Abstract
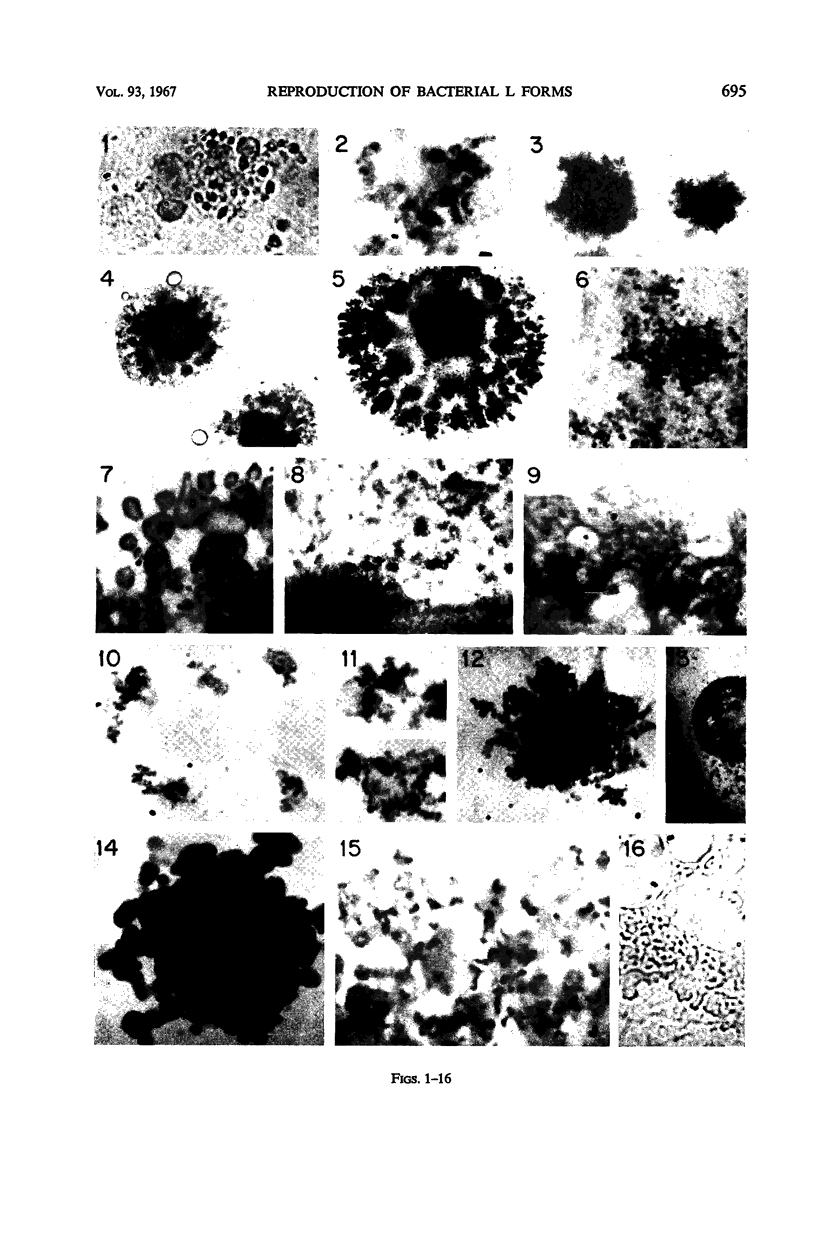
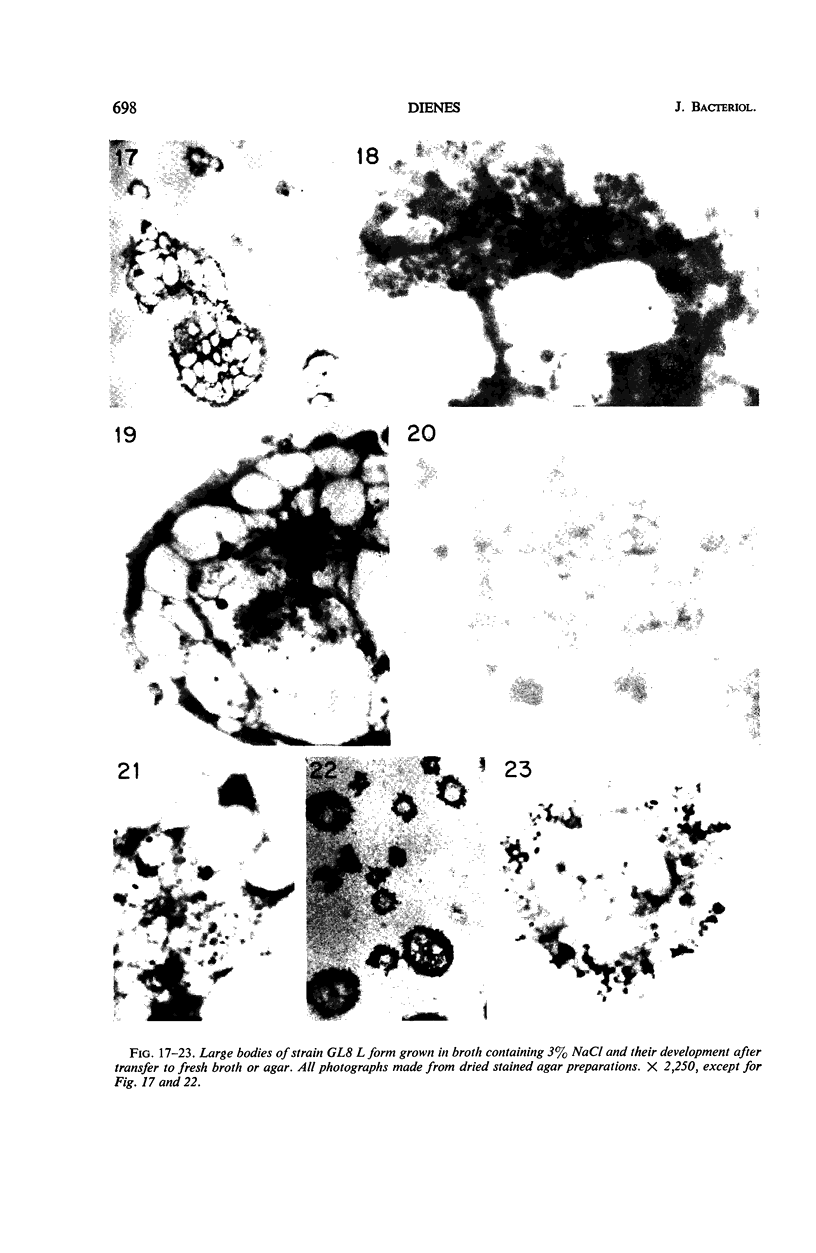
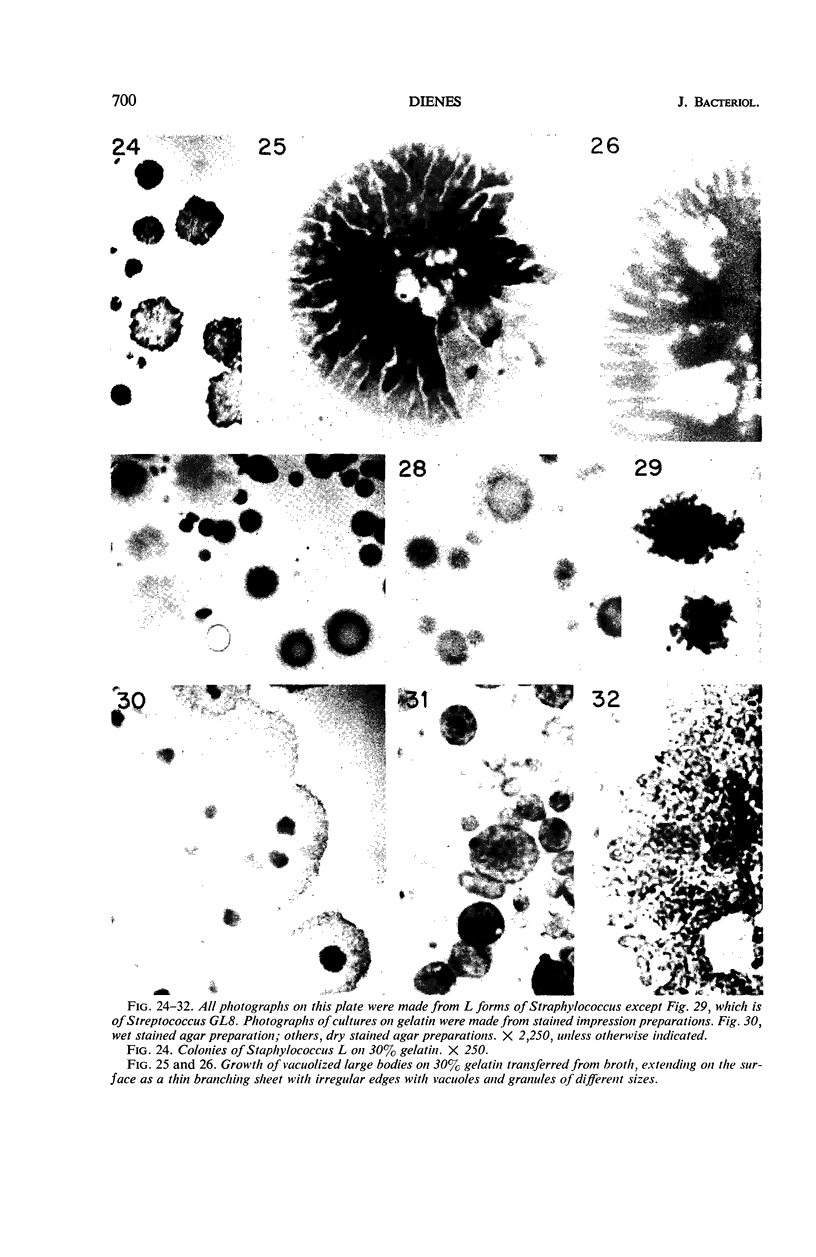
The production of L forms from cocci, the conditions necessary for their multiplication, and their morphology have been studied for several years. In each strain studied, only a few organisms produced L forms. Transplants from these grew poorly at first, and growth on agar and in broth became abundant only after long cultivation. Multiplication in the form of small granules was observed only when the organisms were embedded in agar and occasionally in coagulated blood serum. On the surface of hard agar, the organisms increased in size but did not multiply. Abundant growth developed on membrane filters of appropriate size, extending into the filters as branching irregular masses. On gelatin, on most samples of coagulated serum, and on silica gel, the organisms grew to a very large size, and occasionally colonies developed by multiplication of large bodies. This multiplication occurred by irregular enlargement and separation into fragments. Growth in broth and in semisolid agar also occurred by multiplication of large bodies, but, in addition, the development of viable granules was observed inside the large bodies in broth culture. After the L forms