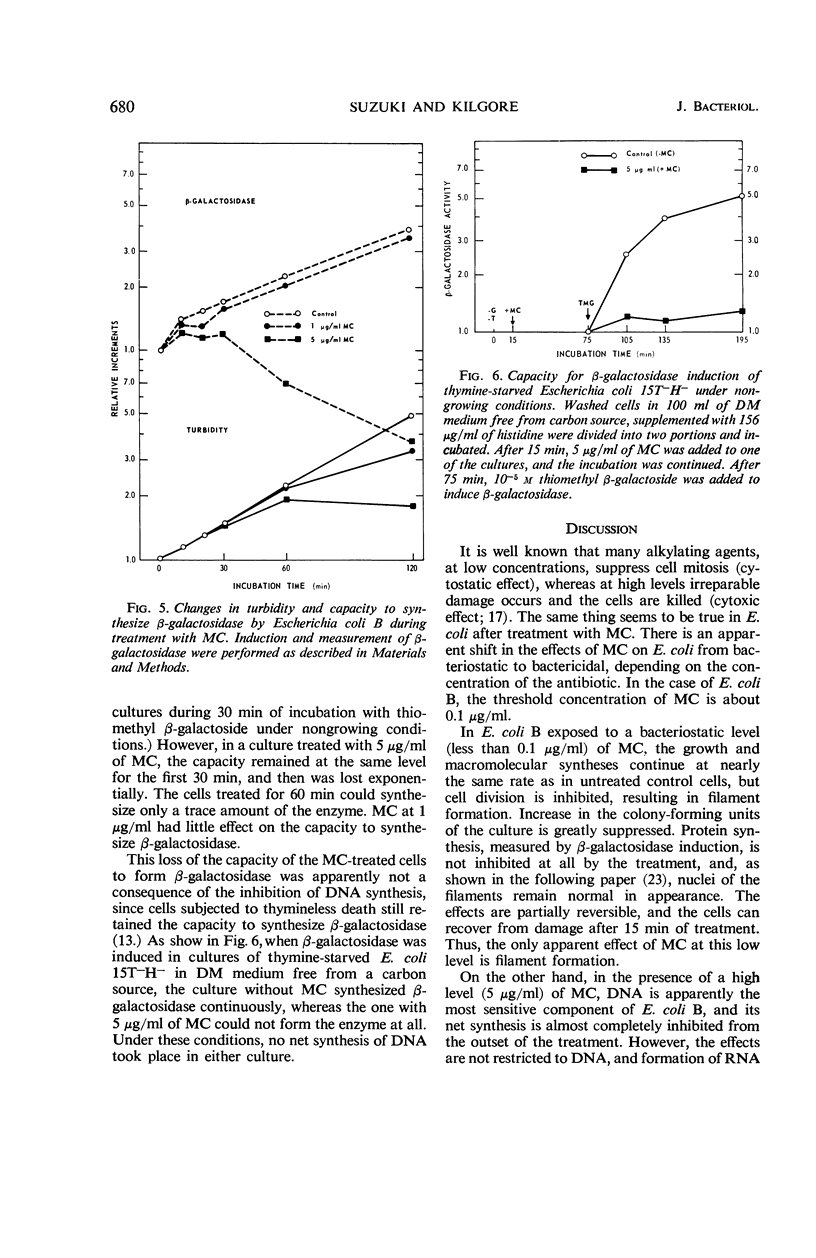
Abstract
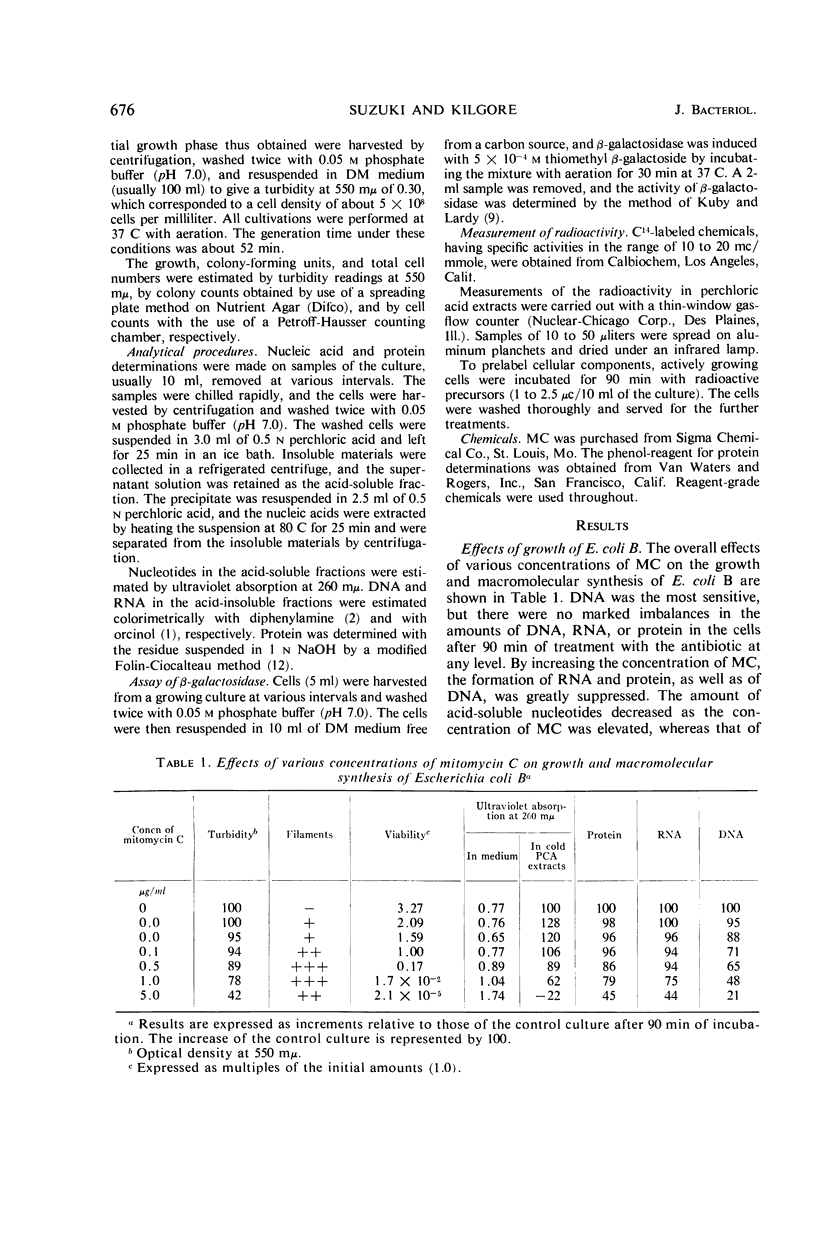
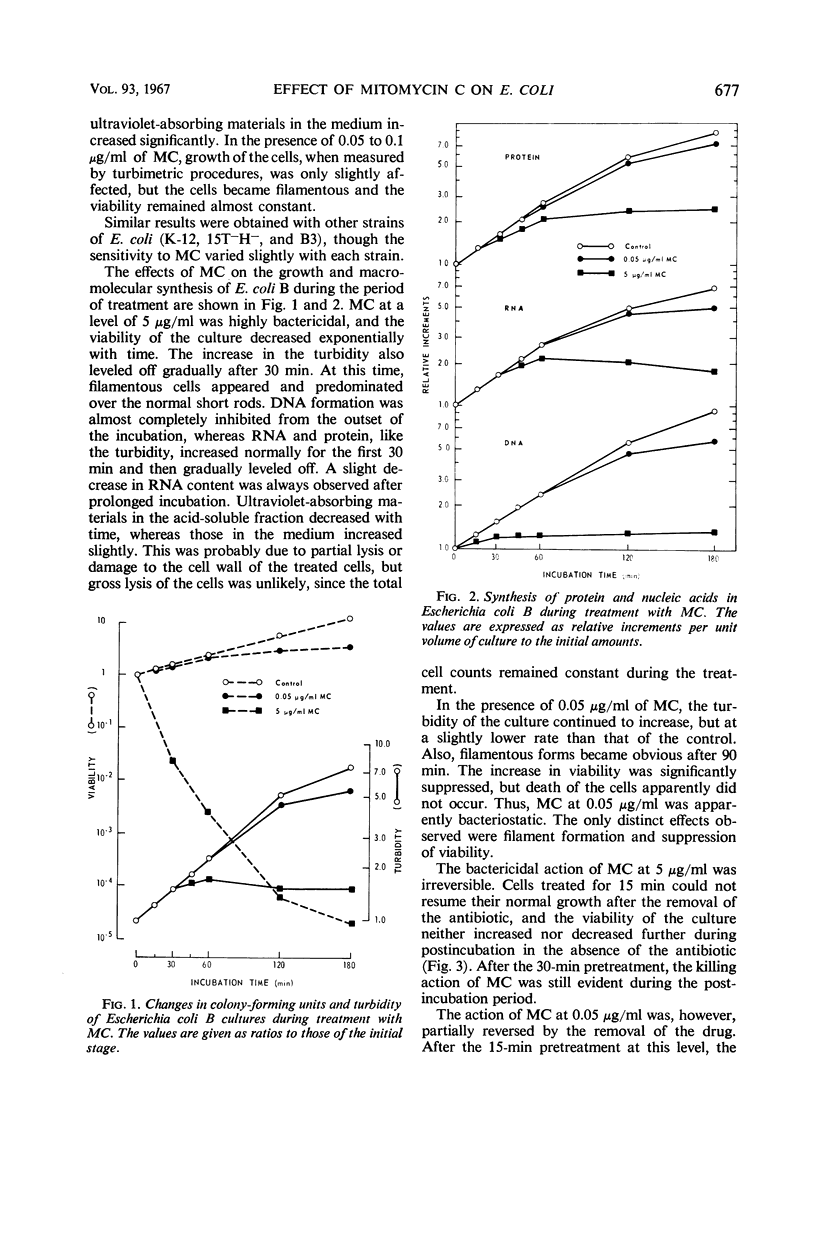
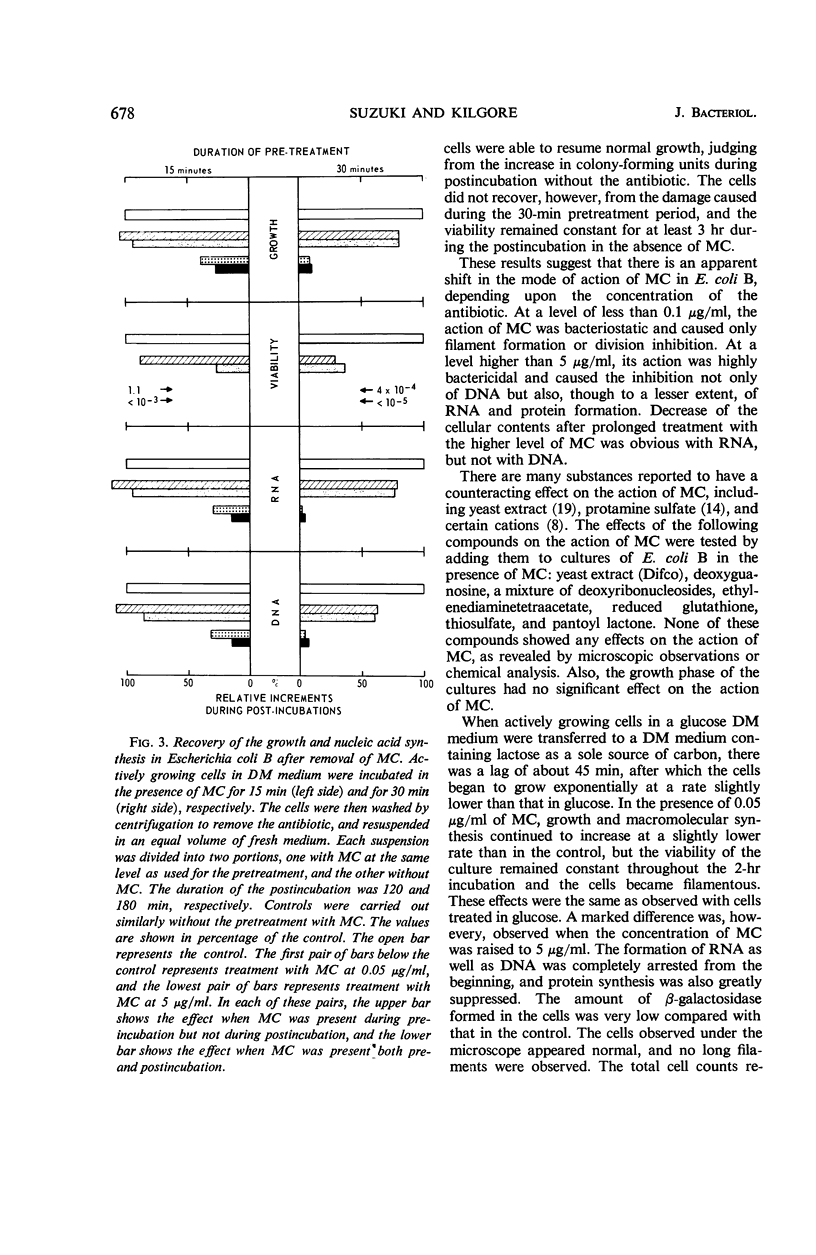
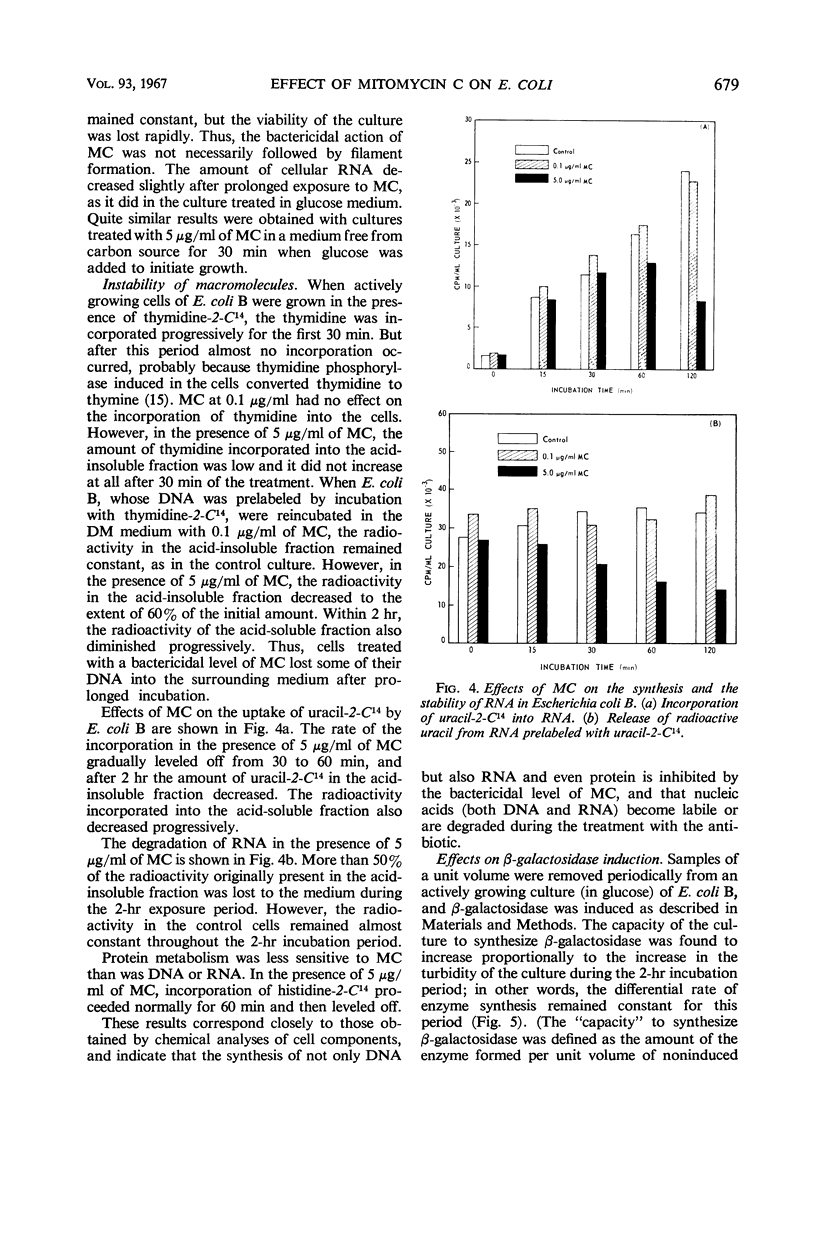
When cells of Escherichia coli B growing in a glucose-synthetic medium were treated with mitomycin C, the effects produced by the antibiotic varied, depending on the concentration. When the concentration was reduced to less than 0.1 μg/ml, the action of the antibiotic was bacteriostatic; cell elongation resulted, but no effect on the synthesis of cellular macromolecules was apparent. At higher levels (more than 5 μg/ml), mitomycin C was highly bactericidal and inhibited deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis almost completely. The exposure of growing cells to a bactericidal level of mitomycin C resulted also in a delayed inhibition of the synthesis of ribonucleic acid (RNA) and protein. The capacity of the treated cells to synthesize β-galactosidase inducibly in a medium free from a carbon source remained constant for the first 30 min and then was destroyed progressively