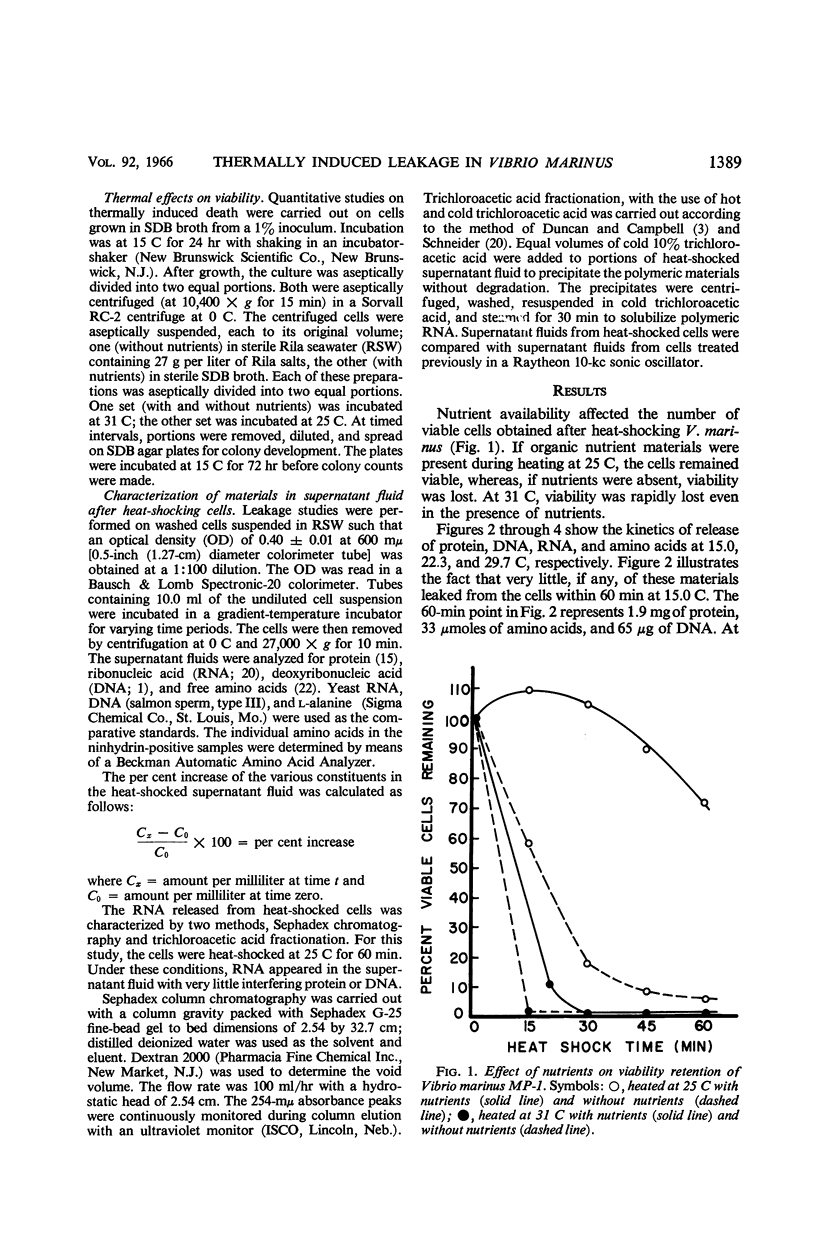
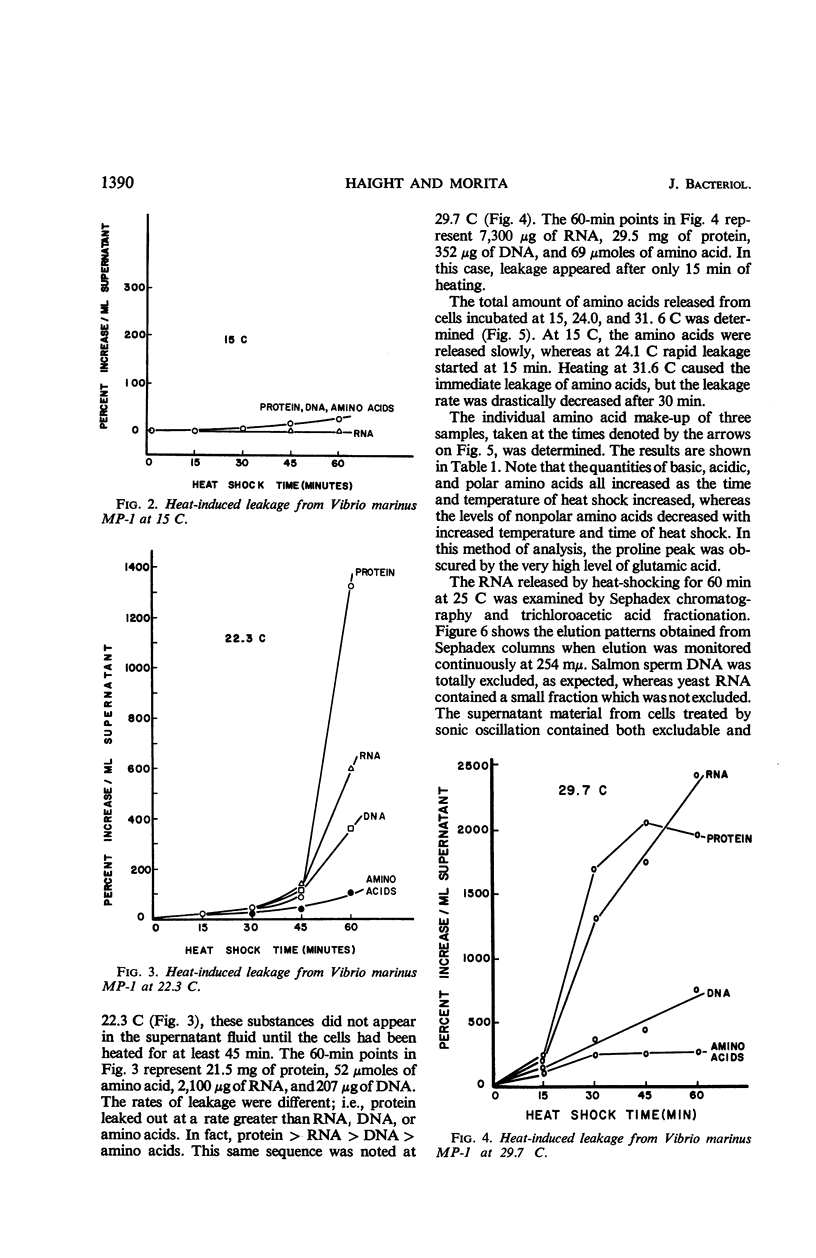
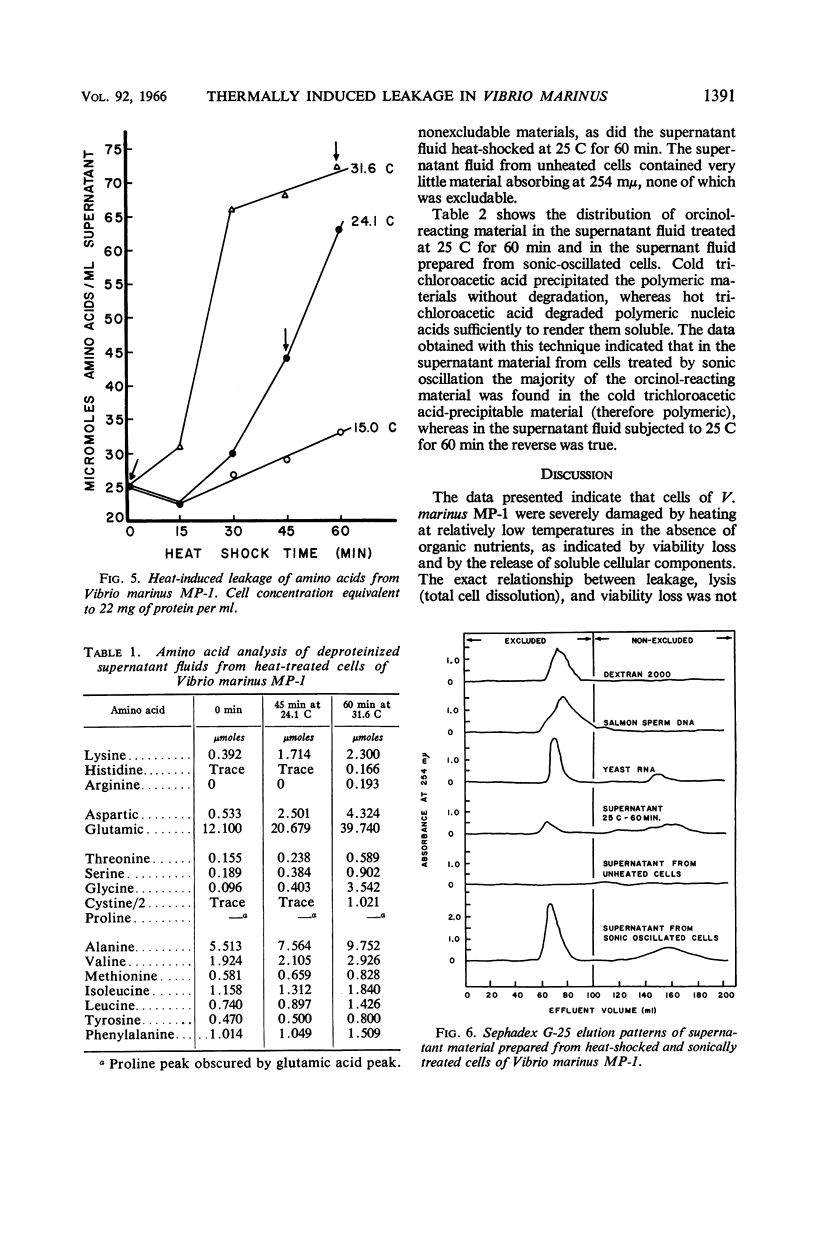
Haight, Rodger D. (Oregon State University, Corvallis), and Richard Y. Morita. Thermally induced leakage from Vibrio marinus, an obligately psychrophilic bacterium. J. Bacteriol. 92:1388–1393. 1966.—Leakage of various cellular components into the surrounding menstruum occurred when Vibrio marinus was subjected to temperatures above 20 C (organism's maximal growth temperature). These materials, listed in decreasing rates of leakage, were identified as protein, deoxyribonucleic acid, ribonucleic acid, and amino acids. The amount of polar amino acids increased as the time and temperature of heat treatment were increased, whereas the nonpolar amino acids decreased. The ribonucleic acid in the supernatant fluid resulting from heat treatment was both polymeric and nonpolymeric. Leakage of cellular components may be one of the reasons that V. marinus MP-1 loses viability when exposed to temperatures above its maximal temperature for growth.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLWELL R. R., MORITA R. Y. REISOLATION AND EMENDATION OF DESCRIPTION OF VIBRIO MARINUS (RUSSELL) FORD. J Bacteriol. 1964 Oct;88:831–837. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.4.831-837.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan M. G., Campbell J. J. OXIDATIVE ASSIMILATION OF GLUCOSE BY PSEUDOMONAS AERUGINOSA. J Bacteriol. 