Abstract
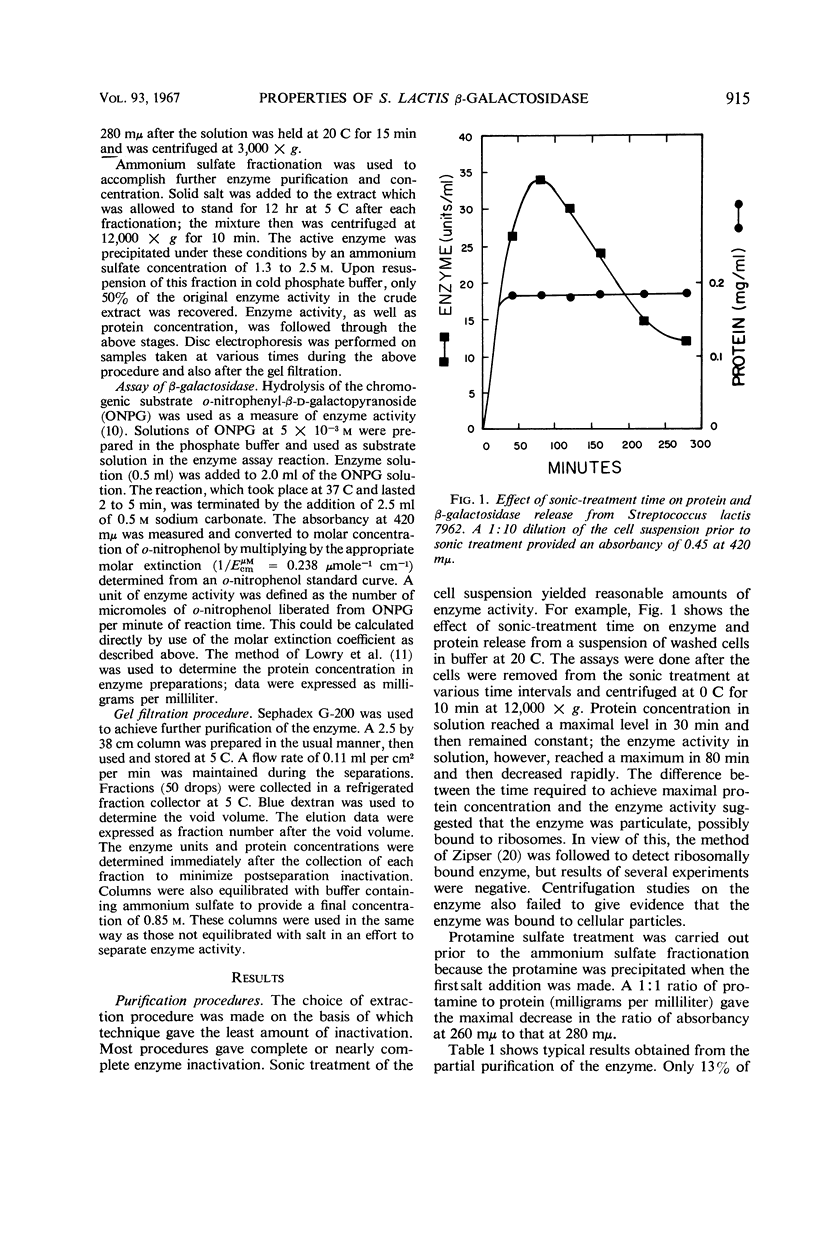
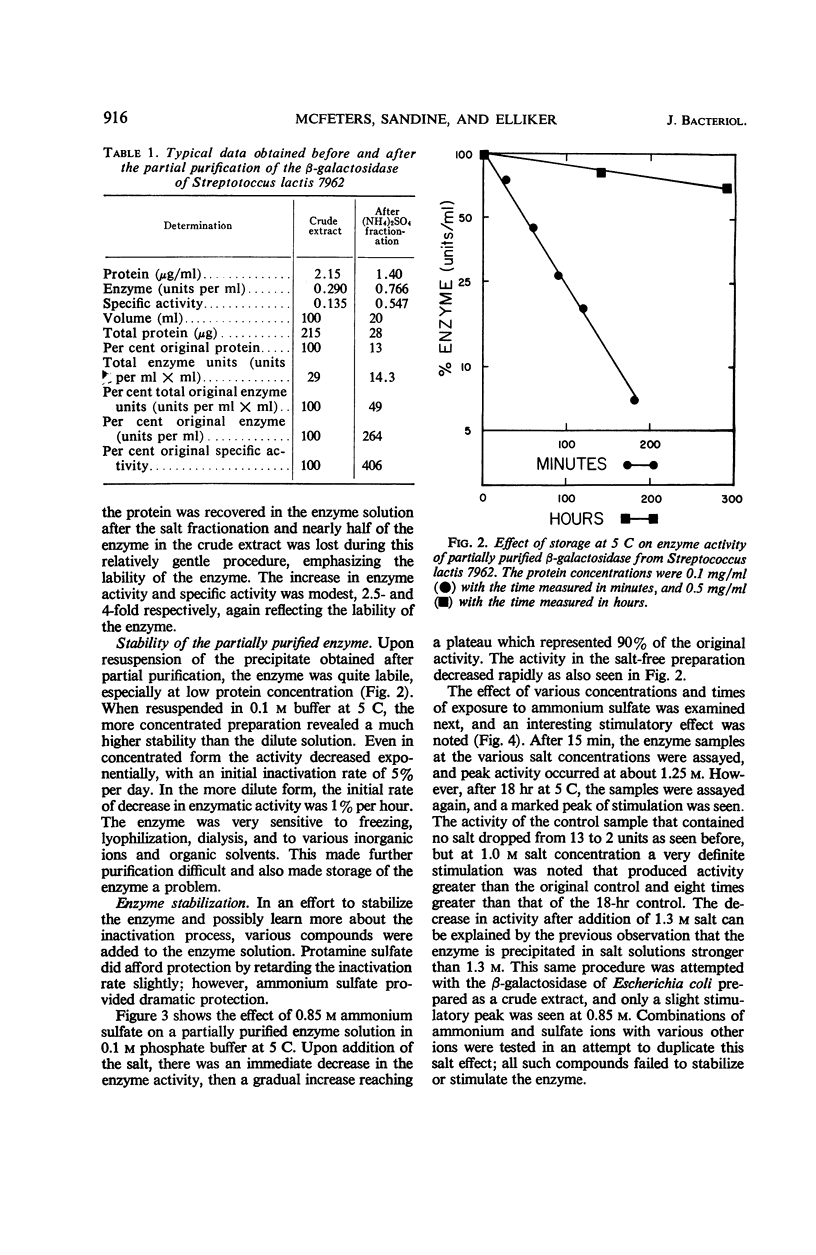
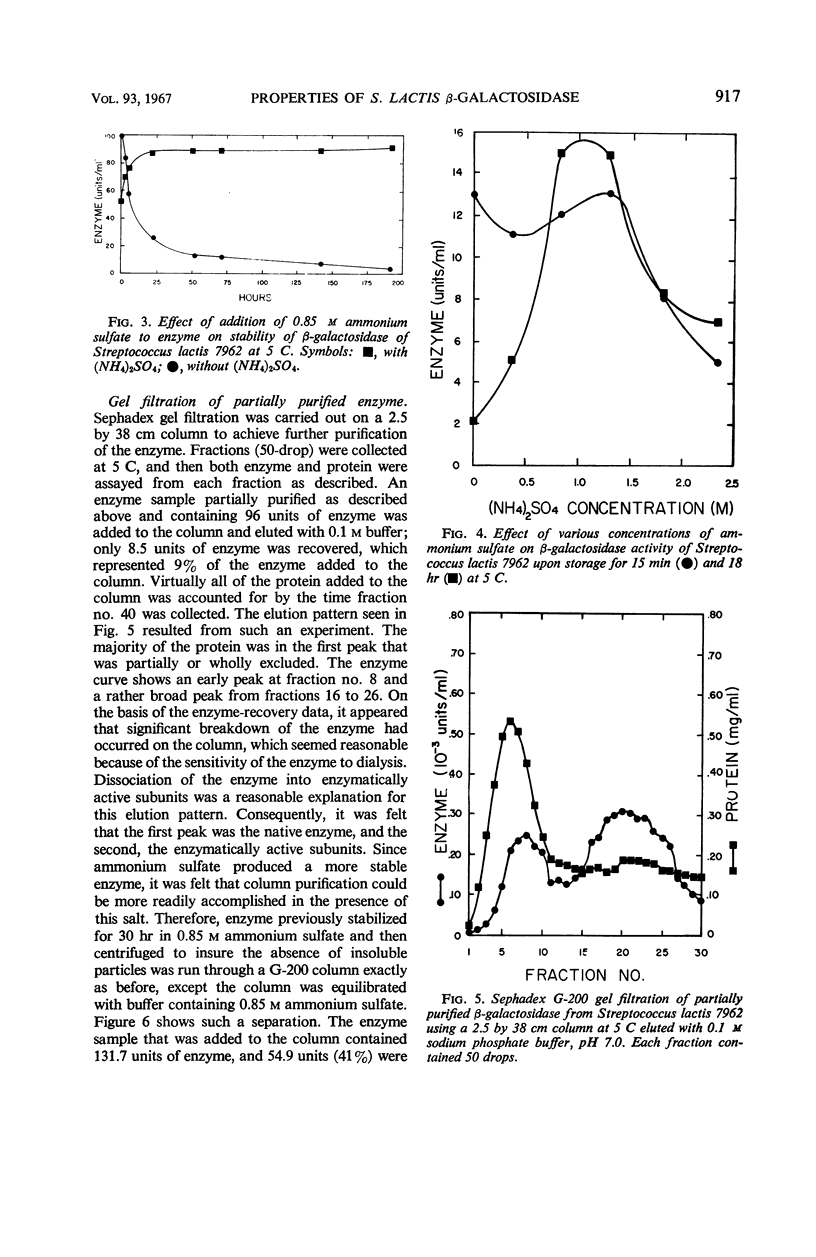
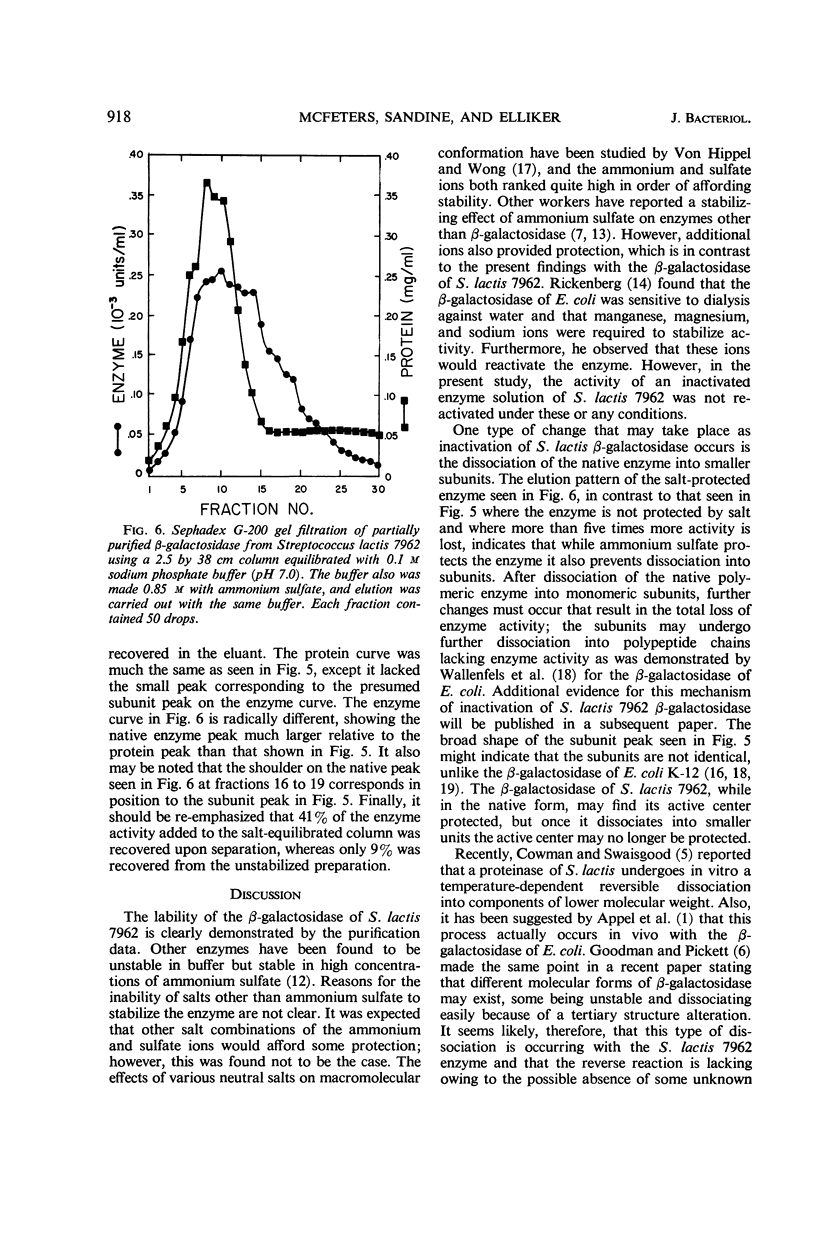
β-Galactosidase of Streptococcus lactis 7962 was partially purified, and its properties were studied. Enzyme from only this strain of numerous lactic streptococci tested was stable in cell exudates prepared by various means. Cell-free extracts of the 7962 strain were prepared by sonic treatment of washed cells previously grown in presence of lactose to fully induce enzyme synthesis. Protamine sulfate precipitation of the nucleic acids and ammonium sulfate precipitation of protein were used for partial purification of the enzyme. The resulting enzyme, when resuspended in cold (5 C) phosphate buffer, was extremely labile. However, ammonium sulfate in high concentrations (0.85 m) stabilized and stimulated β-galactosidase activity. Sephadex G-200 gel filtration was used to achieve further purification and to monitor homogeneity of the enzyme. Separation of the β-galactosidase in buffer at 5 C yielded an enzyme elution pattern showing two peaks of activity. However, addition of the enzyme solution in 0.85 m ammonium sulfate to the column equilibrated with the same salt concentration yielded only one peak of enzyme activity. The data suggested that the native enzyme was dissociating into active subunits which were stabilized in the presence of the ammonium sulfate.