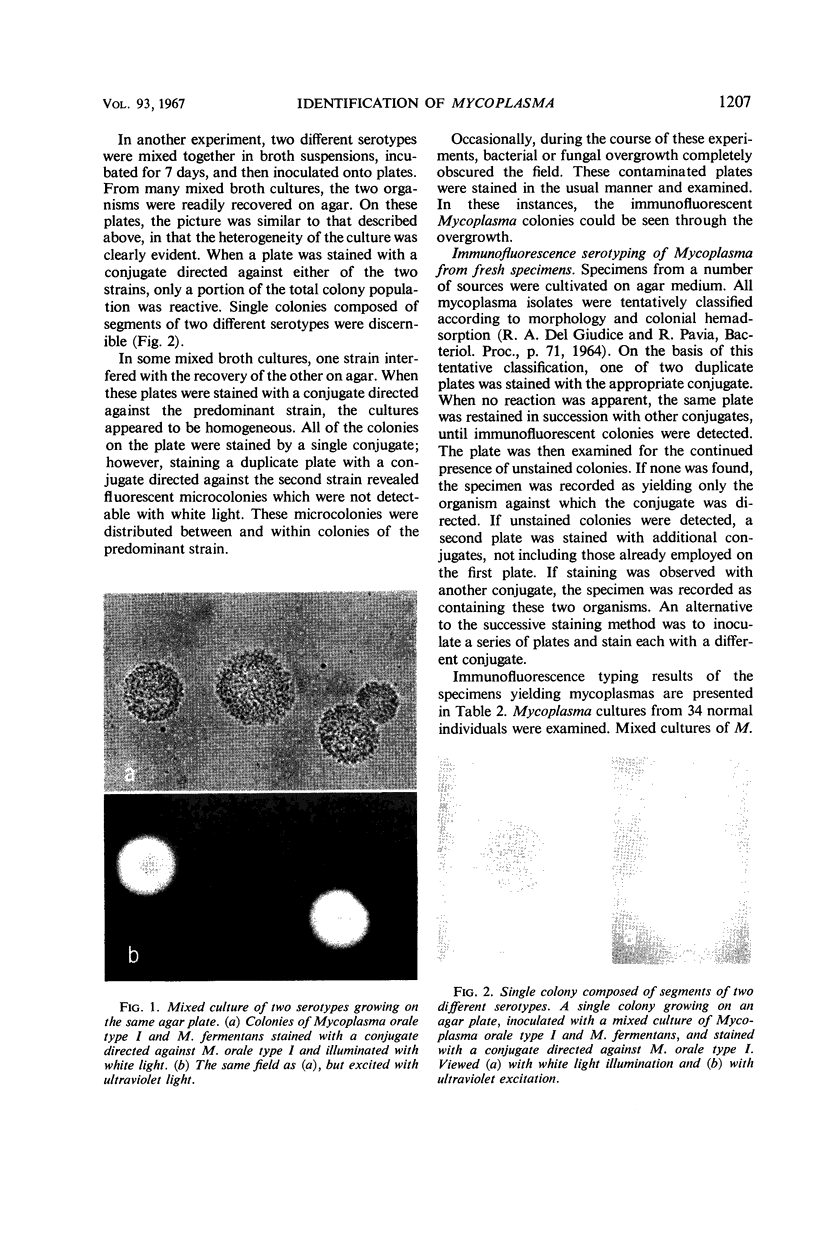
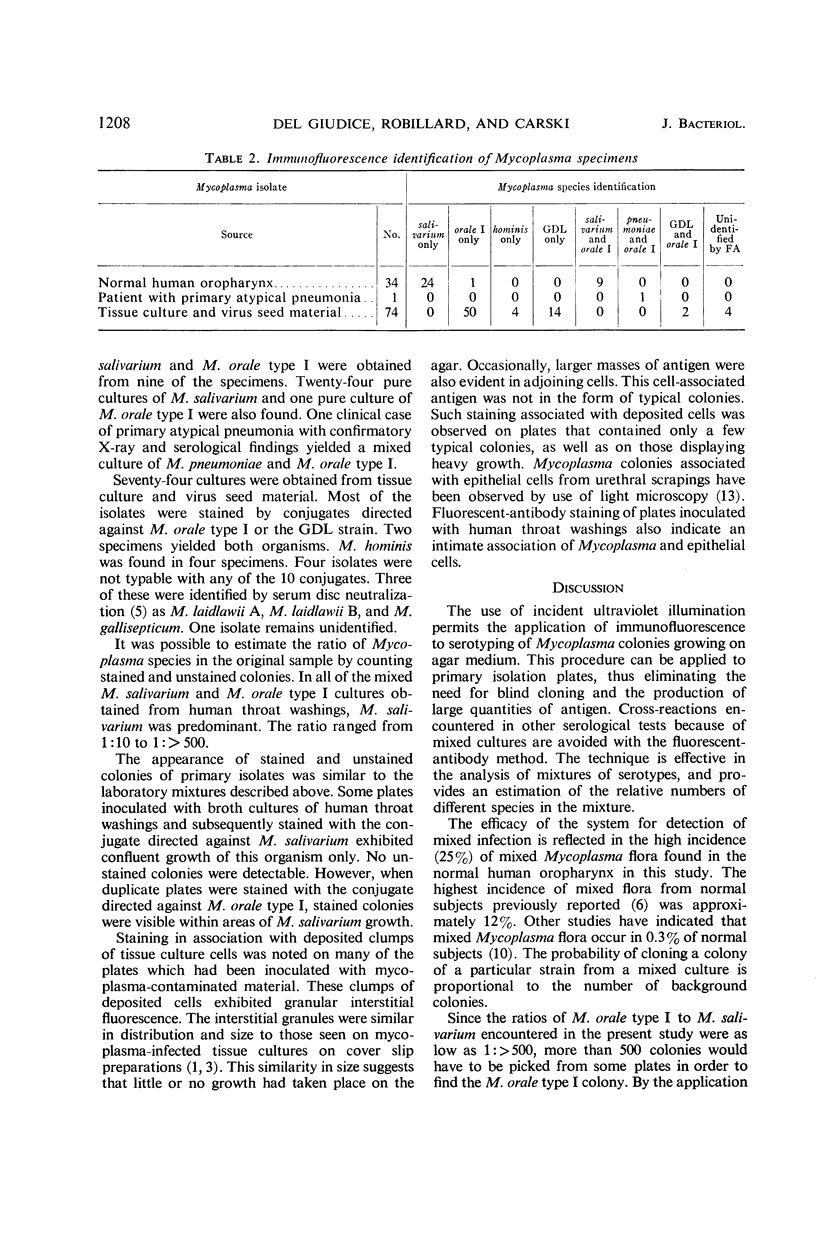
Abstract
The fluorescent-antibody method has been employed for the rapid identification of Mycoplasma colonies growing on agar plates. The method was found to be effective for detection of mixtures of Mycoplasma serotypes growing on primary isolation plates. The technique also helped to define the presence of mycoplasmas which did not produce typical colonies. It was also possible to identify Mycoplasma colonies overgrown by bacterial or fungal contaminants. Conjugates directed against 10 distinct Mycoplasma serotypes have been successfully employed in this system. One of the serotypes is a human oral isolate which has not been previously characterized.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARILE M. F., MALIZIA W. F., RIGGS D. B. Incidence and detection of pleuropneumonia-like organisms in cell cultures by fluorescent antibody and cultural procedures. J Bacteriol. 1962 Jul;84:130–136. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.1.130-136.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUTLER M., LEACH R. H. A MYCOPLASMA WHICH INDUCES ACIDITY AND CYTOPATHIC EFFECT IN TISSUE CULTURE. J Gen Microbiol. 1964 Feb;34:285–294. doi: 10.1099/00221287-34-2-285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARSKI T. R., SHEPARD C. C. Pleuropneumonia-like (mycoplasma) infections of tissue culture. J Bacteriol. 1961 Apr;81:626–635. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.4.626-635.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLYDE W. A., Jr MYCOPLASMA SPECIES IDENTIFICATION BASED UPON GROWTH INHIBITION BY SPECIFIC ANTISERA. J Immunol. 