Abstract
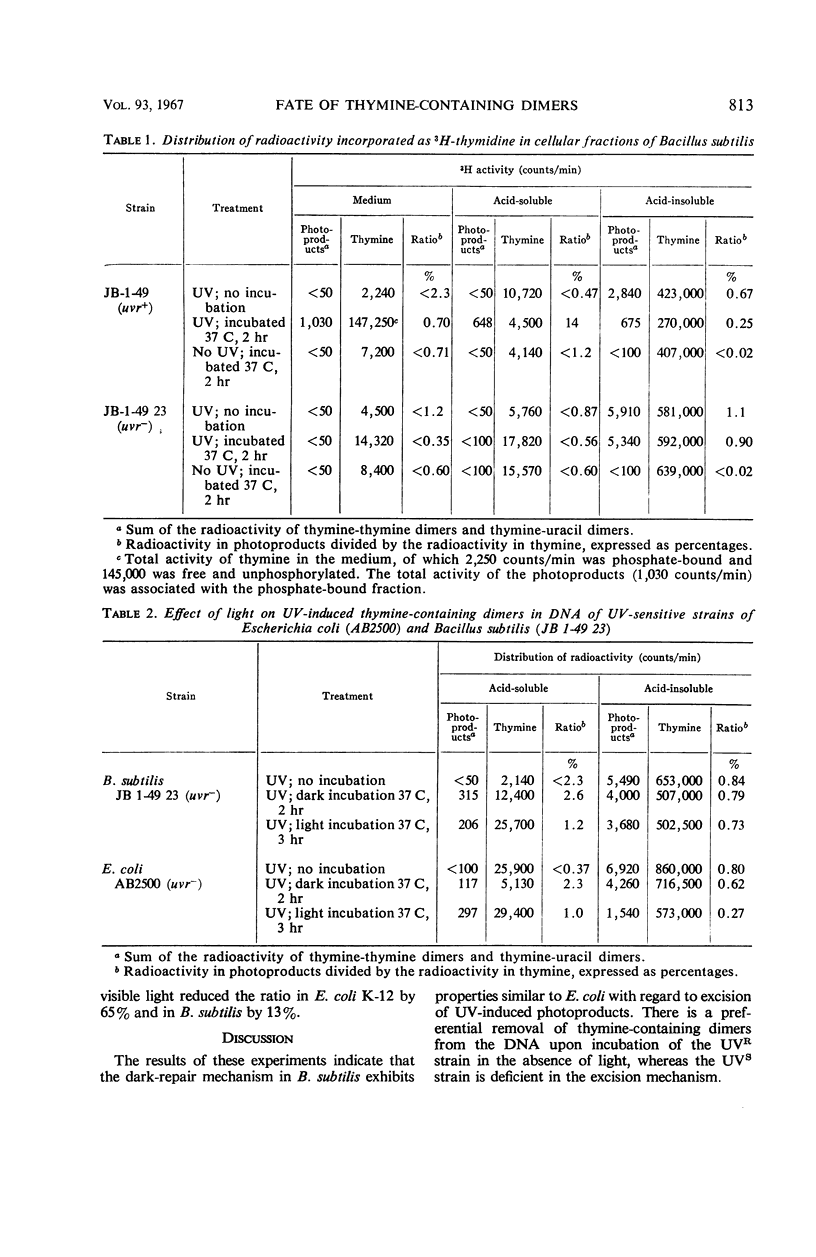
The fate of ultraviolet-induced, thymine-containing dimers in the deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) of Bacillus subtilis was investigated in both the wild type (UVR) and an ultraviolet light-sensitive (UVS) mutant. During incubation in the dark, dimers were excised from the DNA of the UVRB. subtilis, but remained in the DNA of the UVS mutant. About 40% of the excised dimers recovered in the wild type were in the acid-soluble fraction; the remainder were in the incubation medium. A UVS mutant of Escherichia coli K-12, shown previously to be defective in dimer excision, was irradiated with ultraviolet light and incubated under visible light for 3 hr. About 65% of thymine-containing photoproducts were removed from the DNA. These photoproducts were not recovered in the acid-soluble fraction. In comparison, the UVS mutant of B. subtilis lost only 13% of such photoproducts from DNA when exposed to light under the same conditions.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOYCE R. P., HOWARD-FLANDERS P. RELEASE OF ULTRAVIOLET LIGHT-INDUCED THYMINE DIMERS FROM DNA IN E. COLI K-12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Feb;51:293–300. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.2.293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boling M. E., Setlow J. K. The resistance of Micrococcus radiodurans to ultraviolet radiation. 3. A repair mechanism. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jul 20;123(1):26–33. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90155-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLISON S. A., FEINER R. R., HILL R. F. A host effect on bacteriophage survival after ultraviolet irradiation. Virology. 1960 May;11:294–296. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(60)90069-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILL R. F., SIMSON E. A study of radiosensitive and radioresistant mutants of Escherichia coli strain B. J Gen Microbiol. 1961 Jan;24:1–14. doi: 10.1099/00221287-24-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOWARD-FLANDERS P., BOYCE R. P., SIMSON E., THERIOT L. A genetic locus in E. coli K12 that controls the reactivation of UV-photoproducts associated with thymine in DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Dec 15;48:2109–2115. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.12.2109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard-Flanders P., Boyce R. P., Theriot L. Three loci in Escherichia coli K-12 that control the excision of pyrimidine dimers and certain other mutagen products from DNA. Genetics. 1966 Jun;53(6):1119–1136. doi: 10.1093/genetics/53.6.1119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RORSCH A., EDELMAN A., COHEN J. A. The gene-controlled radiation sensitivity in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Feb 26;68:263–270. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90141-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUPERT C. S. Photoreactivation of transforming DNA by an enzyme from bakers' yeast. J Gen Physiol. 