Abstract
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases (PI3Ks) are divided into three classes, which differ in their substrates and products. Class I generates the inositol phospholipids PI(3)P, PI(3,4)P2 and PI(3,4,5)P3, referred as PIP, PIP2, and PIP3 respectively. Class II produces PIP and PIP2, and class III generates only PIP. Substrate and product differences of the three classes are determined by the activation loops of their catalytic domains. Substitution of the class I activation loop with either class II or class III activation loop results in a corresponding change of substrate preference and product restriction. We have evaluated such activation loop substitutions to show that oncogenic activity of class I PI3K is linked to the ability to produce PIP3. We further show that reduction of cellular PIP3 levels by the 5' phosphatase PIPP interferes with PI3K-induced oncogenic transformation. PIPP also attenuates signaling through Akt and TOR. Class III PI3K fails to induce oncogenic transformation. Likewise, a constitutively membrane-bound class I PI3K mutant retaining only the protein kinase is unable to induce transformation. We conclude that PIP3 is an essential component of PI3K-mediated oncogenesis and that inability to generate PIP3 abolishes oncogenic potential.
Introduction
The family of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases (PI3Ks) is grouped into three distinct classes on the basis of lipid substrate specificity and mode of regulation (1). Class I PI3Ks can utilize the non-phosphorylated phosphatidylinositol (PI), the monophosphate (PI(4)P) and the bisphosphate (PI(4,5)P2) phosphatidylinositols as substrates, giving rise to PI(3)P, PI(3,4)P2 and PI(3,4,5)P3 which will be referred to as PIP, PIP2, and PIP3 respectively. Class II PI3Ks utilize PI and PI(4)P as substrates to produce PIP and PIP2 respectively. Class III PI3Ks, however, can only use PI and convert it to PIP. In addition, class I PI3Ks have the capacity to catalyze the addition of a phosphate group to serine residues in proteins (2, 3). The protein substrates include MEK1 (4), the PI3K subunits p85 and p110 and tropomyosin (5). Structural similarities also place some protein kinases close to PI3K (PI3K-related kinases, e.g. TOR)
In the PI3K pathway, signaling molecules downstream of PI3K, such as PDK-1 (phosphoinositide-dependent kinase) and Akt (murine thymoma viral oncoprotein homolog), bind PIP2 and PIP3 with near equal affinity (6). The binding of these signaling molecules provides a mechanism for their recruitment to the plasma membrane and allows PDK-1 to phosphorylate Akt. Phosphorylation of Akt by PDK-1 enhances the kinase activity of Akt and results in the phosphorylation of downstream targets (7). The crystal structure of the pleckstrin homology (PH) domain of Akt in complex PIP3 reveales significant ionic interactions between basic PH domain residues and the phosphates at the D3 and D4 positions of phosphatidylinositol (6, 8, 9). No binding occurs between the PH domain and the phosphate at the D5 position providing a structural basis for the lower binding affinity of Akt for PI(4,5)P2.
The phosphorylation of lipids by PI3K is antagonized by the phosphatase PTEN (phosphatase and tensin homolog), which removes the phosphate group from the D3 position of the inositol ring of PIP3 (10). PTEN negatively regulates the biological function of PI3K and inhibits the activation of signaling molecules downstream of PI3K (11). In cancer cells with loss-of-function mutations of PTEN, levels of PIP3 are increased (12), and Akt and its downstream targets show enhanced activation (12). Lipid phosphatases that remove the phosphate group from the D5 position of the inositol ring, including SHIP (SH2-containing inositol 5'-phosphatase) (13), SHIP2 (SH2-containing inositol 5'-phosphatase 2) (14) and PIPP (proline-rich inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase) (15), also attenuate PI3K signaling (15-17). The fact that these phosphatases reduce Akt activation and signaling suggests PIP3 may be a critical mediator of PI3K signaling.
Here we show that PIP3 is required for the transforming properties of all oncogenic PI3Ks. We also show that class III PI3K which can only produce PIP cannot transform cells. In addition, the protein kinase activity of the γ isoform of class I PI3K by itself is insufficient to cause oncogenic transformation.