1964 Jun;92:958–965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark H. W., Bailey J. S., Fowler R. C., Brown T. M. IDENTIFICATION OF MYCOPLASMATACEAE BY THE FLUORESCENT ANTIBODY METHOD. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jan;85(1):111–118. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.1.111-118.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRIFFIN C. W., CARSKI T. R., WARNER G. S. Labeling procedures employing crystalline fluorescein isothiocyanate. J Bacteriol. 1961 Oct;82:534–537. doi: 10.1128/jb.82.4.534-537.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAYFLICK L., CHANOCK R. M. MYCOPLASMA SPECIES OF MAN. Bacteriol Rev. 1965 Jun;29:185–221. doi: 10.1128/br.29.2.185-221.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leach R. H., Butler M. Compraison of mycoplasmas associated with human tumors, leukemia, and tissue cultures. J Bacteriol. 1966 Mar;91(3):934–941. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.3.934-941.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purcell R. H., Somerson N. L., Fox H., Wong D. C., Turner H. C., Chanock R. M. Identification of acid-inducing agent and related mycoplasma as mycoplasma hyorhinis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1966 Aug;37(2):251–253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHEPARD M. C. T-Form colonies of pleuropneumonialike organisms. J Bacteriol. 1956 Mar;71(3):362–369. doi: 10.1128/jb.71.3.362-369.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOMERSON N. L., PURCELL R. H., TAYLOR-ROBINSON D., CHANOCK R. M. HEMOLYSIN OF MYCOPLASMA PNEUMONIAE. J Bacteriol. 1965 Mar;89:813–818. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.3.813-818.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]