1960 Jan;43:573–595. doi: 10.1085/jgp.43.3.573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riklis E. Studies on mechanism of repair of ultraviolet-irradiated viral and bacterial DNAin vivo and in vitro. Can J Biochem. 1965 Jul;43(7):1207–1219. doi: 10.1139/o65-132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAUERBIER W. The influence of the metabolic state of the host bacteria on the survival of phage T1 irradiated with ultraviolet light. Virology. 1962 May;17:164–170. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90093-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SETLOW R. B., CARRIER W. L. THE DISAPPEARANCE OF THYMINE DIMERS FROM DNA: AN ERROR-CORRECTING MECHANISM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Feb;51:226–231. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.2.226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STACEY K. A., SIMSON E. IMPROVED METHOD FOR THE ISOLATION OF THYMINE-REQUIRING MUTANTS OF ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Bacteriol. 1965 Aug;90:554–555. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.2.554-555.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Searashi T., Strauss B. Relation of the repair of damage induced by a monofunctional alkylating agent to the repair of damage induced by ultraviolet light in Bacillus subtilis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Sep 22;20(6):680–687. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90069-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setlow R. B., Carrier W. L., Bollum F. J. Pyrimidine dimers in UV-irradiated poly dI:dC. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 May;53(5):1111–1118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.5.1111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setlow R. B., Carrier W. L. Pyrimidine dimers in ultraviolet-irradiated DNA's. J Mol Biol. 1966 May;17(1):237–254. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80105-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss B., Searashi T., Robbins M. Repair of DNA studied with a nuclease specific for UV-induced lesions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Sep;56(3):932–939. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.3.932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TSUBOI K. K., PRICE T. D. Isolation, detection and measure of microgram quantities of labeled tissue nucleotides. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1959 Mar;81(1):223–237. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(59)90192-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WITKIN E. M. Modification of mutagenesis initiated by ultraviolet light through postteatment of bacteria with basic dyes. J Cell Comp Physiol. 1961 Dec;58(3):135–144. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030580413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WULFF D. L., RUPERT C. S. Disappearance of thymine photodimer in ultraviolet irradiated DNA upon treatment with a photoreactivating enzyme from baker's yeast. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1962 Apr 20;7:237–240. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(62)90181-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