Results
Transformation by all class I PI3Ks requires production of PIP3
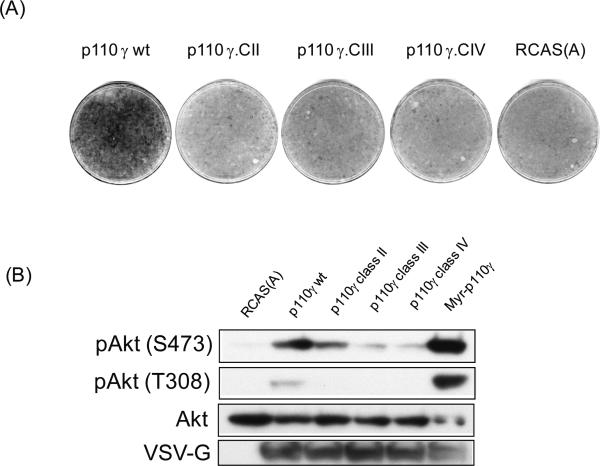
Previous studies from our laboratory showed that lipid kinase activity was required for transformation by p110γ and by the H1047R mutant of p110α (18). As PI3K produces several lipid products, we sought to identify the phospholipids that mediate the oncogenic signal of PI3K. We substituted a short sequence of the activation loop within the kinase domain of p110γ with the corresponding representative sequence from class II PI3K (PI3KC2α), class III PI3K (Vps34p) and from the PI3K-related kinase, TOR, here referred to as class IV (3, 4). This substitution changes the lipid substrate specificity and the subsequent lipid product specificity. Only the wild-type class I protein can produce PIP3 along with PIP2 and PIP (4). p110y with the class II substitution can only produce PIP2 and PIP whereas p110y with the class III substitution can only produce PIP (4). These p110γ hybrids were expressed with the RCAS (avian retroviral vector replication competent leucosis virus with splice acceptor) vector in CEF (chicken embryo fibroblasts). Of all the constructs evaluated, only the wild-type p110γ induced focus formation (Figure 1A). Expression of wild-type p110γ and of the myristylated, constitutively active p110γ induced phosphorylation of Akt at both serine 473 and threonine 308 (Figure 1B). Expression of p110γ with the class II substitution caused a slight increase in Akt phosphorylation at serine 473, but no phosphorylation was detected at threonine 308. Neither class III nor class IV substitutions of p110γ induced significant phosphorylation of Akt at serine 473 or threonine 308 over background levels. All hybrid proteins were expressed at similar levels (Figure 1B). These observations suggest that PIP3 is required for oncogenic transformation. However, it is not known whether PIP3 alone is sufficient for transformation or whether PIP2 is also essential.
Figure 1.
Transformation and PI3K/Akt signaling by class I PI3K γ requires production of PIP3. (A) Cellular transformation. The indicated constructs were transfected into CEF as stated in the experimental procedures. Cells were overlaid with nutrient agar for 14 days before staining with crystal violet. RCAS(A) is shown as negative control. (B) Analysis of Akt phosphorylation in cells transfected with the indicated constructs. Antibodies used were phospho-Akt (p-Akt) either serine 473 or threonine 308, total Akt (Akt) and VSV-G for tagged proteins.
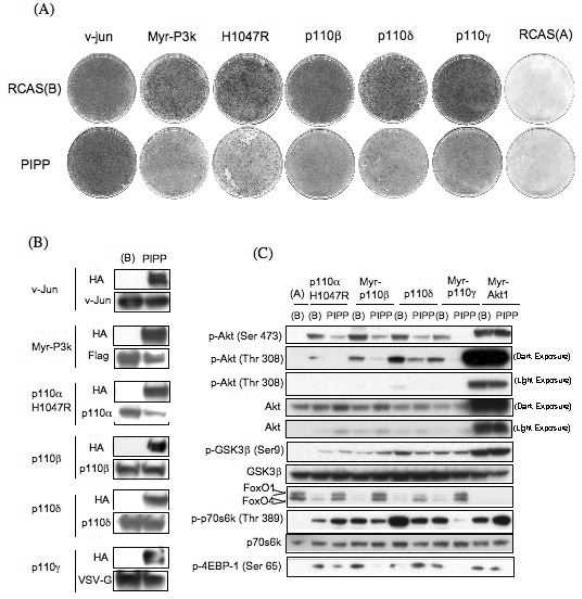
To confirm that PIP3 is an indispensable component of the oncogenic signal of all class I PI3K isoforms with the effect of the 5′-phosphatase PIPP on transformation was studied (15). PIPP is a lipid phosphatase that dephosphorylates inositol lipids at the D5 position of the inositol headgroup of either PIP3 or PI(4,5)P2 and consequently has been shown to reduce the level of PIP3 at the plasma membrane (15). Expression of PIPP or of the related 5'-phosphatase, SHIP, reduces the level of Akt phosphorylation at serine 473 (15, 19). The catalytic subunits of class I PI3K, p110β, p110γ, p110δ and the H1047R mutant of p110α were expressed in CEF along with PIPP or vector alone. PIPP significantly reduced the number of foci formed by all p110 isoforms but had no effect on focus formation by the v-Jun oncoprotein which was used as control (Figure 2A). The expression of PIPP resulted in some reduction in the levels of Myc-P3K and of p110αH1047R, but did not significantly affect the levels of p110β, p110γ or p110δ (Fig. 2B). Although we cannot rule out that the reduced abundance of Myc-P3K and of p110αH1047R contributed to lower focus counts, we consider this possibility unlikely, because even at these reduced expression levels, Myc-P3K and p110αH1047R were efficient focus formers in control experiments.