1962 Oct;84(4):784–792. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.4.784-792.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards O. F., Rettger L. F. Relation of Certain Respiratory Enzymes to the Maximum Growth Temperatures of Bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1937 Nov;34(5):489–515. doi: 10.1128/jb.34.5.489-515.1937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evison L. M., Rose A. H. A comparative study on the biochemical bases of the maximum temperatures for growth of three psychrophilic micro-organisms. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Sep;40(3):349–364. doi: 10.1099/00221287-40-3-349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAGEN P. O., KUSHNER D. J., GIBBONS N. E. TEMPERATURE-INDUCED DEATH AND LYSIS IN A PSYCHROPHILIC BACTERIUM. Can J Microbiol. 1964 Dec;10:813–822. doi: 10.1139/m64-106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAGEN P. O., ROSE A. H. Studies on the biochemical basis of the low maximum temperature in a psychrophilic cryptococcus. J Gen Microbiol. 1962 Jan;27:89–99. doi: 10.1099/00221287-27-1-89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- INGRAHAM J. L., BAILEY G. F. Comparative study of effect of temperature on metabolism of psychrophilic and mesophilic bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1959 May;77(5):609–613. doi: 10.1128/jb.77.5.609-613.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iandolo J. J., Ordal Z. J. Repair of thermal injury of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jan;91(1):134–142. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.1.134-142.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATES M., HAGEN P. O. INFLUENCE OF TEMPERATURE ON FATTY ACID COMPOSITION OF PSYCHROPHILIC AND MESOPHILIC SERRATIA SPECIES. Can J Biochem. 1964 Apr;42:481–488. doi: 10.1139/o64-055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAUFMANN O. W., HARMON L. G., PAIL THORP O. C., PFLUG I. J. Effect of heat treatment on the growth of surviving cells. J Bacteriol. 1959 Dec;78:834–838. doi: 10.1128/jb.78.6.834-838.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORITA R. Y., BURTON S. D. INFLUENCE OF MODERATE TEMPERATURE ON GROWTH AND MALIC DEHYDROGENASE ACTIVITY OF A MARINE PSYCHROPHILE. J Bacteriol. 1963 Nov;86:1025–1029. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.5.1025-1029.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STRANGE R. E., SHON M. EFFECTS OF THERMAL STRESS ON VIABILITY AND RIBONUCLEIC ACID OF AEROBACTER AEROGENES IN AQUEOUS SUSPENSION. J Gen Microbiol. 1964 Jan;34:99–114. doi: 10.1099/00221287-34-1-99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UPADHYAY J., STOKES R. L. Temperature-sensitive formic hydrogenlyase in a psychrophilic bacterium. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jan;85:177–185. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.1.177-185.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


