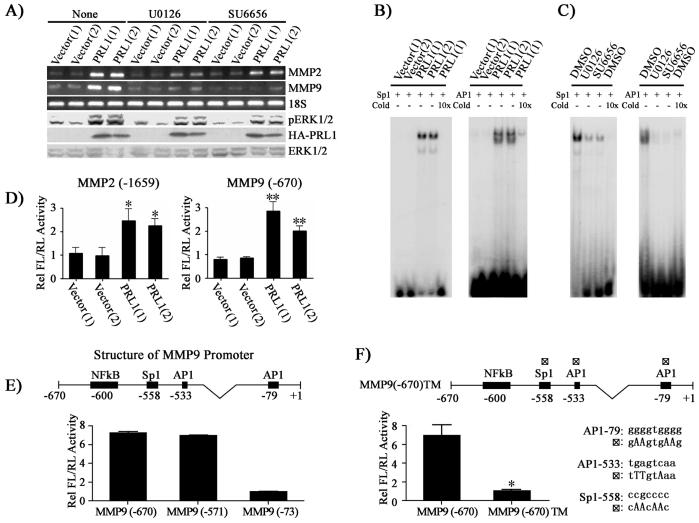
Figure 4.
PRL1 increases MMP2 and MMP9 expression through Src and ERK1/2 mediated AP1 and Sp1 activation. (A) Inhibition of Src (2.5 μM SU6656) or ERK1/2 (1 μM U0126) lead to reduced MMP2 and MMP9 expression. MMP2 and MMP9 expression was measured by RT-PCR, and pERK1/2, ERK1/2 and HA-PRL1 were determined by Western blot analysis. (B) AP1 and Sp1 transcriptional factors are involved in the PRL1-induced MMP2 and MMP9 expression. Nuclear extracts of control and PRL1 cell lines were prepared. Electrophoretic mobility shift assays were performed with 5 μg of nuclear extract with 20,000 cpm of labeled Sp1 or AP1 probe. Competition analysis was performed in the presence of a 10-fold molar excess of unlabeled probes. (C) Sp1 and AP1 activation requires Src and ERK1/2 activity. Cells were preincubated with either Src (SU6656, 2.5 μM) or MEK1/2 (U0126, 1 μM) inhibitor, and the DNA binding activity of AP1 and Sp1 were determined using gel shift assays. (D, E, F) Requirement of AP1 and Sp1 for PRL1-induced MMP2 and MMP9 expression. Control and PRL1 cell lines were co-transfected with either 200 ng of the MMP2 or the MMP9 luciferase reporter constructs (D) or MMP9 deletion mutant luciferase reporter constructs (E) or a MMP9 luciferase reporter construct (MMP9 (-670)TM) with all three AP1 and Sp1 sites mutated (changes in nucleotides were made according to the consensus sequences and published data (38, 39) and depicted in the figure) (F) together with 10 ng Renilla-TK luciferase reporter as an internal control. After 48 hr, cells were lysed and dual luciferase measurements were performed. Firefly luficerase values were normalized against Renilla luciferase values. Relative luciferase activity was normalized to vector control cell (D) or to MMP9 (-73) (E) or to MMP9 (-670)TM (F). Results were presented as mean ± S.D. *, p<0.05 and **, p<0.01.