Figure 2.
Expression of PIPP interferes with cellular transformation and Akt signaling of class I PI3Ks. (A) Cellular transformation assay. The indicated constructs were transfected in to CEF either with or without PIPP, and cells were overlaid with nutrient agar for 14 days before staining with crystal violet. RCAS(A) and v-jun-transfected CEF are shown as controls. (B) Expression of PIPP does not affect the expression of class I PI3K isoforms. The expression levels of indicated constructs were analyzed with either isoform specific antibodies (p110α, β, δ) or against the VSV tag (p110y). PIPP was detected with HA antibody. (C) PIPP interferes with PI3K/Akt signaling. Downstream targets of PI3K show reduced phosphorylation when cotransfected with PIPP and FoxO protein degradation is attenuated.
The level of Akt phosphorylation at threonine 308 and serine 473 mediated by all PI3K isoforms was also reduced in CEF expressing PIPP (Figure 2C). As a measure of Akt activity, we determined the levels of the Akt substrates in PIPP-transfected CEF. FoxO1 (forkhead box O transcription factor) is a transcriptional regulator that controls the expression of several genes involved in cell proliferation including p21,Cip1 (20) and cyclin D2 (21). FoxO1 is phosphorylated on threonine 24 and serine 253 by Akt which then results in the nuclear exclusion and proteolytic degradation of FoxO1 (22, 23). In CEF transformed by PI3K or Akt, FoxO1 is undetectable (24). Expression of PIPP attenuated the degradation of FoxO1 induced by oncogenic PI3K.
The transformation by class I PI3K isoforms is sensitive to inhibition by rapamycin, suggesting that the activity of the TOR (target of rapamycin) kinase is essential for transformation (18). We analyzed the phosphorylation state of two substrates of TOR that are involved in translational control: S6K (p70 S6-kinase) and 4E-BP1 (eukaryotic initiation factor 4E-binding protein 1). S6K is phosphorylated by TOR on threonine 389, and this activation is required for the phosphorylation ribosomal protein S6 by S6K (25). 4E-BP1 binds to eIF4E (eukaryotic initiation factor 4E) and thereby prevents assembly of the cap-binding complex that initiates translation of mRNAs. 4E-BP1 is phosphorylated by TOR on serine 65, and this phosphorylation releases eIF4E from 4E-BP1, allowing assembly of the initiation complex (26). Expression of PIPP reduced the phosphorylation of both S6K and 4E-BP1. This observation suggests that reduced levels of PIP3 result in lower activity of TOR. To control for a possible effect of PIPP downstream of Akt or directly on Akt itself, we repeated the above analysis with constitutively active, myristylated Akt (Myr-Akt). PIPP expression did not affect Myr-Akt expression or signaling. We conclude that the effect of PIPP on PI3K signaling is due to a reduction in the levels of PIP3. In the absence of a myristylation signal, Akt depends on PIP3 for activation which in turn mediates the oncogenic signaling of PI3K.
