Abstract
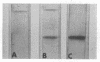
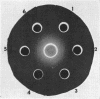
The α-amylase (α-1,4-glucan 4-glucanohydrolase, EC 3.2.1.1) of Bacillus subtilis strain W23 is less negatively-charged than the α-amylase of B. amyloliquefaciens strain F, as determined by electrophoretic mobility in polyacrylamide gel at pH 8.6. The α-amylase of strain W23 is immunologically unrelated to the α-amylase of strain F, as judged by lack of cross-reaction in Ouchterlony immunodiffusion studies. The pH range of maximal activity for the enzyme of strain W23 was 5.7 to 6.7, with a maximum at 6.3. The pH range of activity for the α-amylase of strain F was 5.5 to 6.5, with a maximum at 5.9. No significant difference was found in the effect of temperature on the activity of the α-amylase of strain W23 and strain F. α-Amylase production by strain W23 occurs throughout the 7-hr growth period, whereas enzyme production by strain F does not begin until the culture enters the stationary phase of growth. The total amounts of enzyme produced by strains W23 and F after 7 hr of growth were 0.3 and 25.5 units/ml, respectively.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- COLEMAN G., ELLIOTT W. H. Studies on alpha-amylase formation by Bacillus subtilis. Biochem J. 1962 May;83:256–263. doi: 10.1042/bj0830256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman G., Grant M. A. Characteristics of alpha-amylase formation by Bacillus subtilis. Nature. 1966 Jul 16;211(5046):306–307. doi: 10.1038/211306a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUKUMOTO J., YAMAMOTO T., TSURU D. Effects of carbon sources and base analogues of nucleic acid on the formation of bacterial amylase. Nature. 1957 Aug 31;180(4583):438–439. doi: 10.1038/180438b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN D. M., COLARUSSO L. J. THE PHYSICAL AND GENETIC CHARACTERIZATION OF A TRANSFORMABLE ENZYME: BACILLUS SUBTILIS ALPHA-AMYLASE. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Aug 26;89:277–290. doi: 10.1016/0926-6569(64)90216-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNT J. A., OTTENSEN M. A comparison of three proteinases from various strains of Bacillus subtilis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Apr 1;48:411–412. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90498-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OTTESEN M., SPECTOR A. A comparison of two proteinases from Bacillus subtilis. C R Trav Lab Carlsberg. 1960;32:63–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POSTGATE J. R., CAMPBELL L. L. IDENTIFICATION OF COLEMAN'S SULFATE-REDUCING BACTERIUM AS A MESOPHILIC RELATIVE OF CLOSTRIDIUM NIGRIFICANS. J Bacteriol. 1963 Aug;86:274–279. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.2.274-279.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith E. L., Markland F. S., Kasper C. B., DeLange R. J., Landon M., Evans W. H. The complete amino acid sequence of two types of subtilisin, BPN' and Carlsberg. J Biol Chem. 1966 Dec 25;241(24):5974–5976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WELKER N. E., CAMPBELL L. L. EFFECT OF CARBON SOURCES ON FORMATION OF ALPHA-AMYLASE BY BACILLUS STEAROTHERMOPHILUS. J Bacteriol. 1963 Oct;86:681–686. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.4.681-686.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welker N. E., Campbell L. L. Unrelatedness of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens and Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(4):1124–1130. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.4.1124-1130.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]