with time. Prolonged incubation with the bactericidal level of mitomycin C caused a degradation of cellular nucleic acids, particularly RNA. The degraded nucleic acid components were eventually released into the medium.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHEER S., TCHEN T. T. Effect of mitomycin C on the synthesis of induced bita-galactosidase in E. coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1962 Oct 17;9:271–274. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(62)90072-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CUMMINGS D. J. MACROMOLECULAR SYNTHESIS DURING SYNCHRONOUS GROWTH OF ESCHERICHIA COLI B/R. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Feb 8;95:341–350. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(65)90498-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coles N. W., Gross R. The effect of mitomycin C on the induced synthesis of penicillinase in Staphylococcus aureus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Jul 26;20(3):366–371. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90374-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. D., MINGIOLI E. S. Mutants of Escherichia coli requiring methionine or vitamin B12. J Bacteriol. 1950 Jul;60(1):17–28. doi: 10.1128/jb.60.1.17-28.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FENWICK M. L. The influence of poliovirus infection of RNA synthesis in mammalian cells. Virology. 1963 Mar;19:241–249. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90061-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRULA M. M., GRULA E. A. Reversal of mitomycin c-induced growth and division inhibition in a species of Erwinia. Nature. 1962 Sep 15;195:1126–1127. doi: 10.1038/1951126a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KERSTEN H., KERSTEN W., LEOPOLD G., SCHNIEDERS B. EFFECT OF MITOMYCIN C ON DNAASE AND RNA IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Mar 23;80:521–523. doi: 10.1016/0926-6550(64)90159-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KERSTEN H., KERSTEN W. ZUR WIRKUNGSWEISE VON MITOMYCIN C, II. EINFLUSS VON MITOMYCIN C, CHLORAMPHENICOL UND MG2 AUF DEN RNA- UND DNA-STOFFWECHSEL IN BAKTERIEN. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1963;334:141–153. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1963.334.1.141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAKADA D. Thymine starvation and beta-galactosidase synthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Apr 2;55:505–511. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90983-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAKATA Y., NAKATA K., SAKAMOTO Y. On the action mechanism of mitomycin C. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1961 Dec 20;6:339–343. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(61)90141-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RACHMELER M., GERHART J., ROSNER J. Limited thymidine uptake in Escherichia coli due to an inducible thymidine phosphorylase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Apr 29;49:222–225. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90888-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REICH E., SHATKIN A. J., TATUM E. L. Bacteriocidal action of mitomycin C. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Oct 14;53:132–149. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90800-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEKIGUCHI M., TAKAGI Y. Effect of mitomycin C on the synthesis of bacterial and viral deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Jul 15;41:434–443. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)90040-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUZUKI H., KILGORE W. W. MITOMYCIN C: EFFECT ON RIBOSOMES OF ESCHERICHIA COLI. Science. 1964 Dec 18;146(3651):1585–1587. doi: 10.1126/science.146.3651.1585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SZYBALSKI W., IYER V. N. CROSSLINKING OF DNA BY ENZYMATICALLY OR CHEMICALLY ACTIVATED MITOMYCINS AND PORFIROMYCINS, BIFUNCTIONALLY "ALKYLATING" ANTIBIOTICS. Fed Proc. 1964 Sep-Oct;23:946–957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H., Pangborn J., Kilgore W. W. Filamentous cells of Escherichia coli formed in the presence of mitomycin. J Bacteriol. 1967 Feb;93(2):683–688. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.2.683-688.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