The activation loop does not determine oncogenicity
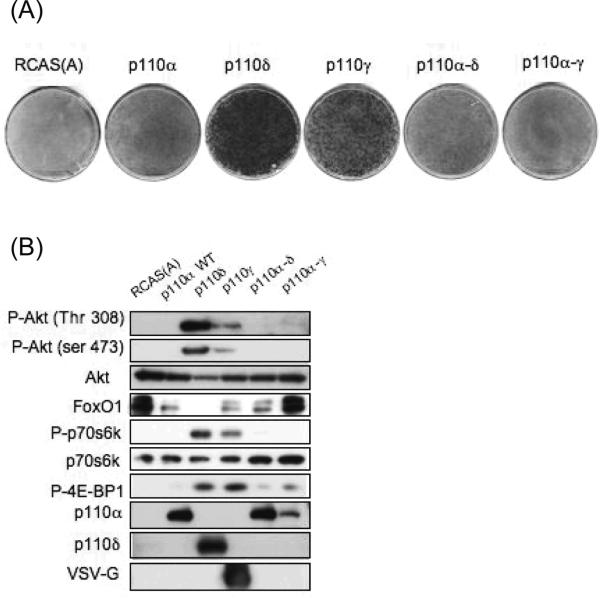
The activation loop of the catalytic domain of PI3K is critical in determining lipid substrate specificity and overall activity. In an effort to determine whether the activation loop defines the different oncogenic potencies of the class I PI3K isoforms we replaced the activation loop of the wild-type p110α with the activation loop of p110δ or p110γ. Wild-type p110α is not oncogenic and does not transform CEF whereas both p110δ and p110γ potently induce focus formation in CEF (18). p110α with the activation loop of p110δ (p110α-δ) and p110α with the activation loop of p110γ (p110α- γ) did not acquire the ability to transform CEF and in this respect behaved like wild-type p110α (Figure 3). In addition, the lipid kinase activity of p110α-δ and p110a-γ was similar to wild-type p110α (supplementary figure 1). These data show that oncogenic activity inherent in the wild-type non-alpha isoforms of class I p110 cannot be transferred solely with the activation loop.
Figure 3.
The activation loop of class I PI3Ks is not a sufficient determinant of oncogenicity. (A) Cellular transformation assay with wild-type PI3K isoforms (α, δ, γ) and hybrid p110α-δ and p110α-y. RCAS(A) and wild-type p110α are shown as negative controls. (B) PI3K/Akt signaling in transfected cells with hybrid constructs show the same phosphorylation status as wild-type p110α.
Protein kinase activity is not sufficient for activation of Akt or for transformation
All class I p110 isoforms exhibit intrinsic protein serine kinase activity as well as lipid kinase activity. p110γ autophosphorylates and phosphorylates several other proteins including the PI3K regulatory subunit p85, MEK1 (4) and non-muscle tropomyosin (5). Mutants of p110α H1047R and of p110γ that retain only the ability to phosphorylate proteins (lipid kinase inactive) cannot induce transformation in CEF (18). As myristylation increases the oncogenicity of p110γ and p110β and renders these proteins to constitutively activate Akt and several substrates downstream of Akt, a myristylated protein kinase-only p110γ was produced. This construct did not induce focus formation in CEF and did not activate Akt phosphorylation (data not shown). Therefore, the protein kinase activity alone cannot mediate the oncogenic properties of PI3K, even when p110 is constitutively localized to the membrane.
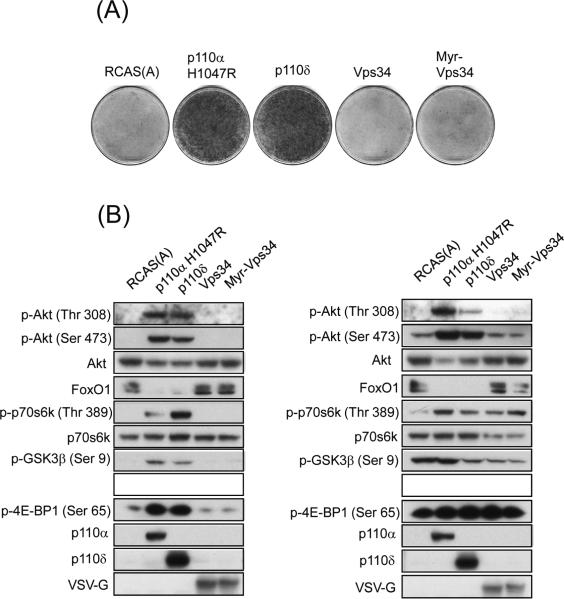
Class III PI3K, hVps34, does not cause oncogenic transformation
hVps34 is the human homolog of yeast Vps34p and the only member of class III PI3K in mammals (27). hVps34 can utilize phosphatidylinositol (PI) in a phosphorylation reaction to produce PIP (27). We cloned hVps34 into the RCAS expression vector and transfected the construct into CEF. Focus formation was not observed in CEF expressing either wild-type or a myristylated form of hVps34 (Figure 4A). Expression of the wild-type or of the myristylated form of hVps34 did not increase the phosphorylation status of Akt, S6K, 4E-BP1, GSK3β (glycogen synthase kinase-3 β) or cause a change in the level of FoxO1 (Figure 4B). The signaling of hVps34 did not change in the presence or absence of serum. Both the wild-type and myristylated Vps34 exhibited the ability to phosphorylate PI in an in vitro lipid kinase assay (supplementary figure 1).
