Abstract
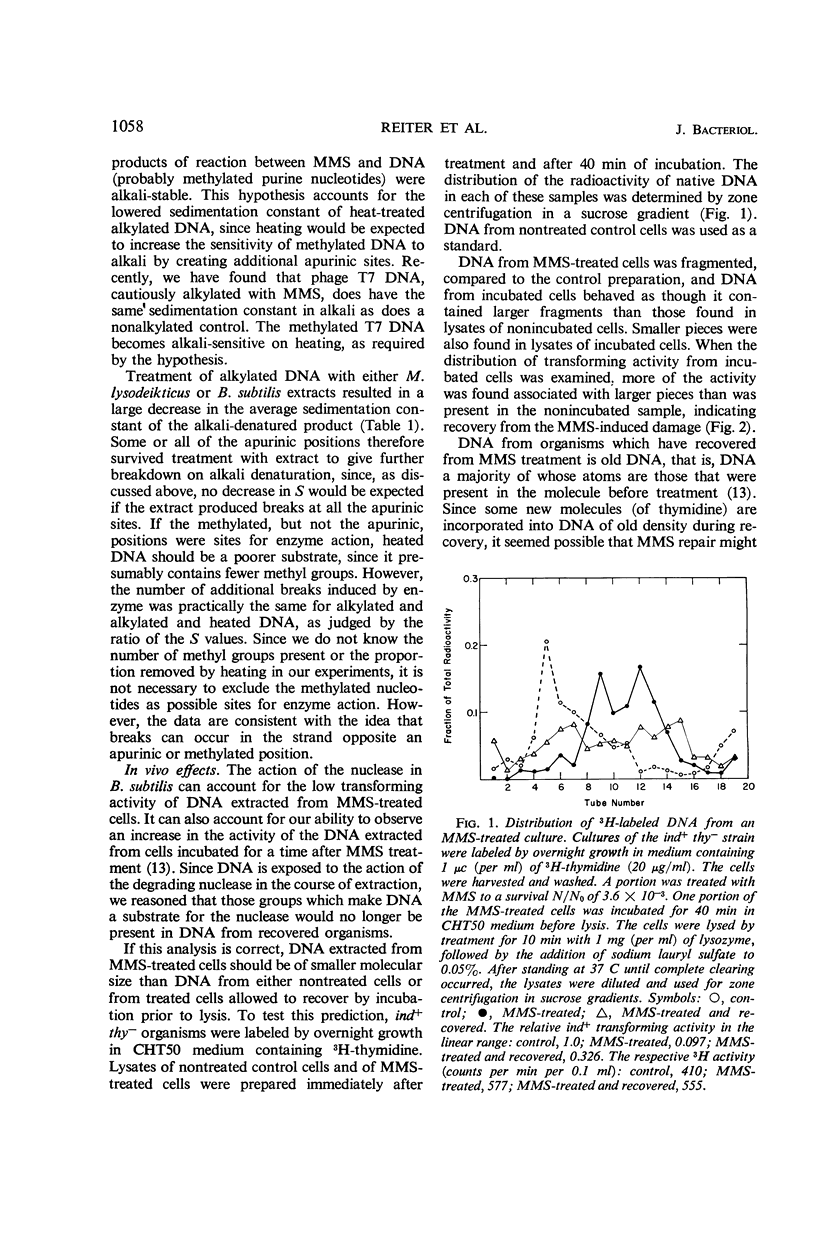
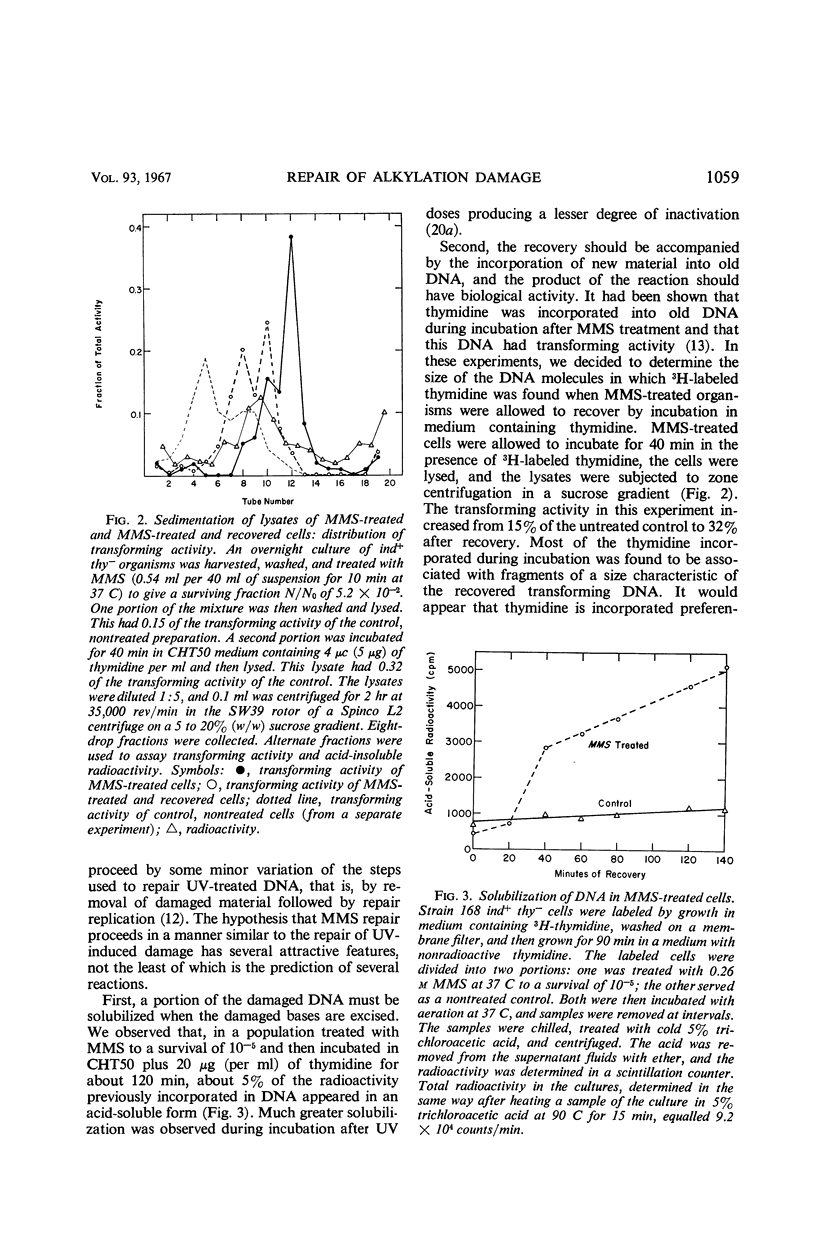
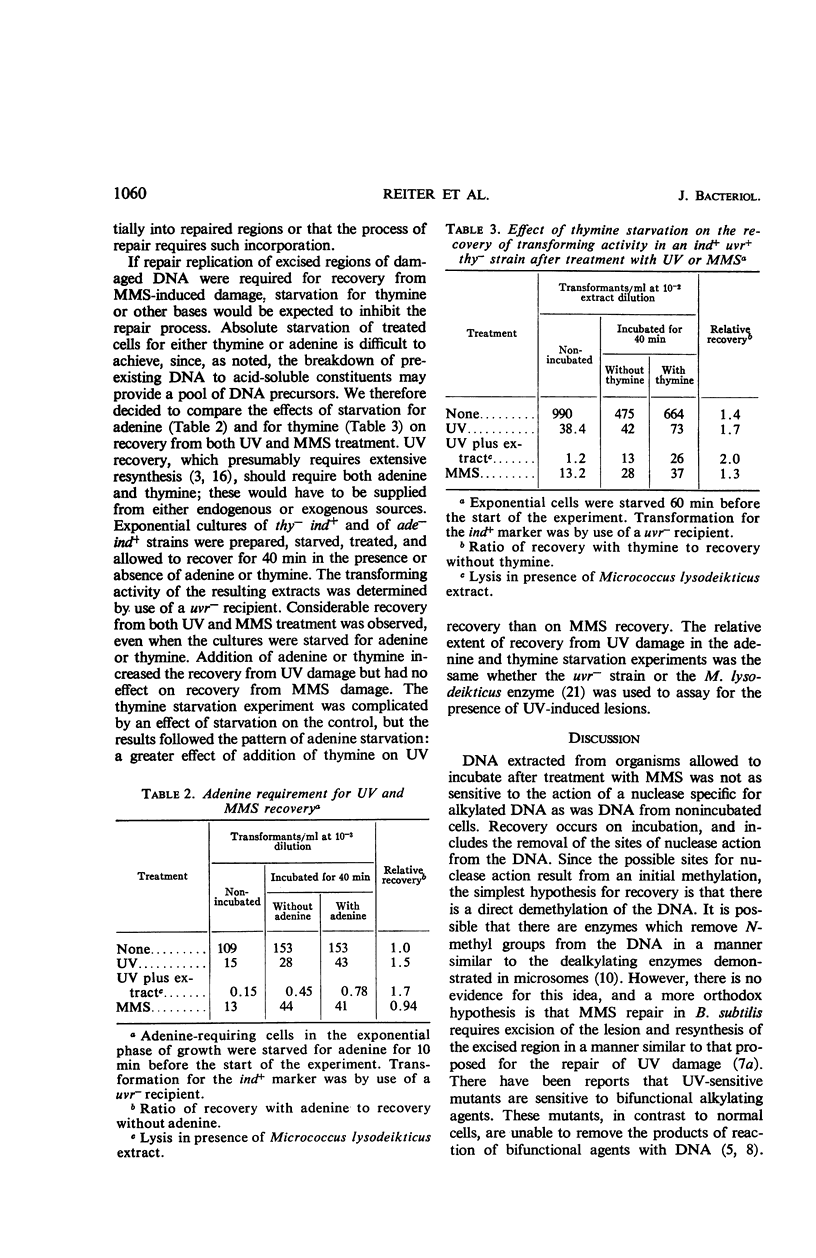
A nuclease present in extracts of Bacillus subtilis inserts breaks in deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) treated with the monofunctional alkylating agent, methyl methanesulfonate (MMS), but the nature of the sites within the alkylated macromolecule at which these breaks occur is not known. DNA extracted from B. subtilis cells that have recovered from MMS damage has lost its susceptibility to enzyme action. The recovery process is accompanied by some DNA breakdown and by the incorporation of thymidine. Some recovery from ultraviolet irradiation (UV) and MMS occurred in organisms starved for thymine or adenine, but UV recovery was stimulated by their addition. It is possible that MMS recovery proceeds by a process of excision and repair similar to, but not identical with, UV repair.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anagnostopoulos C., Spizizen J. REQUIREMENTS FOR TRANSFORMATION IN BACILLUS SUBTILIS. J Bacteriol. 1961 May;81(5):741–746. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.5.741-746.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOYCE R. P., HOWARD-FLANDERS P. RELEASE OF ULTRAVIOLET LIGHT-INDUCED THYMINE DIMERS FROM DNA IN E. COLI K-12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Feb;51:293–300. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.2.293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROOKES P., LAWLEY P. D. EFFECTS OF ALKYLATING AGENTS ON T2 AND T4 BACTERIOPHAGES. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:138–144. doi: 10.1042/bj0890138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodmer W. F. Integration of deoxyribonuclease-treated DNA in bacillus subtilis transformation. J Gen Physiol. 1966 Jul;49(6):233–258. doi: 10.1085/jgp.49.6.233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brookes P., Lawley P. D. The reaction of mono- and di-functional alkylating agents with nucleic acids. Biochem J. 1961 Sep;80(3):496–503. doi: 10.1042/bj0800496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVISON P. F., FREIFELDER D., HOLLOWAY B. W. INTERRUPTIONS IN THE POLYNUCLEOTIDE STRANDS IN BACTERIOPHAGE DNA. J Mol Biol. 1964 Jan;8:1–10. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80142-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freifelder D., Uretz R. B. Mechanism of photoinactivation of coliphage T-7 sensitized by acridine orange. Virology. 1966 Sep;30(1):97–103. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(66)81013-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard-Flanders P., Boyce R. P. DNA repair and genetic recombination: studies on mutants of Escherichia coli defective in these processes. Radiat Res. 1966;(Suppl):156+–156+. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawley P. D., Brookes P. Molecular mechanism of the cytotoxic action of difunctional alkylating agents and of resistance to this action. Nature. 1965 May 1;206(983):480–483. doi: 10.1038/206480a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PETTIJOHN D., HANAWALT P. EVIDENCE FOR REPAIR-REPLICATION OF ULTRAVIOLET DAMAGED DNA IN BACTERIA. J Mol Biol. 1964 Aug;9:395–410. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80216-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiter H., Strauss B., Marone R., Robbins M. Actinomycin D inhibition of UV-dark repair in Bacillus subtilis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Sep 22;24(6):892–898. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90333-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiter H., Strauss B. Repair of damage induced by a monofunctional alkylating agent in a transformable, ultraviolet-sensitive strain of Bacillus subtilis. J Mol Biol. 1965 Nov;14(1):179–194. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80239-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHUSTER R. C. DARK REPAIR OF ULTRAVIOLET INJURY IN E. COLI DURING DEPRIVATION OF THYMINE. Nature. 1964 May 9;202:614–615. doi: 10.1038/202614a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SETLOW R. B., CARRIER W. L. THE DISAPPEARANCE OF THYMINE DIMERS FROM DNA: AN ERROR-CORRECTING MECHANISM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Feb;51:226–231. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.2.226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STRAUSS B. S. Differential destruction of the transforming activity of damaged deoxyribonucleic acid by a bacterial enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Sep 15;48:1670–1675. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.9.1670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STRAUSS B. S. Recovery of deoxyribonucleic acid from the effects of alkylation. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Jan;30:89–103. doi: 10.1099/00221287-30-1-89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Searashi T., Strauss B. Relation of the repair of damage induced by a monofunctional alkylating agent to the repair of damage induced by ultraviolet light in Bacillus subtilis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Sep 22;20(6):680–687. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90069-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuster R. C., Boyce R. P. The excision of thymine dimer from the DNA of UV-irradiated E. coli 15 T-A-U during thymine deprivation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1964 Jul 27;16(5):489–496. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(64)90381-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss B., Reiter H., Searashi T. Recovery from ultraviolet- and alkylating-agent-induced damage in Bacillus subtilis. Radiat Res. 1966;(Suppl):201+–201+. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss B., Searashi T., Robbins M. Repair of DNA studied with a nuclease specific for UV-induced lesions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Sep;56(3):932–939. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.3.932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAMM C., SHAPIRO H. S., LIPSHITZ R., CHARGAFF E. Distribution density of nucleotides within a desoxyribonucleic acid chain. J Biol Chem. 1953 Aug;203(2):673–688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


