Abstract
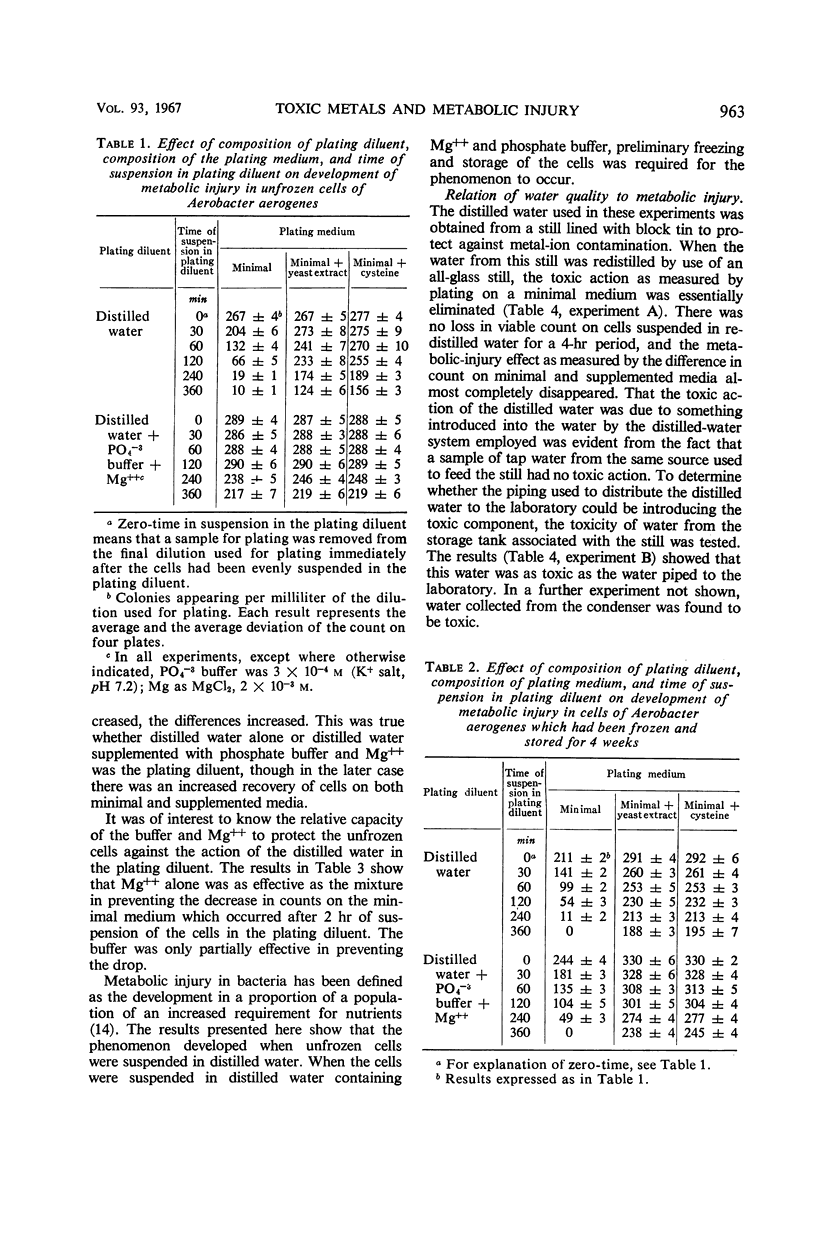
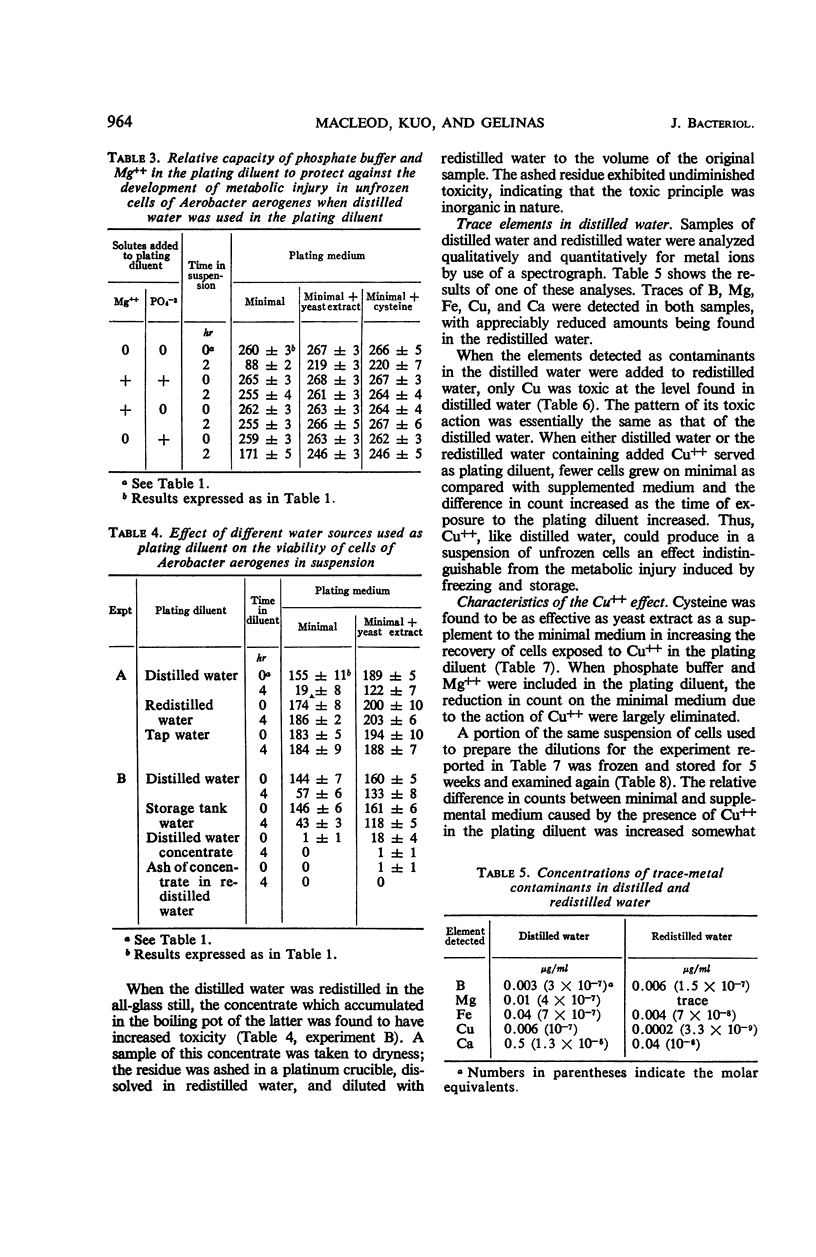
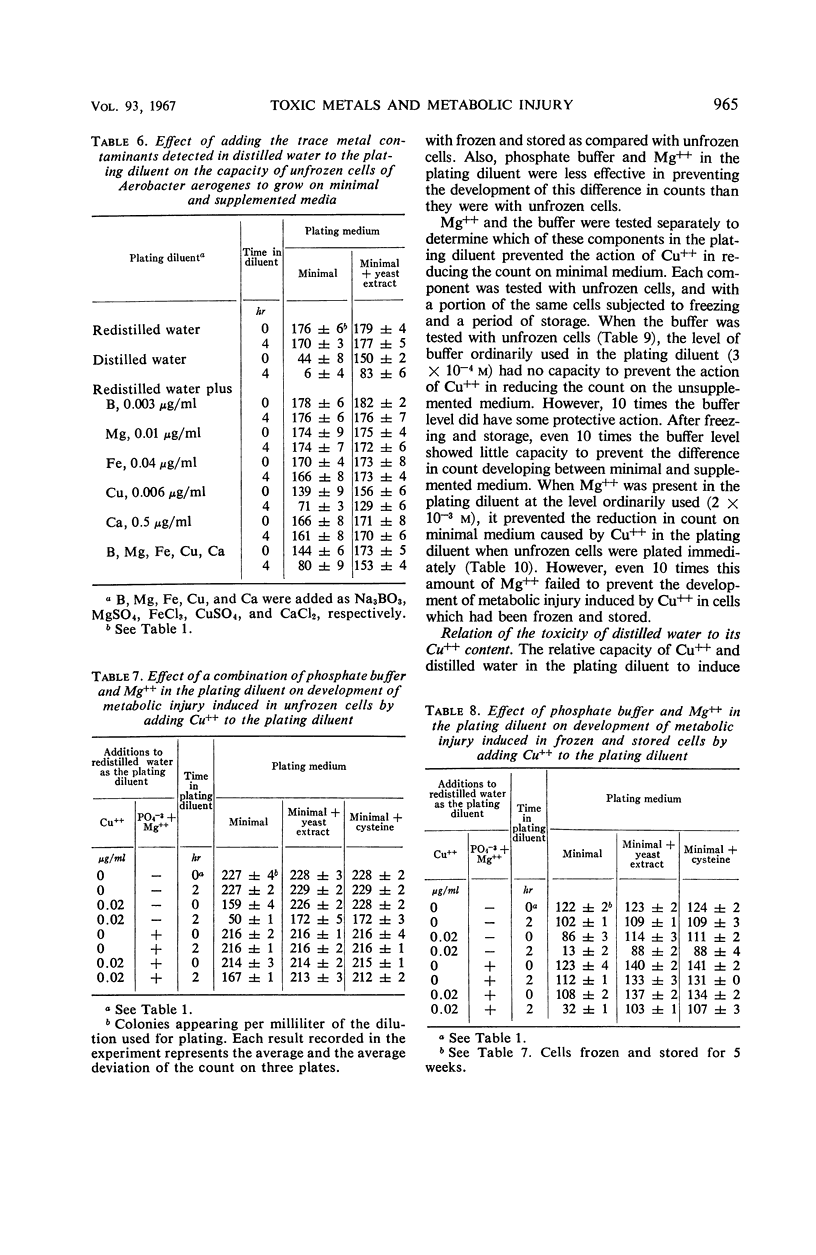
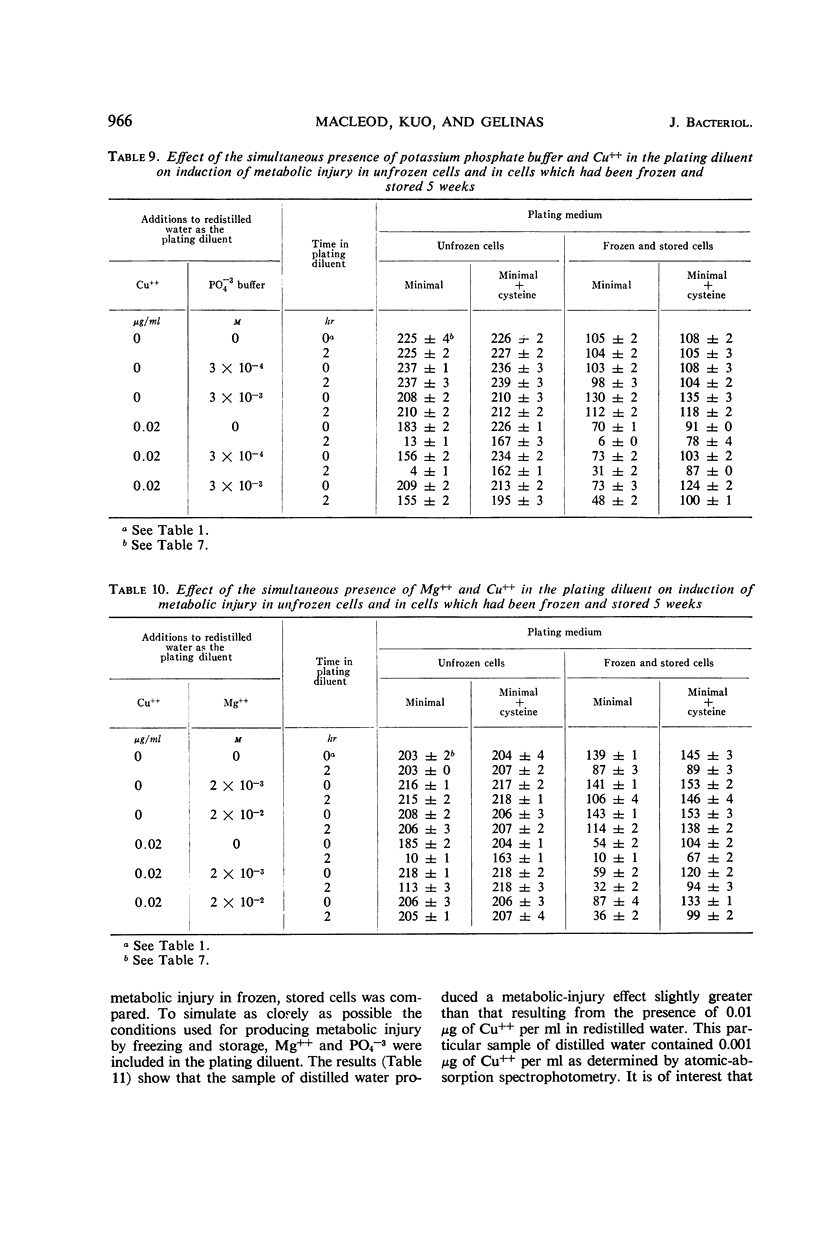
When distilled water from a tin-lined still served as the plating diluent, cells of Aerobacter aerogenes developed symptoms of metabolic injury as evidenced by increased counts on supplemented, as compared with minimal, plating medium. Cysteine was as effective as yeast extract as a supplement to the minimal medium in increasing the viable count. Mg++ and, to a lesser extent, phosphate buffer at the concentrations tested protected unfrozen cells, but not cells which had been frozen and stored, against the loss of capacity to grow on minimal medium. When the plating diluent consisted of distilled water redistilled in an all-glass still, the symptoms of metabolic injury did not appear. Spectrographic