began to grow abundantly, their nutritional requirements were simple; they no longer required animal serum. Their ability to multiply and their morphological characteristics depended to a large extent on the physical properties of the environment.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BANDUR B. M., DIENES L. L FORMS ISOLATED FROM A STRAIN OF SERRATIA. J Bacteriol. 1963 Oct;86:829–836. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.4.829-836.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIENES L. L type cultures isolated from streptococci. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1953 Jul;83(3):579–583. doi: 10.3181/00379727-83-20424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIENES L., SHARP J. T. The role of high electrolyte concentration in the production and growth of L forms of bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1956 Feb;71(2):208–213. doi: 10.1128/jb.71.2.208-213.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dienes L., Madoff S. Development and growth of L forms of bacteria and PPLO on membrane filters. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Feb;121(2):334–339. doi: 10.3181/00379727-121-30772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dienes L. Permanent stained agar preparation of Mycoplasma and of L forms of bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1967 Feb;93(2):689–692. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.2.689-692.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREUNDT E. A. Morphology and classification of the PPLO. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1960 Jan 15;79:312–325. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1960.tb42693.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks J. H. Host-dependent microbes. Bacteriol Rev. 1966 Mar;30(1):114–135. doi: 10.1128/br.30.1.114-135.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MADOFF S., DIENES L. L forms from pneumococci. J Bacteriol. 1958 Sep;76(3):245–250. doi: 10.1128/jb.76.3.245-250.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MADOFF S. Isolation and identification of PPLO. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1960 Jan 15;79:383–392. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1960.tb42702.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHARP J. T. L Colonies from hemolytic streptocci: new technic in the study of L forms of bacteria. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1954 Oct;87(1):94–97. doi: 10.3181/00379727-87-21297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]