Figure 4.
Class III PI3K, hVps34 is not oncogenic in CEF. (A) Focus formation of indicated constructs. RCAS(A) is shown as a negative control, p110α H1047R and p110δ serve as positive controls. (B) Vps34 and Myr-Vps34 do not activate PI3K targets under normal (left panel) or low serum conditions (right panel). Both proteins are VSV-G tagged and detected with a specific antibody against the VSV-G epitope.
Discussion
The three classes of PI3Ks are characterized by the specific sets of phospholipids which they can use as substrates. Consequently, each class of PI3K generates a characteristic set of products, dictated by substrate preferences. There are three phosphatidylinositol products with a phosphate at the D3 position, PIP, PIP2, and PIP3. Here we present evidence suggesting that PIP3 is an essential component of the oncogenic signal that originates in PI3K. It is not known, however, whether PIP3 is the only PI3K product required for oncogenicity. A possible participation of PIP2 and PIP cannot be excluded on the basis of the available data, but these latter products of PI3K are clearly not sufficient for oncogenicity.
The activation loop hybrids of p110γ with the ability to produce a restricted set of phospholipids link oncogenic activity to the ability to produce PIP3. The PIPP phosphatase which reduces intracellular levels of PIP3 effectively interferes with the PI3K-induced oncogenic transformation but fails to affect an oncogenic signal that is not dependent on the PI3K - Akt pathway.
The phospholipid products of PI3K recruit Akt and its activating kinase PDK-1, allowing PDK-1 to phosphorylate Akt on threonine 308. PDK-1 and Akt bind to PIP3 with high affinity. Both also bind to PI(4,5)P2, but weakly, suggesting that the most efficient activation of Akt is mediated by PIP3 (28, 29). Our results suggest that phosphorylation of Akt on both threonine 308 and serine 473 is dependent on PIP3.
It is conceivable that other proteins which preferentially bind PIP3 over PIP2 are involved in PI3K-induced oncogenic transformation. Some of these PIP3-binding proteins are the tyrosine kinase Btk (Bruton's tyrosine kinase) (30), the ARNO (Arf nucleotide-binding site opener) and GRP1 (general receptor for phosphoinositides -1) guanine tri-phosphate exchange factors (31) and the Sos (son of sevenless) and Gab1 (Grb2 associated binder) adaptor proteins (32). The tyrosine kinase Btk has been shown to cause oncogenic transformation by acquiring gain-of-function mutations (33, 34). In addition, Btk appears to be a target of the BCR-Abl fusion protein, as inhibition of Btk by a small molecule inhibitor induces apoptosis of BCR-Abl-expressing leukemia cells as effectively as inhibition of BCR-Abl itself (35). The oncoprotein Ras can be activated by Shc (Src homology 2 domain containing protein) via the adaptors Sos and Gab1 which has revealed these adaptors as novel targets for anticancer therapy (36). Possible roles of these PIP3-binding proteins in PI3K signaling remain to be explored.
The central role of PIP3 in PI3K-induced oncogenic transformation is also reflected by the elevated levels of PIP3 seen in many cancers. This fact highlights the potential tumor suppressor nature of 5'-phosphatases and suggests that loss-of-function mutations or down regulation of these phosphatases may be a marker of increased PI3K signaling in tumors. This suggestion is supported by the finding that another 5'-phosphatase, SHIP, (Src homology 2 domain-containing inositol polyphosphate phosphatase) is inactivated in adult T-cell leukemia which displays high levels of phosphorylated Akt (37). Our results with PIPP are in accord with previous work which shows that the 5'phosphatases SHIP-1 and SHIP-2 can attenuate Akt signaling (38).
Our studies failed to detect an oncogenic potential in class III PI3K. Class III PI3K is represented by one protein in humans, hVps34. This homolog of the yeast enzyme Vps34p can only utilize PI to produce PIP (39). One of the physiological roles of hVps34 is to regulate trafficking of lysosomal enzymes through the trans-Golgi network (40). PIP interacts with FYVE domains of proteins (41), and our results suggest FYVE domain containing proteins are not sufficient for oncogenic transformation.
Our results document an essential role of PIP3 in the oncogenic functions of PI3Ks.