analysis revealed the presence of 10−7m Cu++ in the distilled water, and Cu++ added to redistilled water serving as the plating diluent reproduced the metabolic injury effects induced by distilled water. It was concluded that freezing and storage damaged the cell membrane, rendering it more penetrable by toxic elements which were thereby enabled to act at sites in the cell where Mg++ and other solutes in the plating diluent could not serve as effective antagonists. Increased recovery of cells on supplemented medium could be ascribed to the capacity of the supplements to remove toxic elements which had become bound to the cells during suspension in the plating diluent.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARPAI J. Nonlethal freezing injury to metabolism and motility of Pseudomonas fluorescens and Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol. 1962 Jul;10:297–301. doi: 10.1128/am.10.4.297-301.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss C. W., Speck M. L. Identification of nutritional components in trypticase responsible for recovery of Escherichia coli injured by freezing. J Bacteriol. 1966 Mar;91(3):1098–1104. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.3.1098-1104.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss C. W., Speck M. L. Release of biologically active peptides from Escherichia coli at subzero temperatures. J Bacteriol. 1966 Mar;91(3):1105–1111. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.3.1105-1111.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAKAMURA M., DAWSON D. A. Role of suspending and recovery media in the survival of frozen Shigella sonnei. Appl Microbiol. 1962 Jan;10:40–43. doi: 10.1128/am.10.1.40-43.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PASSOW H., ROTHSTEIN A. The binding of mercury by the yeast cell in relation to changes in permeability. J Gen Physiol. 1960 Jan;43:621–633. doi: 10.1085/jgp.43.3.621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POSTGATE J. R., HUNTER J. R. The survival of starved bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1962 Oct;29:233–263. doi: 10.1099/00221287-29-2-233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STRAKA R. P., STOKES J. L. Metabolic injury to bacteria at low temperatures. J Bacteriol. 1959 Aug;78:181–185. doi: 10.1128/jb.78.2.181-185.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STRANGE R. E., POSTGATE J. R. PENETRATION OF SUBSTANCES INTO COLD-SHOCKED BACTERIA. J Gen Microbiol. 1964 Sep;36:393–403. doi: 10.1099/00221287-36-3-393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



