Abstract
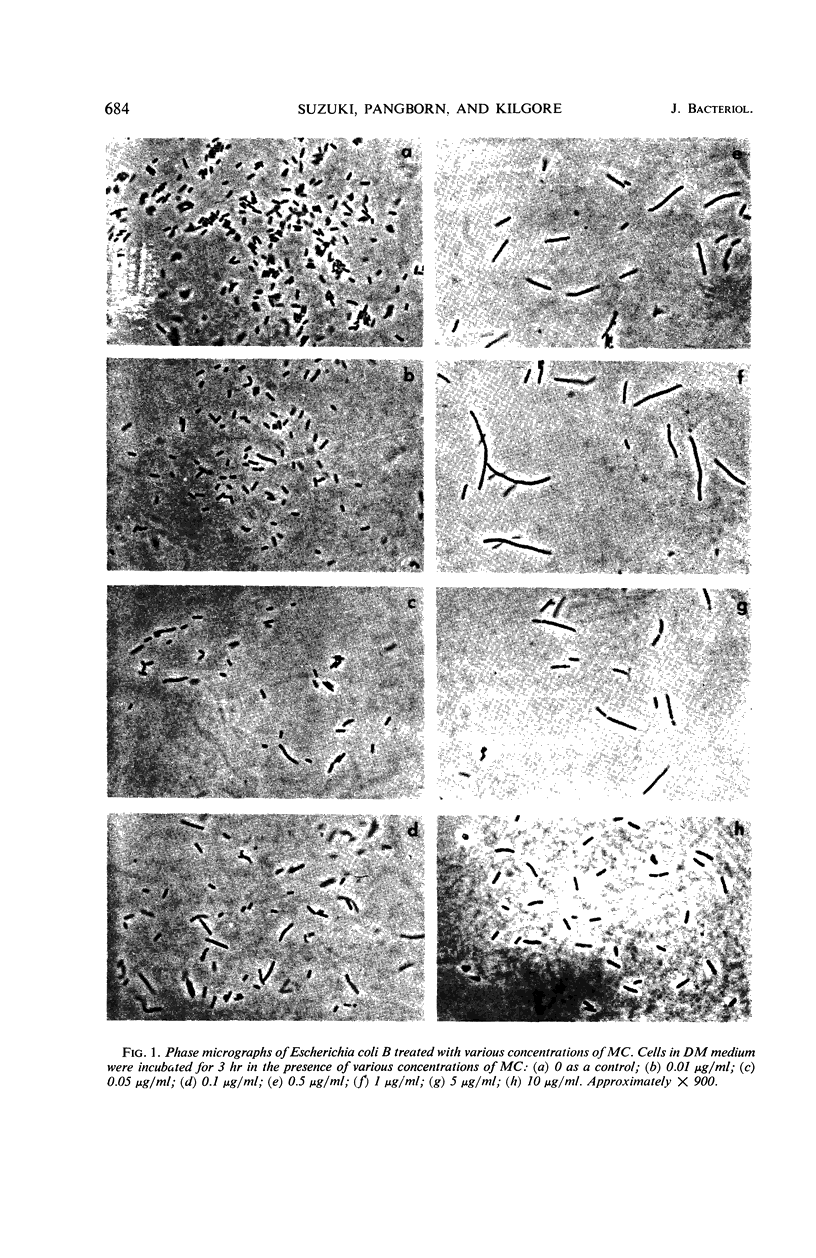
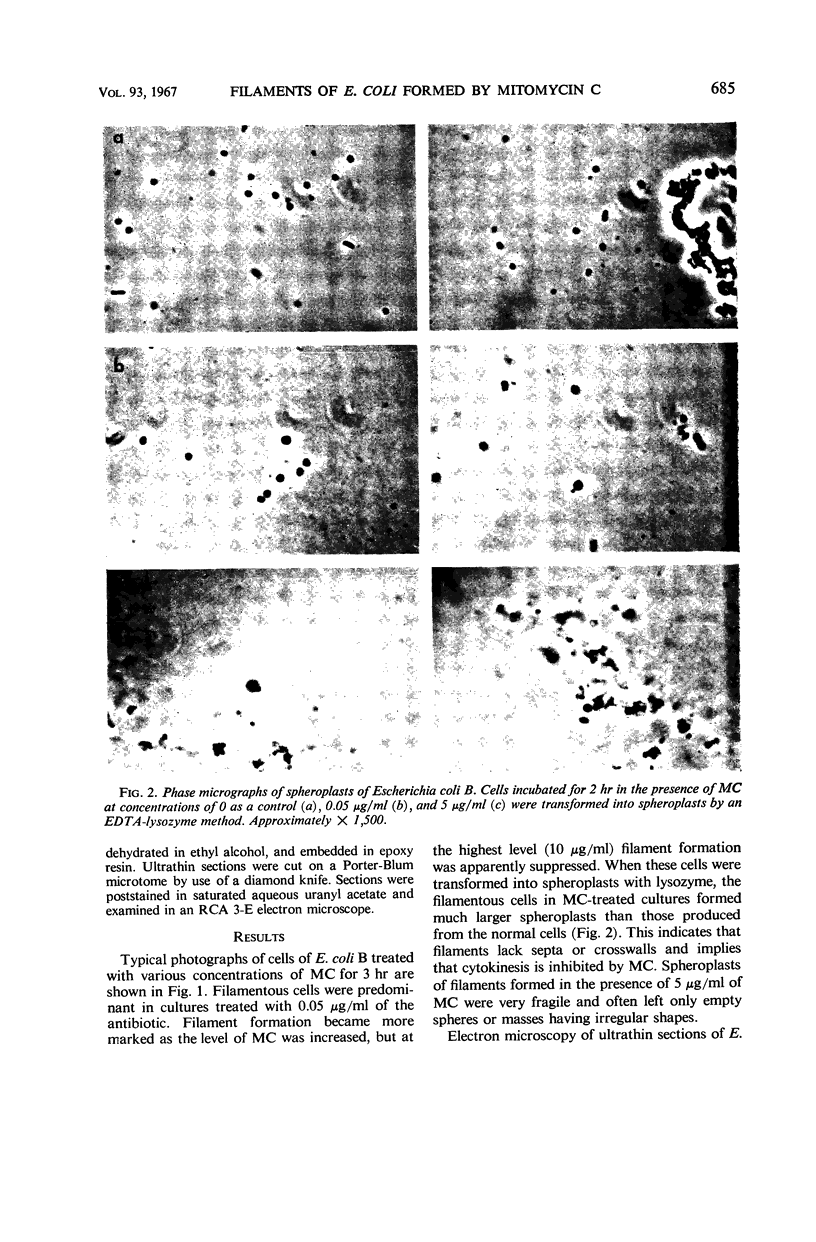
The effects of mitomycin C on cell elongation of Escherichia coli B were studied. Filament formation was most marked in cultures treated with a moderate level (1 μg/ml) of the antibiotic, becoming less obvious at higher levels (10 μg/ml). Cells treated with a bacteriostatic concentration (0.1 μg/ml or less) of mitomycin C were also significantly elongated. The filamentous or elongated cells appeared to lack septa, since their spheroplasts were considerably larger than those formed from normal cells. The appearance of empty spheres also indicated some defects in the surfaces of the filamentous cells. Electron micrographs of the filaments revealed a characteristic difference in the arrangement of the nuclei in the filaments formed in the presence of low (0.1 μg/ml) and high (5 μg/ml) concentrations of mitomycin C. The filaments formed by the low level of mitomycin C had normal well-defined nuclear bodies distributed along the long axis, whereas those formed by the elevated level of the antibiotic contained smaller nuclei. The latter were characteristically confined to the center of the cells and did not extend out to the tips of the filaments.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler H. I., Hardigree A. A. Growth and Division of Filamentous Forms of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jul;90(1):223–226. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.1.223-226.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEERING R. A. Studies on division inhibition and filament formation of Escherichia coli by ultraviolet light. J Bacteriol. 1958 Aug;76(2):123–130. doi: 10.1128/jb.76.2.123-130.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DURHAM N. N. INHIBITION OF MICROBIAL GROWTH AND SEPARATION BY D-SERINE, VANCOMYCIN, AND MITOMYCIN C. J Bacteriol. 1963 Sep;86:380–386. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.3.380-386.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRULA M. M., GRULA E. A. Reversal of mitomycin c-induced growth and division inhibition in a species of Erwinia. Nature. 