Abstract
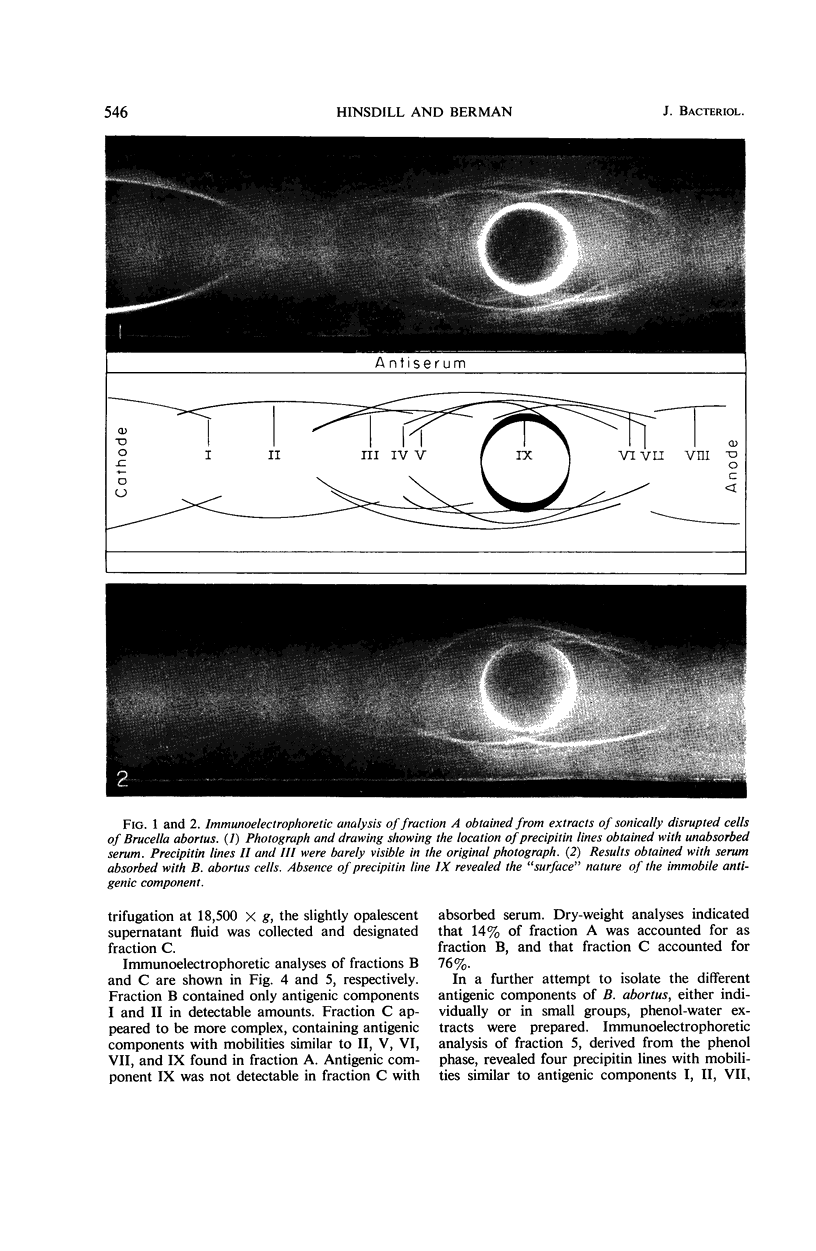
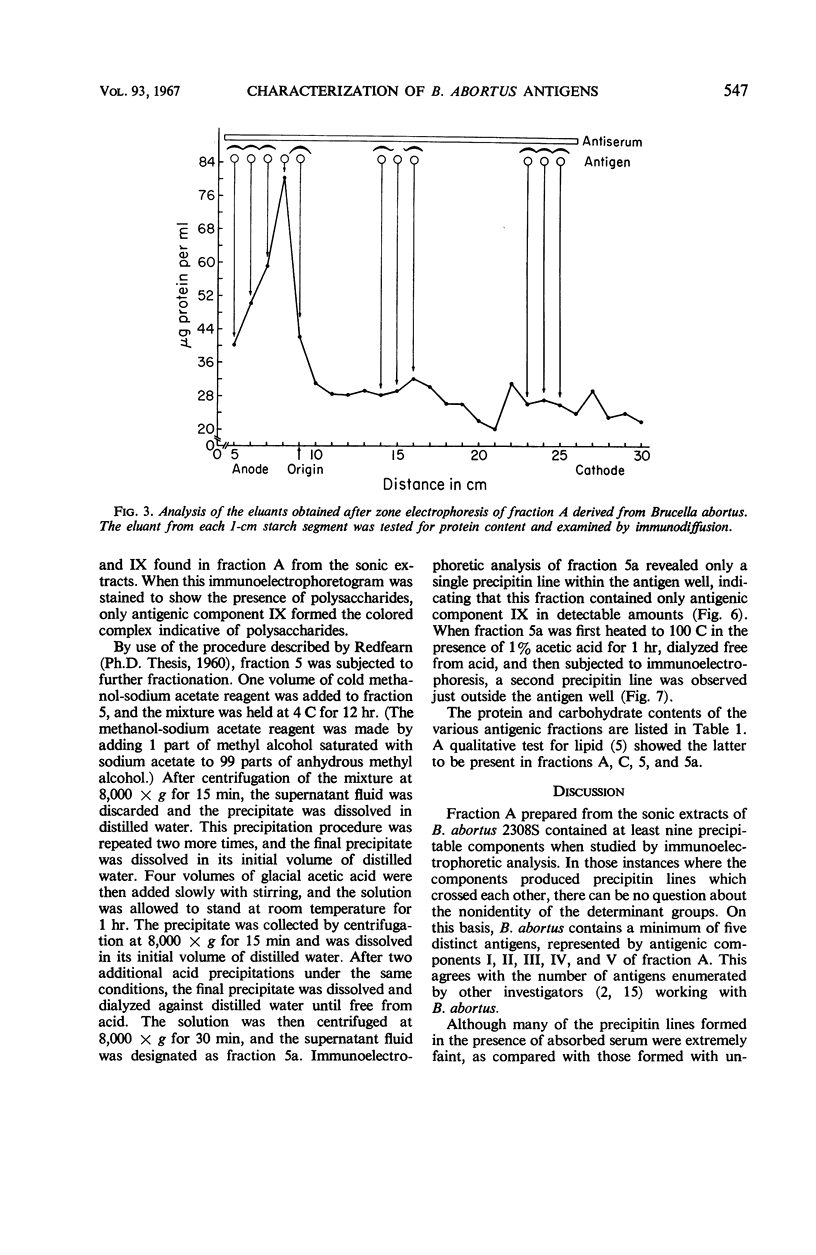
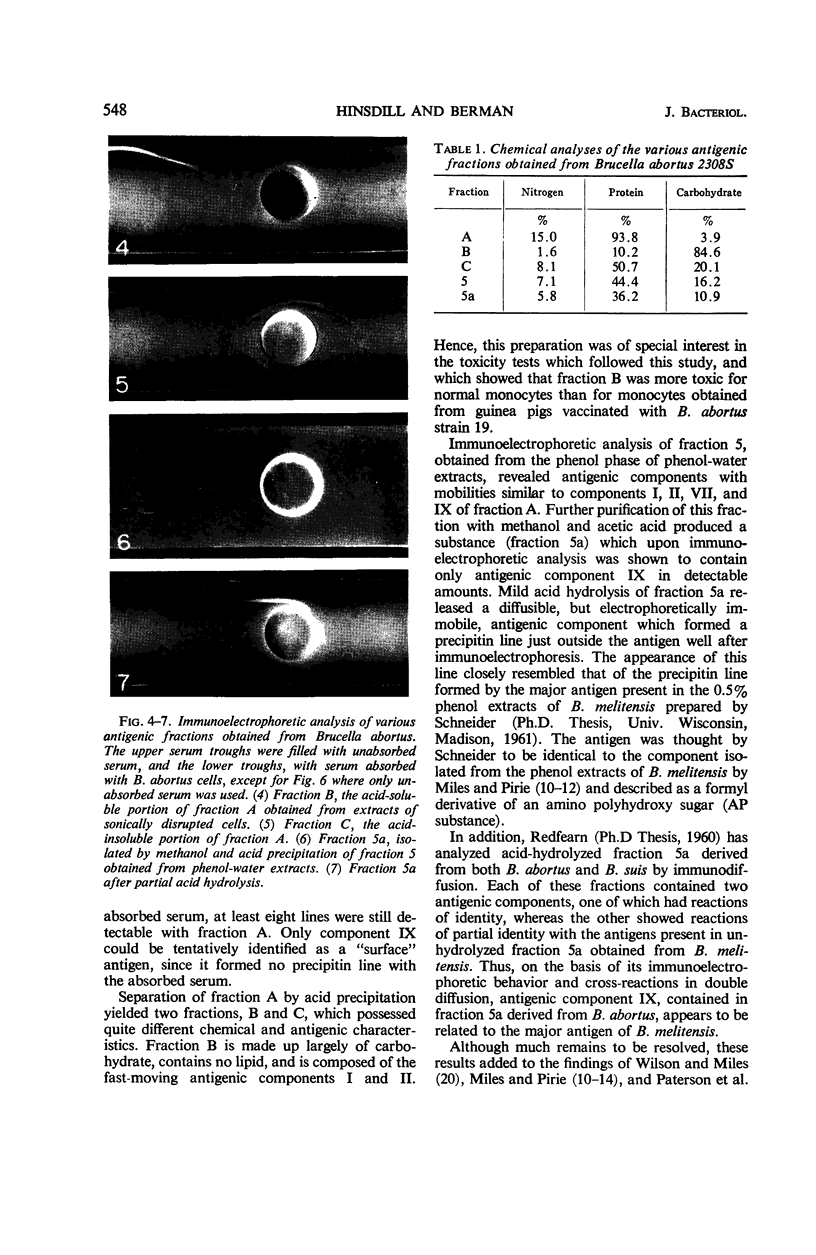
Extracts of Brucella abortus 2308S, prepared either by aqueous extraction of sonically ruptured cells or by phenol-water extraction of whole cells, were subjected to various fractionation procedures and then analyzed to determine their immunoelectrophoretic patterns and chemical properties. Fraction A, prepared from sonic extracts, contained at least nine precipitable components when analyzed by immunoelectrophoresis. Of these, five components gave reactions of nonidentity with each other and, hence, represented separate antigens having unrelated determinant groups. Antigenic component IX, found in both the phenol and sonic extracts, did not form a precipitin line in the presence of serum that had been adsorbed with whole cells and was therefore tentatively identified as a “surface” antigen. From several lines of evidence, component IX was thought to be a lipopolysaccharide similar to the AP substance described by Miles and Pirie and shown by them to carry the “abortus” and “melitensis” determinant groups.