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- APPEL S. H., ALPERS D. H., TOMKINS G. M. MULTIPLE MOLECULAR FORMS OF BETA-GALACTOSIDASE. J Mol Biol. 1965 Jan;11:12–22. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80167-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CITTI J. E., SANDINE W. E., ELLIKER P. R. BETA-GALACTOSIDASE OF STREPTOCOCCUS LACTIS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Apr;89:937–942. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.4.937-942.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesbro W. R., Stuart D., Burke J. J., 2nd Multiple molecular weight forms of staphylococcal nuclease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 21;23(6):783–792. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90555-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chilson O. P., Kitto G. B., Pudles J., Kaplan N. O. Reversible inactivation of dehydrogenases. J Biol Chem. 1966 May 25;241(10):2431–2445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowman R. A., Swaisgood H. E. Temperature-dependent association-dissociation of Streptococcus lactis intracellular proteinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 21;23(6):799–803. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90557-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman R. E., Pickett M. J. Delayed lactose fermentation by enterobacteriaceae. J Bacteriol. 1966 Aug;92(2):318–327. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.2.318-327.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOYCE B. K., GRISOLIA S. Variations in malic dehydrogenase activity, with lyophilization, dialysis, and conditions of incubation. J Biol Chem. 1961 Mar;236:725–729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAKIUGHI K., KATO S., IMANISHI A., ISEMURA T. ASSOCIATION AND DISSOCIATION OF BACILLUS SUBTILIS ALPHA-AMYLASE MOLECULE. II. STUDIES ON MONOMER-DIMER TRANSFORMATION BY GEL FILTRATION. J Biochem. 1964 Feb;55:102–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPLAN N. O. Symposium on multiple forms of enzymes and control mechanisms. I. Multiple forms of enzymes. Bacteriol Rev. 1963 Jun;27:155–169. doi: 10.1128/br.27.2.155-169.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEDERBERG J. The beta-d-galactosidase of Escherichia coli, strain K-12. J Bacteriol. 1950 Oct;60(4):381–392. doi: 10.1128/jb.60.4.381-392.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- METZENBERG R. L., HALL L. M., MARSHALL M., COHEN P. P. Studies on the biosynthesis of carbamyl phosphate. J Biol Chem. 1957 Dec;229(2):1019–1025. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANDINE W. E., ELLIKER P. R., HAYS H. Cultural studies on Streptococcus diacetilactis and other members of the lactic Streptococcus group. Can J Microbiol. 1962 Apr;8:161–174. doi: 10.1139/m62-021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEERS E., Jr, CRAVEN G. R., ANFINSEN C. B., BETHUNE J. L. EVIDENCE FOR NONIDENTICAL CHAINS IN THE BETA-GALACTOSIDASE OF ESCHERICHIA COLI K12. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jun;240:2478–2484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VONHIPPEL P. H., WONG K. Y. NEUTRAL SALTS: THE GENERALITY OF THEIR EFFECTS ON THE STABILITY OF MACROMOLECULAR CONFORMATIONS. Science. 1964 Aug 7;145(3632):577–580. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3632.577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALLENFELS K., SUND H., WEBER K. DIE UNTEREINHEITEN DER BETA-GALAKTOSIDASE AUS E. COLI. Biochem Z. 1963;338:714–727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZIPSER D. A STUDY OF THE UREA-PRODUCED SUBUNITS OF BETA-GALACTOSIDASE. J Mol Biol. 1963 Aug;7:113–121. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(63)80040-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZIPSER D. STUDIES ON THE RIBOSOME-BOUND BETA-GALACTOSIDASE OF ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Mol Biol. 1963 Dec;7:739–751. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(63)80120-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



