Abstract
Background:
There are limited data regarding the hypoxia pathway in familial breast cancers. We therefore performed a study of hypoxic factors in BRCA1, BRCA2 and BRCAX breast cancers.
Methods:
Immunoperoxidase staining for HIF-1α, PHD1, PHD2, PHD3, VEGF and FIH was carried out in 125 (38 BRCA1, 33 BRCA2 and 54 BRCAX) breast carcinomas. These were correlated with clinicopathological parameters and the intrinsic breast cancer phenotypes.
Results:
BRCA1 tumours correlated with positivity for HIF-1α (P=0.008) and negativity for PHD3 (P=0.037). HIF-1α positivity (P=0.001), PHD3 negativity (P=0.037) and nuclear FIH negativity (P=0.011) was associated with basal phenotype. HIF-1α expression correlated with high tumour grade (P=0.009), negative oestrogen receptor (ER) status (P=0.001) and the absence of lymph node metastasis (P=0.028). Nuclear FIH expression and PHD3 correlated with positive ER expression (P=0.024 and P=0.035, respectively). BRCA1 cancers with positive HIF-1α or cytoplasmic FIH had a significantly shorter relapse-free survival (P=0.007 and P=0.049, respectively).
Conclusions:
The aggressive nature of BRCA1 and basal-type tumours may be partly explained by an enhanced hypoxic drive and hypoxia driven ER degradation because of suppressed PHD and aberrantly located FIH expression. This may have important implications, as these tumours may respond to compounds directed against HIF-1α or its downstream targets.
Keywords: HIF-1α, FIH, breast, BRCA1, familial
Carriers of germline mutations in BRCA1 and BRCA2 have a predisposition for developing breast and/or ovarian cancer. The cumulative risk of breast carcinoma in carriers of BRCA1/BRCA2 mutations ranges from 45–84% by 70 years of age (Antoniou et al, 2003). There are chromosomal, morphological and immunohistochemical differences between spontaneous and BRCA-associated tumour (Lakhani et al, 2000; Jonsson et al, 2005; Palacios et al, 2005). Thus BRCA1 mutation associated breast cancers are generally poorly differentiated and more frequently display typical and atypical medullary-like morphology than sporadic tumours (Lakhani et al, 2000). Furthermore, BRCA1 tumours show a so-called ‘triple negative’ phenotype being oestrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PgR) and HER2 negative (Palacios et al, 2003). BRCA1 tumours also harbour p53 mutations (Sensi et al, 2003) and express basal and myoepithelial markers such as cytokeratins (CK) 5, CK14, α-actin and p63 in keeping with a basal-like phenotype (Jacquemier et al, 2005; Laakso et al, 2005; Lakhani et al, 2005). Although reports suggesting lobular carcinomas are more frequent in BRCA2 carriers, no similarly defined phenotype has been described for BRCA2-associated tumours, which usually show a ductal, no special type morphology and ER positivity (Armes et al, 1998). These observations suggest specific and distinct neoplastic pathways in germline BRCA mutation-related breast cancers compared with sporadic cancer pathways.
Hypoxia is a hallmark of many cancers that has been associated with diminished therapeutic response and with an increasing probability of malignant progression (Vaupel, 2004). Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) is the key regulator of the hypoxia response. HIF-1 consists of two subunits, HIF-1α and HIF-1β. Although HIF-1β is a nuclear protein that is constitutively expressed and is independent of oxygen tension, the HIF-1α protein is induced and continuously degraded under normoxia by the ubiquitin–proteasome pathway in the cytoplasmic cellular compartment (Salceda and Caro, 1997; Huang et al, 1998). However, under hypoxic conditions HIF-1α translocates to the nucleus where it heterodimerizes with HIF-1β (Vaupel, 2004). This HIF-1 complex then regulates the expression of its target genes through binding with hypoxia responsive elements in the promoter regions of target genes (Bos et al, 2003; van der Groep et al, 2008) including erythropoietin, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), glycolytic enzymes, transferrin and a variety of other proteins that enhance tumour survival, invasion and metastasis (Semenza, 2000; Vaupel, 2004).