1962 Sep 15;195:1126–1127. doi: 10.1038/1951126a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLENBERGER E., RYTER A., SECHAUD J. Electron microscope study of DNA-containing plasms. II. Vegetative and mature phage DNA as compared with normal bacterial nucleoids in different physiological states. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1958 Nov 25;4(6):671–678. doi: 10.1083/jcb.4.6.671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KERSTEN H., KERSTEN W. ZUR WIRKUNGSWEISE VON MITOMYCIN C, II. EINFLUSS VON MITOMYCIN C, CHLORAMPHENICOL UND MG2 AUF DEN RNA- UND DNA-STOFFWECHSEL IN BAKTERIEN. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1963;334:141–153. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1963.334.1.141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAGEE W. E., MILLER O. V. Dissociation of the synthesis of host and viral deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Jun 11;55:818–826. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90894-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATSUMOTO I., LARK K. G. ALTERED DNA ISOLATED FROM CELLS TREATED WITH MITOMYCIN C. Exp Cell Res. 1963 Oct;32:192–196. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(63)90089-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REICH E., SHATKIN A. J., TATUM E. L. Bacteriocidal action of mitomycin C. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Oct 14;53:132–149. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90800-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHATKIN A. J., REICH E., FRANKLIN R. M., TATUM E. L. Effect of mitomycin C on mammalian cells in culture. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Mar 5;55:277–289. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90783-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SZYBALSKI W., IYER V. N. CROSSLINKING OF DNA BY ENZYMATICALLY OR CHEMICALLY ACTIVATED MITOMYCINS AND PORFIROMYCINS, BIFUNCTIONALLY "ALKYLATING" ANTIBIOTICS. Fed Proc. 1964 Sep-Oct;23:946–957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H., Kilgore W. W. Effects of mitomycin C on macromolecular synthesis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1967 Feb;93(2):675–682. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.2.675-682.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]