Material and Methods
Plasmid Construction
All wild-type and myristylated class I PI3K isoforms constructs were described previously (18). p110 γ constructs with replaced catalytic core of class II, III and IV enzymes as well as p110α-δ and p110α-γ hybrid constructs are designed as described in Bondeva et al., 1998. (4)
All PI3K, hVps34 coding sequences were ultimately cloned into the avian retroviral vector RCAS.Sfi, a modified version of RCAS (42).
PI3-Kinase Assay
In vitro PI3-kinase activity was analyzed as described (43) , with minor modifications. The immune complexes were prepared by incubating 400 μg protein with 5 μl of anti-p110α antibody for 2 h at 4°C, followed by 2 h of incubation with Protein A-agarose. The beads were washed three times with lysis buffer and twice with TNE (10 mM Tris, pH 7.5/100 mM NaCl/1 mM EDTA). Subsequently, the immune complexes were incubated with 50 μl of kinase reaction buffer containing 20 mM Hepes (pH 7.5), 10 mM MgCl2, 200 μg/ml phosphatidylinositol (sonicated), 60 μM ATP, and 200 μCi/ml (1 Ci/37 GBq) [γ-32P]ATP for 5 min at room temperature. The reaction was terminated by adding 80 μl of 1 N HCl, and the phosphorylated lipids were extracted with 160 μl of chloroform/methanol (1:1). Samples were dried down and dissolved in chloroform and spotted onto Silica Gel 60 TLC plates (EMD, San Diego, CA). The plates were developed in a borate buffer system (44) and visualized by autoradiography.
Cell Culture
Primary cultures of CEF were prepared from White Leghorn embryos purchased from Charles River Breeding Laboratories (Preston, CT). Each transfection with DNA or infection with avian retrovirus was performed with newly prepared CEF. CEF were routinely cultured in F-10
Focus Assays
For focus assays CEF were infected with RCAS virus containing the relevant oncogene as previously described (45). Cells were fed nutrient agar every other day and then stained with crystal violet to visualize the foci of transformed cells. Inhibitors were prepared in 100% DMSO and added at the desired concentration to the nutrient agar overlays. An equivalent amount of 100% DMSO was added to cells as a control.
Interference of PIPP with oncogenic transformation
Cells were transfected with different RCAS vectors expressing PIPP and oncogenic p110 constructs. PIPP was expressed by RCAS carrying the subgroup B envelope protein (RCAS B) and the p110 proteins were expressed with RCAS carrying the subgroup A envelope protein (RCAS A). For efficient expression of two proteins in the same cell, it is essential to use RCAS vectors with different envelope proteins to avoid competition for the same cell surface receptor. A v-jun expressing vector was used as a control.
Western Analysis
Cell lysates were prepared from CEF that had been transfected with DNA using the DMSO/polybrene method (46). For serum starvation, subconfluent cultures were kept in Ham's F-10 medium with 0.5% FCS and 0.1% chicken serum for 40 hours prior to 2 hour of starvation in F-10 Ham's medium alone. Inhibitors or DMSO were added at the appropriate concentration during the final 2 hours in serum-free F-10 Ham's medium. Western blotting was performed as previously described in refs. (18, 43, 47).
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
Work of the authors is supported by grants from the National Cancer Institute. This is manuscript number 20002 of The Scripps Research Institute.