The level and activity of HIF-1α subunit is tightly regulated through a number of post-translational modifications. In the presence of oxygen, three prolyl hydroxylase enzymes (PHD), PHD1, PHD2 and PHD3 cause site-specific hydroxylation of two proline residues, P402 and P564, within the oxygen-dependent degradation domain of HIF-1α. This allows for the recognition of HIF-1α by the tumour suppressor von Hippel-Lindau protein, which targets HIF-1α for degradation (Boddy et al, 2005). In addition, hydroxylation of the asparagine residue 803 by factor inhibiting HIF (FIH) reduces its transcriptional activity through interfering with cofactor binding (Lando et al, 2002). However, under hypoxic conditions these hydroxylase enzymes are less active because of the paucity of molecular oxygen, resulting in both an increase in the level of nuclear HIF-1α and its activity (Boddy et al, 2005).
In sporadic breast cancer, previous studies have shown that HIF-1α overexpression has a role in breast carcinogenesis and is correlated with a poor prognosis (Generali et al, 2006). However, little is known about the role of HIF-1α in hereditary breast carcinogenesis with only one report in a small series (n=30) suggesting overexpression of HIF-1α present in a higher frequency in BRCA1-related cancers than sporadic cancers (van der Groep et al, 2008). Given the importance of all pathway members in the control of hypoxia-induced gene expression, our aims were to: (1) determine the level and pattern of expression of HIF-1α, PHDs and FIH in a large cohort of familial breast cancers, (2) correlate expression with conventional clinicopathological parameters, (3) investigate expression in familial breast cancers stratified by intrinsic breast cancer phenotypes and (4) explore their role in patient survival.
Materials and methods
Patients and tumour tissue microarrays
Tumour tissue microarray cores (1 mm cores) with fourfold redundancy for 147 familial invasive breast cancers were collected from the kConFab biorepository. For the purposes of this study, classification of BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations and sequence variants was according to designations listed for research purposes on the kConFab website (www.kconfab.org/index.shtml). The BRCAX breast cancers are defined by familial breast cancer in families without a known BRCA1 and BRCA2 pathogenic mutation. General inclusion criteria for the BRCAX subgroup were families with breast cancer meeting kConFab category 1 and 1B eligibility criteria and with a breast cancer pathology report held by kConFab.
The flow of patients through the study according to the REMARK criteria is listed in Table 1 (McShane et al, 2005). Of the 147 cases, 9 cases were excluded because of the lack of tissue available for array construction and a further 13 cases were excluded because of the absence of tumour on the array available for staining. The final cohort was composed of 125 cases composed of 38BRCA1, 33BRCA2 and 54 BRCAX cases.
Table 1. Flow of familial breast cancer patients through the study, according to REMARK criteria (McShane et al, 2005).
| BRCA1 | BRCA2 | BRCAX | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female patients collected for study | 45 | 36 | 66 | 147 |
| Patients with tissue available | 42 | 33 | 63 | 138 |
| Tumours present on array | 38 | 33 | 54 | 125 |
| Tumours with tissue on array and survival data | 34 | 30 | 52 | 116 |
These were compared with a cohort of 186 sporadic cancers collected from the John Radcliffe Hospital, Oxford, UK, which was characterised in a previous study (Tan, 2008). All patients had operable breast carcinomas and were not diagnosed with metastatic disease at the time of presentation. Information regarding patient characteristics, including age, tumour size, grade, histology, nodal status, ER and HER-2 status were collected from the clinical and pathological records (Table 2). Using stratification of intrinsic phenotypes based on Nielsen et al (2004) tumours were placed into luminal (ERα positive, HER2 negative, cytokeratin (CK) 5/6 and/or EGFR negative or positive), basal (HER2 and ERα negative; CK5/6 and/or EGFR positive), HER2 (HER2 positive, ERα, CK5/6 and EGFR negative or positive) and null/negative (HER2, ERα, CK5/6 and EGFR negative).
