Fig. 1.
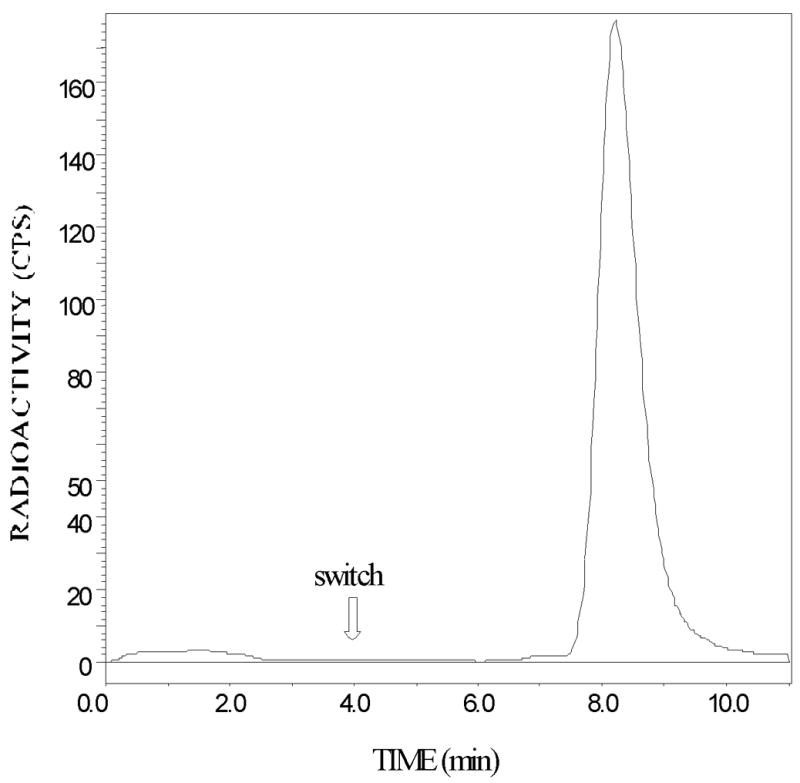
Column-switch chromatography of (S)-5-[123I]iodo-3-(2-azetidinylmethoxy)pyridine (5-[123I]IA) added to human plasma of a 32-year-old male nonsmoker (Subject 4). In the first 4 minutes of the column-switch method (Hilton et al., 2000), 4mL of plasma is passed through a capture column (Oasis Sorbent, Waters Associates, 4.6 × 19 mm) at 2mL/min followed by a wash with 1% acetonitrile in water. The effluent containing polar species passes through the flow cell of a radiation detector. The parent compound and lipophilic metabolites (if present), which bind to the capture column, are eluted and transferred to the analytical column (Zorbax Extend C18 4.6 × 250 mm) in 50% acetonitrile in triethylamine-HCl buffer pH 11 at a flow rate of 1 mL/min. Radioactivity in this effluent is measured by passage through the radiation detector. The column-switching procedure (Hilton et al., 2000) permits the identification of 5IA after the switch.