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker P. J., Wilson J. B. Hypoferremia in mice and its application to the bioassay of endotoxin. J Bacteriol. 1965 Oct;90(4):903–910. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.4.903-910.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DURRUM E. L., PAUL M. H., SMITH E. R. B. Lipid detection in paper electrophoresis. Science. 1952 Oct 17;116(3016):428–430. doi: 10.1126/science.116.3016.428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNKEL H. G., SLATER R. J. Zone electrophoresis in a starch supporting medium. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1952 May;80(1):42–44. doi: 10.3181/00379727-80-19516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles A. A. The properties of antigenic preparations from Brucella melitensis: Hydrolysis and acetylation of the amino-polyhydroxy compound derived from the antigen. With an Addendum by J. St L. Philpot. Biochem J. 1939 Oct;33(10):1716–1726. doi: 10.1042/bj0331716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles A. A. The properties of antigenic preparations from Brucella melitensis: The hydrolysis of the formamino linkage. Biochem J. 1939 Oct;33(10):1709–1715. doi: 10.1042/bj0331709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OLITZKI A. L. Studies on the antigenic structure of virulent and nonvirulent brucellae with the aid of the agar gel precipitation technique. Br J Exp Pathol. 1959 Oct;40:432–440. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- URIEL J., GRABAR P. A new technique for direct detection of glycoproteins and polysaccharides after electrophoresis or immunoelectrophoresis in agar gel. Anal Biochem. 1961 Feb;2:80–82. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(61)90042-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITE P. G., WILSON J. B. Differentiation of smooth and nonsmooth colonies of Brucellae. J Bacteriol. 1951 Feb;61(2):239–240. doi: 10.1128/jb.61.2.239-240.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]