Table 2. Clinical and tumour characteristics (n=125).
| BRCA1, n (%) | BRCA2, n (%) | BRCAX, n (%) | All familial, n (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | ||||
| Median (range), years | ||||
| < 40 years | 16 (42%) | 9 (27%) | 8 (15%) | 33 (26%) |
| 40–55 years | 20 (53%) | 13 (40%) | 29 (54%) | 62 (50%) |
| 55–69 years | 2 (5%) | 9 (27%) | 14 (26%) | 25 (20%) |
| >70 years | 0 | 2 (6%) | 3 (5%) | 5 (4%) |
| Tumour size | ||||
| < 20 mm | 29 (76%) | 16 (52%) | 25 (53%) | 68 (60%) |
| > 20 mm | 9 (24%) | 15 (48%) | 22 (47%) | 46 (40%) |
| Unknown | 0 | 2 | 7 | 9 |
| Nodal status | ||||
| Negative | 35 (92%) | 23 (74%) | 30 (63%) | 88 (76%) |
| Positive | 3 (8%) | 8 (26%) | 17 (37%) | 28 (24%) |
| Unknown | 0 | 2 | 7 | 9 |
| Grade | ||||
| I | 0 | 1 (4%) | 6 (13%) | 7 (7%) |
| II | 2 (6%) | 14 (48%) | 14 (31%) | 30 (29%) |
| III | 30 (94%) | 14 (48%) | 25 (56%) | 67 (64%) |
| Unknown | 6 | 4 | 9 | 19 |
| ER-α | ||||
| Negative | 29 (85%) | 5 (17%) | 15 (31%) | 49 (44%) |
| Positive | 5 (15%) | 24 (83%) | 33 (69%) | 62 (56%) |
| Unknown | 4 | 4 | 6 | 14 |
| PgR | ||||
| Negative | 27 (84%) | 10 (35%) | 23 (48%) | 60 (55%) |
| Positive | 5 (16%) | 19 (65%) | 25 (52%) | 49 (45%) |
| Unknown | 6 | 4 | 6 | 16 |
| HER2 status | ||||
| Negative | 29 (100%) | 25 (100%) | 38 (87%) | 92 (93%) |
| Positive | 0 | 0 | 7 (13%) | 7 (7%) |
| Unknown | 9 | 8 | 8 | 25 |
| Endocrine therapy | ||||
| Not given | 28 (90%) | 19 (70%) | 28 (61%) | 75 (72%) |
| Given | 3 (10%) | 8 (30%) | 18 (39%) | 29 (28%) |
| Unknown | 7 | 6 | 8 | 21 |
| Chemotherapy | ||||
| Not given | 14 (38%) | 17 (52%) | 20 (43%) | 51 (45%) |
| Given | 23 (62%) | 14 (48%) | 26 (57%) | 63 (55%) |
| Unknown | 1 | 2 | 8 | 11 |
Patients less than 50 years of age with node positive, ER-negative tumours or tumours larger than 3 cm received adjuvant chemotherapy. Patients with hormone responsive tumours who were more than 50 years of age received 5 years of endocrine therapy. Patients were followed up for a median period of 64 months. During this time, 38 patients relapsed and 31 died (the recorded deaths were breast cancer related otherwise were censored).
Immunohistochemistry
TMA sections were cut from each block at 4 μm thick intervals, dewaxed, placed through graded alcohol and placed into water. Antigen retrieval was performed in PT Link (Dako, Glostrup, Denmark) using low pH for PHD1, PHD2 and PHD3 and high pH for HIF-1α, EnVision FLEX Target Retrieval Solution (Dako) for 20 min at 100°C. VEGF required antigen retrieval in pH 8 buffer (20 mM Tris/1 mM EDTA/10 mM sodium citrate) for 2 min in a pressure cooker. Endogenous peroxidase was blocked with EnVision FLEX Peroxidase-Blocking Reagent (Dako) before incubating the sections with respective monoclonal antibodies. PHD1 (112), PHD2 (366G/76), PHD3 (EG188e) and FIH (162c) antibodies were kindly donated by Professor Kevin Gatter, the Nuffield Department, Clinical Laboratory Sciences, John Radcliffe Hospital, Soilleux et al, 2005. Antibodies for VEGF and HIF-1α were purchased from NeoMarkers (Fremont, CA, USA) and BD Transduction Laboratories (Lexington, KY, USA). Antibodies were used at the following concentrations: Neat supernatant for overnight at room temperature for PHD1, PHD2 and PHD3, 1 : 50 for 30 min at room temperature for FIH, 1 : 200 for 30 min at room temperature for VEGF and 1 : 50 overnight at 4°C for HIF-1α. Antigen–antibody complex was detected using Envision FLEX system (EnVision FLEX/HRP and EnVision FLEX DAB+ Chromogen, Dako). All the slides were counterstained with hematoxylin subsequently; they were dehydrated, cleared and mounted for the assessment.