References
- 1.Vanhaesebroeck B, Leevers SJ, Panayotou G, Waterfield MD. Phosphoinositide 3-kinases: a conserved family of signal transducers. Trends Biochem Sci. 1997;22:267–72. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(97)01061-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Dhand R, Hiles I, Panayotou G, et al. PI 3-kinase is a dual specificity enzyme: autoregulation by an intrinsic protein-serine kinase activity. EMBO J. 1994;13:522–33. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06290.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Pirola L, Zvelebil MJ, Bulgarelli-Leva G, Van Obberghen E, Waterfield MD, Wymann MP. Activation loop sequences confer substrate specificity to phosphoinositide 3-kinase alpha (PI3Kalpha ). Functions of lipid kinase-deficient PI3Kalpha in signaling. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:21544–54. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M011330200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bondeva T, Pirola L, Bulgarelli-Leva G, Rubio I, Wetzker R, Wymann MP. Bifurcation of lipid and protein kinase signals of PI3Kgamma to the protein kinases PKB and MAPK. Science. 1998;282:293–6. doi: 10.1126/science.282.5387.293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Naga Prasad SV, Jayatilleke A, Madamanchi A, Rockman HA. Protein kinase activity of phosphoinositide 3-kinase regulates beta-adrenergic receptor endocytosis. Nat Cell Biol. 2005;7:785–96. doi: 10.1038/ncb1278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.DiNitto JP, Lambright DG. Membrane and juxtamembrane targeting by PH and PTB domains. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006;1761:850–67. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2006.04.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Jacinto E, Facchinetti V, Liu D, et al. SIN1/MIP1 maintains rictor-mTOR complex integrity and regulates Akt phosphorylation and substrate specificity. Cell. 2006;127:125–37. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.08.033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Frech M, Andjelkovic M, Ingley E, Reddy KK, Falck JR, Hemmings BA. High affinity binding of inositol phosphates and phosphoinositides to the pleckstrin homology domain of RAC/protein kinase B and their influence on kinase activity. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:8474–81. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.13.8474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Thomas CC, Deak M, Alessi DR, van Aalten DM. High-resolution structure of the pleckstrin homology domain of protein kinase b/akt bound to phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-trisphosphate. Curr Biol. 2002;12:1256–62. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(02)00972-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Maehama T, Dixon JE. The tumor suppressor, PTEN/MMAC1, dephosphorylates the lipid second messenger, phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:13375–8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.22.13375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Stambolic V, Suzuki A, de la Pompa JL, et al. Negative regulation of PKB/Akt-dependent cell survival by the tumor suppressor PTEN. Cell. 1998;95:29–39. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81780-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Haas-Kogan D, Shalev N, Wong M, Mills G, Yount G, Stokoe D. Protein kinase B (PKB/Akt) activity is elevated in glioblastoma cells due to mutation of the tumor suppressor PTEN/MMAC. Curr Biol. 1998;8:1195–8. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(07)00493-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Damen JE, Liu L, Rosten P, et al. The 145-kDa protein induced to associate with Shc by multiple cytokines is an inositol tetraphosphate and phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-triphosphate 5-phosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996;93:1689–93. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.4.1689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Pesesse X, Deleu S, De Smedt F, Drayer L, Erneux C. Identification of a second SH2-domain-containing protein closely related to the phosphatidylinositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase SHIP. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1997;239:697–700. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1997.7538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Ooms LM, Fedele CG, Astle MV, et al. The inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase, PIPP, Is a novel regulator of phosphoinositide 3-kinase-dependent neurite elongation. Mol Biol Cell. 2006;17:607–22. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E05-05-0469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Aman MJ, Lamkin TD, Okada H, Kurosaki T, Ravichandran KS. The inositol phosphatase SHIP inhibits Akt/PKB activation in B cells. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:33922–8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.51.33922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Sasaoka T, Rose DW, Jhun BH, Saltiel AR, Draznin B, Olefsky JM. Evidence for a functional role of Shc proteins in mitogenic signaling induced by insulin, insulinlike growth factor-1, and epidermal growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:13689–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kang S, Denley A, Vanhaesebroeck B, Vogt PK. Oncogenic transformation induced by the p110beta, -gamma, and -delta isoforms of class I phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103:1289–94. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0510772103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Freeburn RW, Wright KL, Burgess SJ, Astoul E, Cantrell DA, Ward SG. Evidence that SHIP-1 contributes to phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate metabolism in T lymphocytes and can regulate novel phosphoinositide 3-kinase effectors. J Immunol. 2002;169:5441–50. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.169.10.5441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Seoane J, Le HV, Shen L, Anderson SA, Massague J. Integration of Smad and forkhead pathways in the control of neuroepithelial and glioblastoma cell proliferation. Cell. 2004;117:211–23. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(04)00298-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Bouchard C, Marquardt J, Bras A, Medema RH, Eilers M. Myc-induced proliferation and transformation require Akt-mediated phosphorylation of FoxO proteins. EMBO J. 2004;23:2830–40. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Biggs WH, 3rd, Meisenhelder J, Hunter T, Cavenee WK, Arden KC. Protein kinase B/Akt-mediated phosphorylation promotes nuclear exclusion of the winged helix transcription factor FKHR1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999;96:7421–6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.13.7421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Brunet A, Bonni A, Zigmond MJ, et al. Akt promotes cell survival by phosphorylating and inhibiting a Forkhead transcription factor. Cell. 1999;96:857–68. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80595-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Aoki M, Jiang H, Vogt PK. Proteasomal degradation of the FoxO1 transcriptional regulator in cells transformed by the P3k and Akt oncoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101:13613–7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0405454101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Burnett PE, Barrow RK, Cohen NA, Snyder SH, Sabatini DM. RAFT1 phosphorylation of the translational regulators p70 S6 kinase and 4E-BP1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998;95:1432–7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.4.1432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Gingras AC, Raught B, Sonenberg N. Regulation of translation initiation by FRAP/mTOR. Genes Dev. 2001;15:807–26. doi: 10.1101/gad.887201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Volinia S, Dhand R, Vanhaesebroeck B, et al. A human phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase complex related to the yeast Vps34p-Vps15p protein sorting system. EMBO J. 1995;14:3339–48. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07340.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Currie RA, Walker KS, Gray A, et al. Role of phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate in regulating the activity and localization of 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1. Biochem J. 1999;337(Pt 3):575–83. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Stokoe D, Stephens LR, Copeland T, et al. Dual role of phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate in the activation of protein kinase B. Science. 1997;277:567–70. doi: 10.1126/science.277.5325.567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Baraldi E, Djinovic Carugo K, Hyvonen M, et al. Structure of the PH domain from Bruton's tyrosine kinase in complex with inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate. Structure. 1999;7:449–60. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(99)80057-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Ferguson KM, Kavran JM, Sankaran VG, et al. Structural basis for discrimination of 3-phosphoinositides by pleckstrin homology domains. Mol Cell. 2000;6:373–84. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(00)00037-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Rameh LE, Arvidsson A, Carraway KL, 3rd, et al. A comparative analysis of the phosphoinositide binding specificity of pleckstrin homology domains. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:22059–66. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.35.22059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Li T, Tsukada S, Satterthwaite A, et al. Activation of Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) by a point mutation in its pleckstrin homology (PH) domain. Immunity. 1995;2:451–60. doi: 10.1016/1074-7613(95)90026-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Park H, Wahl MI, Afar DE, et al. Regulation of Btk function by a major autophosphorylation site within the SH3 domain. Immunity. 1996;4:515–25. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80417-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Hendriks RW, Kersseboom R. Involvement of SLP-65 and Btk in tumor suppression and malignant transformation of pre-B cells. Semin Immunol. 2006;18:67–76. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2005.10.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Yart A, Mayeux P, Raynal P. Gab1, SHP-2 and other novel regulators of Ras: targets for anticancer drug discovery? Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2003;3:177–92. doi: 10.2174/1568009033481976. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Fukuda R, Hayashi A, Utsunomiya A, et al. Alteration of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase cascade in the multilobulated nuclear formation of adult T cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATLL) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102:15213–8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0507184102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Taylor V, Wong M, Brandts C, et al. 5' phospholipid phosphatase SHIP-2 causes protein kinase B inactivation and cell cycle arrest in glioblastoma cells. Mol Cell Biol. 2000;20:6860–71. doi: 10.1128/mcb.20.18.6860-6871.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Yan Y, Backer JM. Regulation of class III (Vps34) PI3Ks. Biochem Soc Trans. 2007;35:239–41. doi: 10.1042/BST0350239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Brown WJ, DeWald DB, Emr SD, Plutner H, Balch WE. Role for phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in the sorting and transport of newly synthesized lysosomal enzymes in mammalian cells. J Cell Biol. 1995;130:781–96. doi: 10.1083/jcb.130.4.781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Burd CG, Emr SD. Phosphatidylinositol(3)-phosphate signaling mediated by specific binding to RING FYVE domains. Mol Cell. 1998;2:157–62. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(00)80125-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Aoki M, Batista O, Bellacosa A, Tsichlis P, Vogt PK. The akt kinase: molecular determinants of oncogenicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998;95:14950–5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.25.14950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Aoki M, Schetter C, Himly M, Batista O, Chang HW, Vogt PK. The catalytic subunit of phosphoinositide 3-kinase: requirements for oncogenicity. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:6267–75. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.9.6267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Walsh JP, Caldwell KK, Majerus PW. Formation of phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate by isomerization from phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991;88:9184–7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.9184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Bos TJ, Monteclaro FS, Mitsunobu F, et al. Efficient transformation of chicken embryo fibroblasts by c-Jun requires structural modification in coding and noncoding sequences. Genes Dev. 1990;4:1677–87. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Kawai S, Nishizawa M. New procedure for DNA transfection with polycation and dimethyl sulfoxide. Mol Cell Biol. 1984;4:1172–4. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.6.1172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Kang S, Bader AG, Vogt PK. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase mutations identified in human cancer are oncogenic. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102:802–7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0408864102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.