Abstract
Cultures of Chromatium strain D and Rhodospirillum rubrum incorporated 14C from phenylacetate-1-14C during anaerobic growth. The radioactivity in the protein fraction of cells was mainly in phenylalanine. Phenylalanine from Chromatium cells grown in phenylacetate-1-14C was labeled at carbon 2. Incorporation of phenylacetate by Chromatium was decreased in the presence of exogenous phenylalanine, and de novo synthesis of phenylalanine from bicarbonate was less in medium containing either phenylalanine or phenylacetate. These organisms, and also certain anaerobic rumen bacteria, apparently carboxylate phenylacetate to synthesize the phenylalanine carbon skeleton. The mechanism of the carboxylation is unknown; however, it appears to be dependent upon anaerobic conditions, since R. rubrum did not synthesize phenylalanine from phenylacetate during aerobic growth in the dark.
Full text
PDF

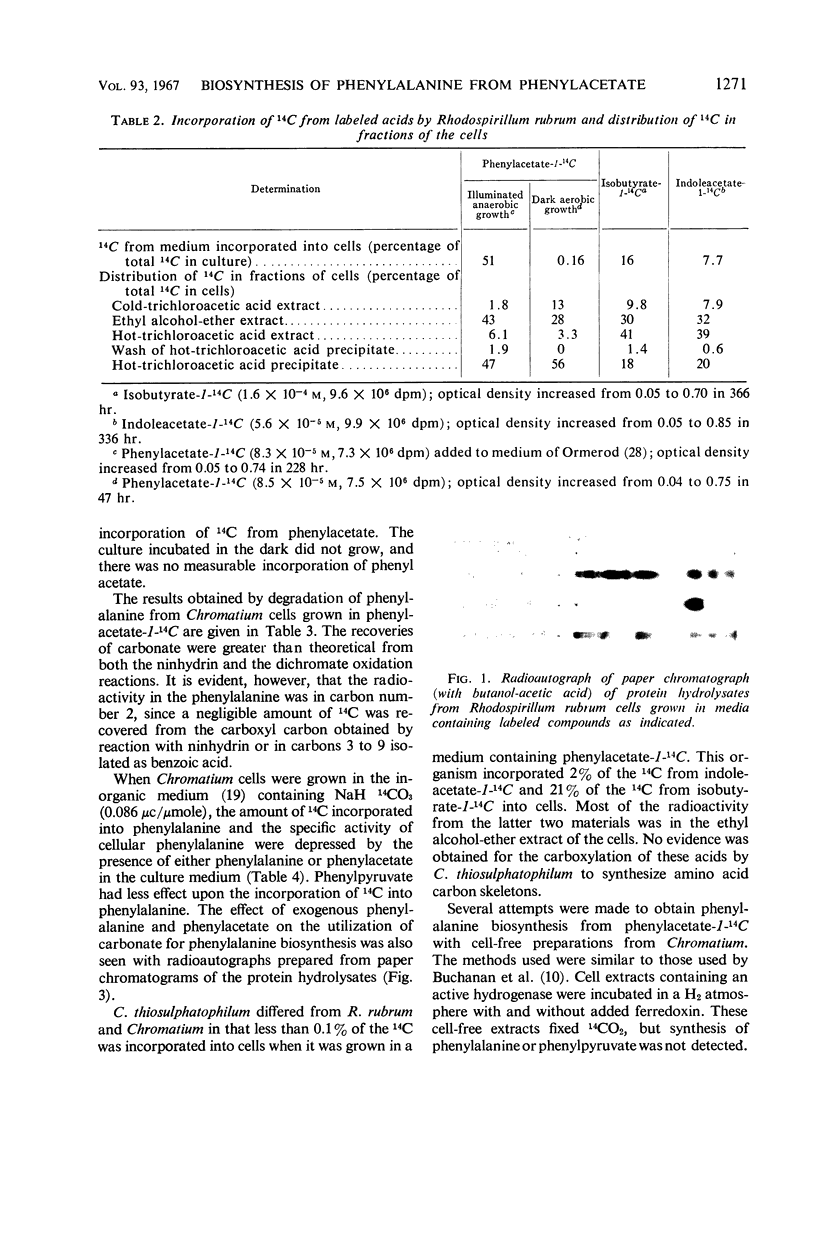
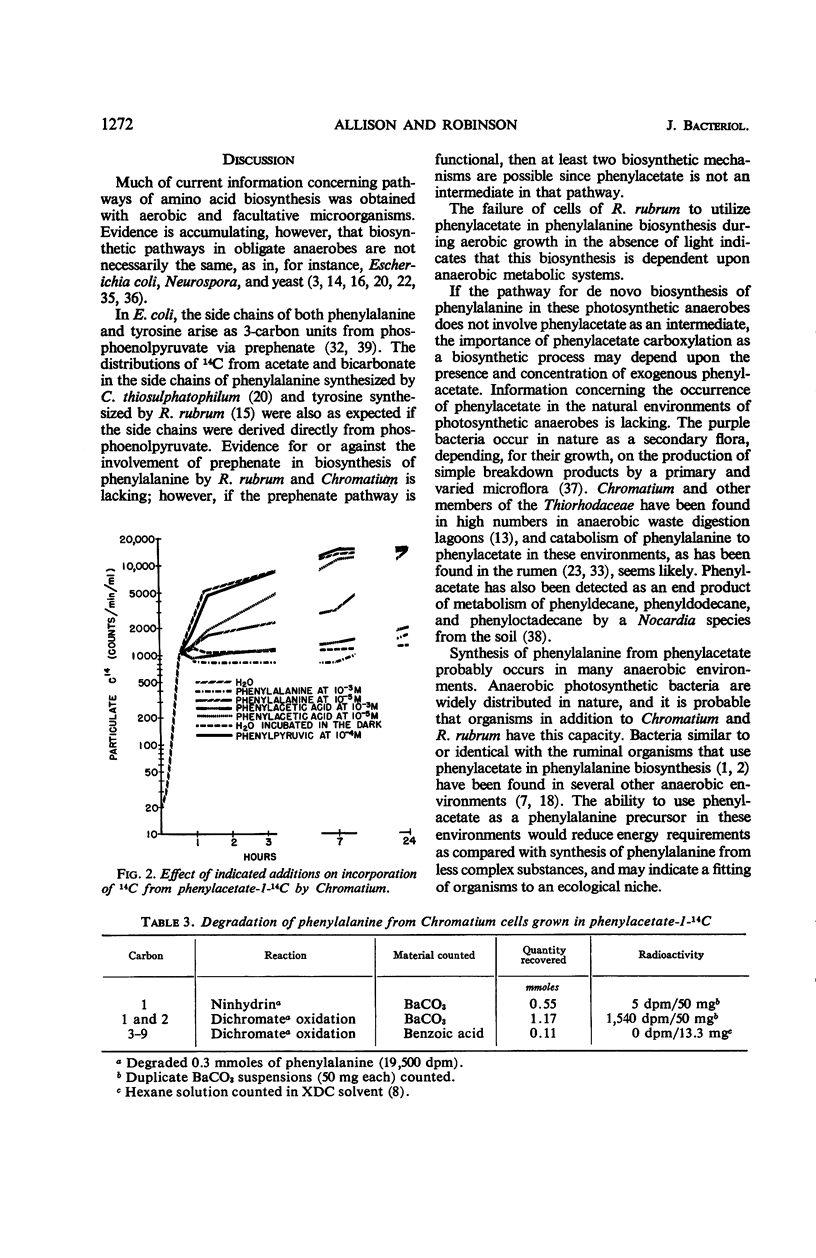



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALLISON M. J., BRYANT M. P. Biosynthesis of branched-chain amino acids from branched-chain fatty acids by rumen bacteria. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1963 May;101:269–277. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(63)80012-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ALLISON M. J., BRYANT M. P., KATZ I., KEENEY M. Metabolic function of branched-chain volatile fatty acids, growth factors for ruminococci. II. Biosynthesis of higher branched-chain fatty acids and aldehydes. J Bacteriol. 1962 May;83:1084–1093. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.5.1084-1093.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ALLISON M. J. PHENYLALANINE BIOSYNTHESIS FROM PHENYLACETIC ACID BY ANAEROBIC BACTERIA FROM THE RUMEN. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Jan 4;18:30–35. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90877-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ANDREW I. G., MORRIS J. G. THE BIOSYNTHESIS OF ALANINE BY CLOSTRIDIUM KLUYVERI. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Jan 4;97:176–179. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(65)90292-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUCHANAN B. B., BACHOFEN R., ARNON D. I. ROLE OF FERREDOXIN IN THE REDUCTIVE ASSIMILATION OF CO2 AND ACETATE BY EXTRACTS OF THE PHOTOSYNTHETIC BACTERIUM, CHROMATIUM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Sep;52:839–847. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.3.839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan B. B., Evans M. C. The synthesis of alpha-ketoglutarate from succinate and carbon dioxide by a subcellular preparation of a photosynthetic bacterium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Oct;54(4):1212–1218. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.4.1212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EL-BAGOURY S., FLETCHER S., MORRISON R. B. Effect of chloramphenicol in maintaining the viability of Escherichia coli. Nature. 1956 Dec 29;178(4548):1467–1467. doi: 10.1038/1781467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILVARG C., BLOCH K. Utilization of glucose-1-C14 for the synthesis of phenylalanine and tyrosine. J Biol Chem. 1952 Dec;199(2):689–698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALL E. R. Investigations on the microbiology of cellulose utilization in domestic rabbits. J Gen Microbiol. 1952 Nov;7(3-4):350–357. doi: 10.1099/00221287-7-3-4-350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENDLEY D. D. Endogenous fermentation in Thiorhodaceae. J Bacteriol. 1955 Dec;70(6):625–634. doi: 10.1128/jb.70.6.625-634.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNGATE R. E. The anaerobic mesophilic cellulolytic bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1950 Mar;14(1):1–49. doi: 10.1128/br.14.1.1-49.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoare D. S., Gibson J. Photoassimilation of acetate and the biosynthesis of amino acids by Chlorobium thiosulphatophilum. Biochem J. 1964 Jun;91(3):546–559. doi: 10.1042/bj0910546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight M., Wolfe R. S., Elsden S. R. The synthesis of amino acids by Methanobacterium omelianskii. Biochem J. 1966 Apr;99(1):76–86. doi: 10.1042/bj0990076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LACOSTE A. M., BLAIZOT J., RAYNAUD P. Catabolisme de la phénylalanine par les bactéries de la panse des ruminants. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1958 Feb 24;246(8):1280–1281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVIN J. G., SPRINSON D. B. THE ENZYMATIC FORMATION AND ISOLATION OF 3-ENOLPYRUVYLSHIKIMATE 5-PHOSPHATE. J Biol Chem. 1964 Apr;239:1142–1150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORMEROD J. G., ORMEROD K. S., GEST H. Light-dependent utilization of organic compounds and photoproduction of molecular hydrogen by photosynthetic bacteria; relationships with nitrogen metabolism. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1961 Sep;94:449–463. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(61)90073-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSEN H. A modified ninhydrin colorimetric analysis for amino acids. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1957 Mar;67(1):10–15. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(57)90241-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWINCK I., ADAMS E. Aromatic biosynthesis. XVI. Aromatization of prephenic acid to p-hydroxyphenylpyruvic acid, a step in tyrosine biosynthesis in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Nov;36:102–117. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90074-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott T. W., Ward P. F., Dawson R. M. The formation and metabolism of phenyl-substituted fatty acids in the ruminant. Biochem J. 1964 Jan;90(1):12–24. doi: 10.1042/bj0900012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOMLINSON N. Carbon dioxide and acetate utilization by Clostridium kluyveri. II. Synthesis of amino acids. J Biol Chem. 1954 Aug;209(2):597–603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOMLINSON N. Carbon dioxide and acetate utilization by Clostridium kluyveri. III. A new path of glutamic acid synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1954 Aug;209(2):605–609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEISS U., GILVARG C., MINGIOLI E. S., DAVID B. D. Aromatic biosynthesis. XI. The aromatization step in the synthesis of phenylalanine. Science. 1954 May 28;119(3100):774–775. doi: 10.1126/science.119.3100.774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Niel C. B. THE CULTURE, GENERAL PHYSIOLOGY, MORPHOLOGY, AND CLASSIFICATION OF THE NON-SULFUR PURPLE AND BROWN BACTERIA. Bacteriol Rev. 1944 Mar;8(1):1–118. doi: 10.1128/br.8.1.1-118.1944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]