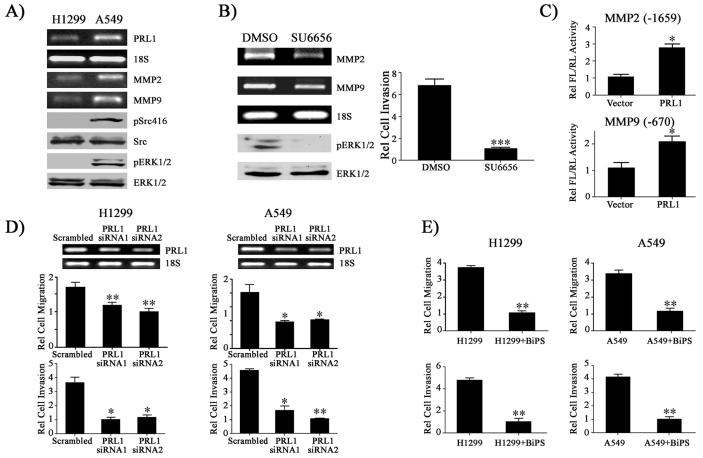
Figure 6.
PRL1 enhances the invasiveness of lung cancer cells by increasing MMP2/9 expression through the Src and ERK1/2 pathways. (A) An increase in PRL1 expression is correlated with Src and ERK1/2 activation as well as enhanced MMP2/9 expression in lung cancer cell lines. (B) Inhibition of Src by SU6656 in A549 cells decreases ERK1/2 activity and suppresses MMP2/9 expression and cell invasion. A549 cells were treated with Src inhibitor SU6656 (2.5 μM) for 4 hr. RNA was prepared and MMP2 and MMP9 expression was determined by RT-PCR. pERK1/2, ERK1/2 were determined by Western blot analysis. For cell invasion assay, A549 cells were treated with either DMSO or SU6656 and the rates of cell invasion were quantitated over 24 hr using the Matrigel assay. Relative cell invasion was normalized with the SU6656 treatment group. Results were presented as mean ± S.D. *** p<0.001. (C) PRL1 induces MMP2/9 expression in lung cancer cell. H1299 cells were co-transfected by 500 ng PRL1 together with either 200 ng of the MMP2 or the MMP9 luciferase reporter constructs with 10 ng Renilla-TK luciferase reporter as an internal control. After 48 hr, cells were lysed and dual luciferase measurements were performed. Firefly luficerase values were normalized against Renilla luciferase values. Relative luciferase activity was normalized to vector control cell. Results were presented as mean ± S.D. *, p<0.05 and **, p<0.01. Knockdown of MMP2 and MMP9 using siRNAs (D) or inhibition of MMP2 and MMP9 using small molecule inhibitor BiSP (0.5 μM) (E) in H1299 and A549 reduce lung cancer cell migration and invasion. Relative cell migration/invasion was normalized to the PRL1 siRNA2 group (D) or to the BiPS treated group (E). Results were presented as mean ± S.D. *, p<0.05 and **, p<0.01.