Abstract
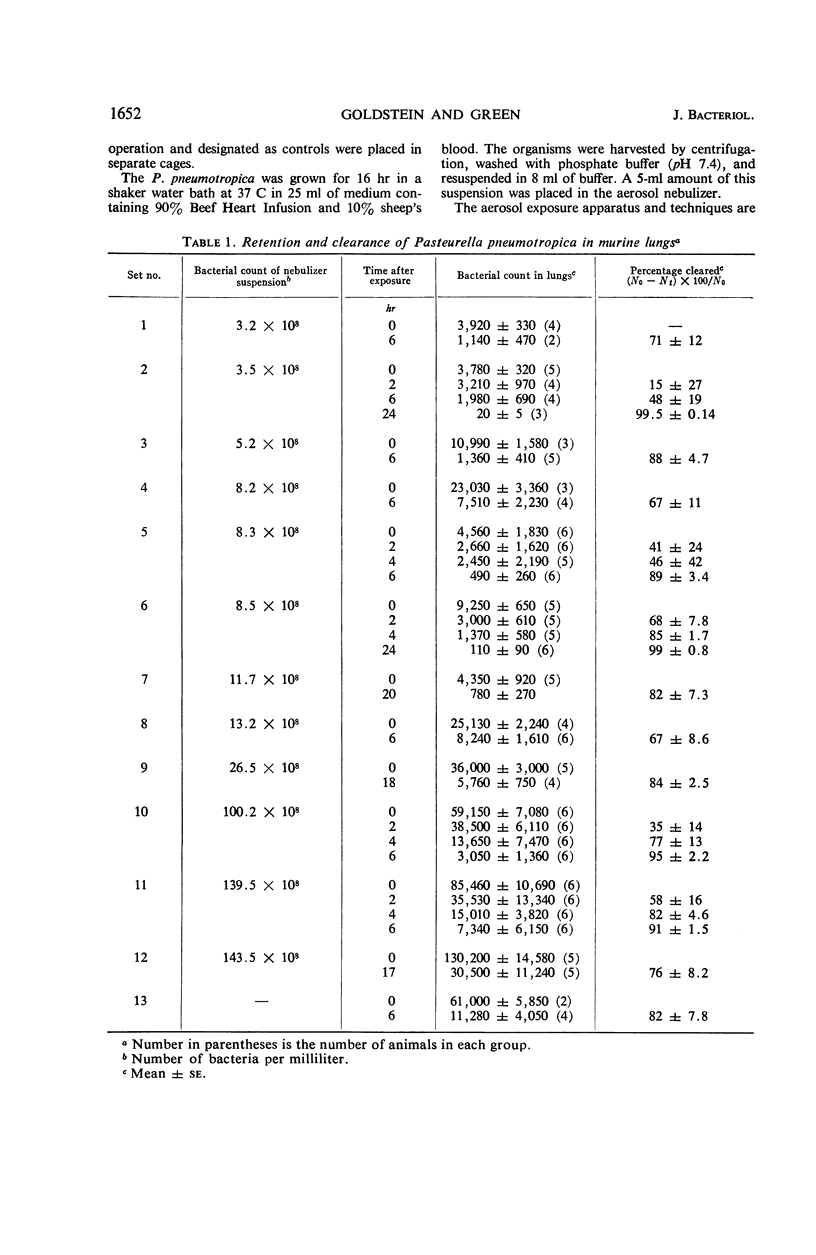
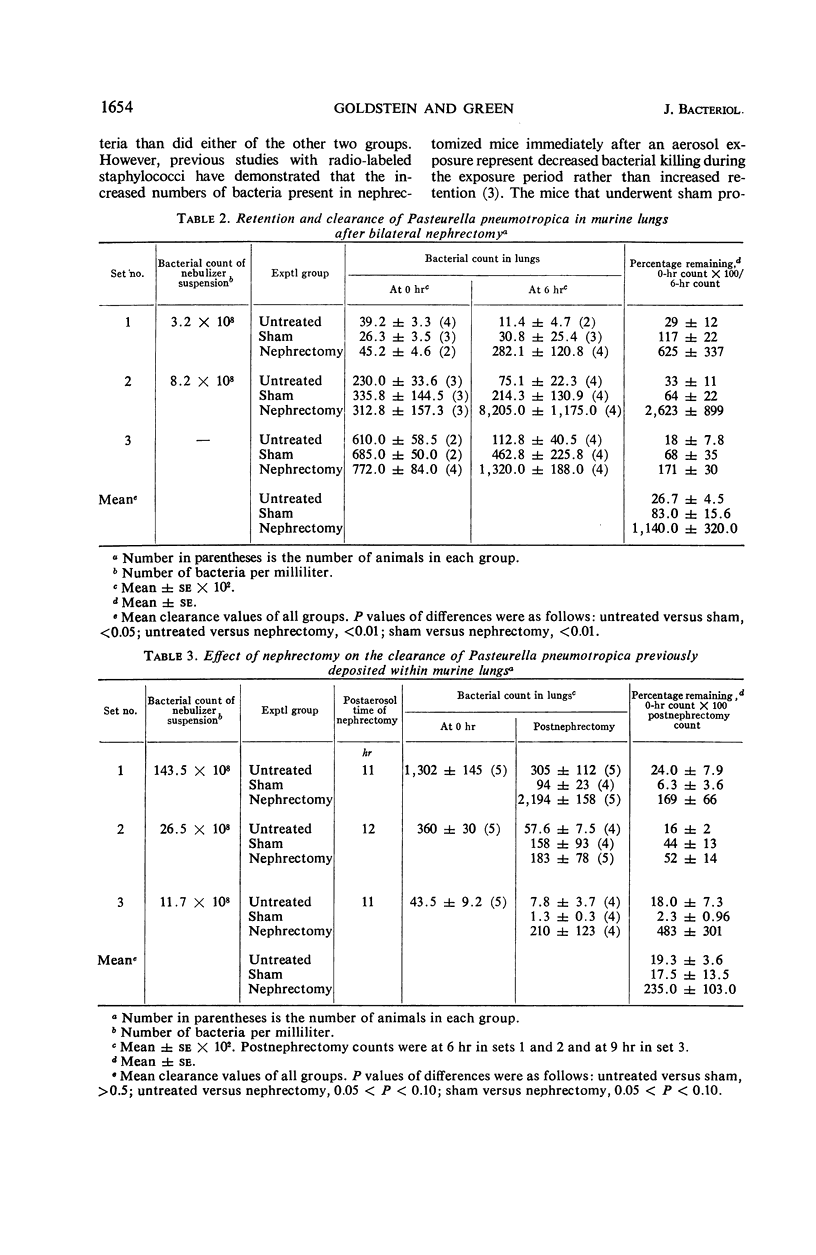
Pasteurella pneumotropica is a potential pulmonary pathogen in mice. In healthy animals, this organism was killed rapidly by the normal function of the intrapulmonary phagocytic defense mechanisms. Impairment of this bactericidal activity by the acute renal failure of nephrectomy resulted in multiplication of the Pasteurella in the lung, both when the animals were nephrectomized first and then infected, and when the animals were infected first and nephrectomized several hours after the infection. The study demonstrates that the pathogenicity of the Pasteurella organisms is governed by the functional state of these pulmonary antibacterial mechanisms.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLUEMLE L. W., Jr, WEBSTER G. D., Jr, ELKINTON J. R. Acute tubular necrosis; analysis of one hundred cases with respect to mortality, complications, and treatment with and without dialysis. AMA Arch Intern Med. 1959 Aug;104(2):180–197. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1959.00270080006002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN G. M., KASS E. H. FACTORS INFLUENCING THE CLEARANCE OF BACTERIA BY THE LUNG. J Clin Invest. 1964 Apr;43:769–776. doi: 10.1172/JCI104961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN G. M., KASS E. H. THE ROLE OF THE ALVEOLAR MACROPHAGE IN THE CLEARANCE OF BACTERIA FROM THE LUNG. J Exp Med. 1964 Jan 1;119:167–176. doi: 10.1084/jem.119.1.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein E., Green G. M. The effect of acute renal failure on the bacterial clearance mechanisms of the lung. J Lab Clin Med. 1966 Oct;68(4):531–542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green G. M., Goldstein E. A method for quantitating intrapulmonary bacterial inactivation in individual animals. J Lab Clin Med. 1966 Oct;68(4):669–677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green G. M., Kass E. H. The influence of bacterial species on pulmonary resistance to infection in mice subjected to hypoxia, cold stress, and ethanolic intoxication. Br J Exp Pathol. 1965 Jun;46(3):360–366. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAURENZI G. A., BERMAN L., FIRST M., KASS E. H. A QUANTITATIVE STUDY OF THE DEPOSITION AND CLEARANCE OF BACTERIA IN THE MURINE LUNG. J Clin Invest. 1964 Apr;43:759–768. doi: 10.1172/JCI104960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAHER J. F., SCHREINER G. E. Cause of death in acute renal failure. Arch Intern Med. 1962 Oct;110:493–504. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1962.03620220085014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OREN R., FARNHAM A. E., SAITO K., MILOFSKY E., KARNOVSKY M. L. Metabolic patterns in three types of phagocytizing cells. J Cell Biol. 1963 Jun;17:487–501. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.3.487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