Scoring criteria and cutoffs
Scoring was done according to a previously used semi-quantitative system (Boddy et al, 2005; Soilleux et al, 2005; Tan et al, 2007; Couvelard et al, 2008). HIF-1α was scored only according to the presence (1+) or absence (0) of nuclear expression. For FIH, and all PHDs (both nuclear and cytoplasmic) and VEGF (cytoplasmic only), the intensity was scored as follows: 0, negative; 1, weak; 2, moderate and 3, strong staining. Using a previous defined cutoff which separates the cohort into approximately two groups of equal numbers (Tan et al, 2007, 2008), tumours were considered positive if >10% of tumour cells showed staining at equal or more than moderate staining. The same cutoff was used for VEGF, as previously defined (Martin et al, 2007; Noike et al, 2008).
Statistical analysis
Comparisons were made using either the one-way ANOVA, log rank or χ2-test where appropriate. Kaplan–Meier survival curves were calculated using tumour recurrence (defined as the first re-appearance of tumour at any site following definitive treatment) and cancer-related death as the end points and compared using a log-rank test. Binary logistic regression was used for multivariate analyses and the Cox proportional hazard regression model was used to identify independent prognostic factors for disease-free and overall survival. Analyses were performed with SPSS 16.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). A two-tailed P-value test was used in all analyses and a P-value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Expression of hypoxia pathway members in familial breast cancers
HIF-1α showed predominantly nuclear expression in tumour cells, whereas PHDs and FIH showed both nuclear and cytoplasmic staining as previously reported (Boddy et al, 2005; Soilleux et al, 2005). Staining for VEGF occurred exclusively in the cytoplasm. The range of expression was variable with HIF-1α ranging from heterogeneous weak to strong nuclear staining, whereas all the PHDs, VEGF and FIH generally displayed more homogenous staining although this was of variable intensity (Supplementary Figure 1).
When stratified by BRCA mutation status, HIF-1α positivity was significantly correlated with BRCA1 (23/32, 72%) compared with BRCA2 (12/32, 38%) and BRCAX (20/49, 41%) associated tumours (P=0.008) (Table 3). Cytoplasmic PHD3 positivity was significantly associated with BRCA2 (23/33, 70%) and BRCAX (39/54, 72%) compared with BRCA1 (18/38, 47%) (P=0.037) tumours, but there was no significant difference in expression of cytoplasmic PHD1 and PHD2 within the familial breast cancer groups (P=0.105 and P=0.615, respectively) (Table 3). BRCA1 tumours were more likely to be negative for nuclear FIH, although this did not reach statistical significance (P=0.062). VEGF, nuclear PHDs and cytoplasmic FIH showed no significant difference between the familial groups (P>0.05).
Table 3. Expression of hypoxia markers stratified by familial subtype.
| BRCA1 n (%) | BRCA2 n (%) | BRCAX n (%) | Total n(%) | P-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HIF-1α | |||||
| Negative | 9 (28) | 20 (63) | 29 (59) | 58 (51) | 0.008 |
| Positive | 23 (72) | 12 (38) | 20 (41) | 55 (49) | |
| PHD1 cytoplasmic | |||||
| Negative | 19 (68) | 9 (39) | 14 (48) | 42 (53) | 0.105 |
| Positive | 9 (32) | 14 (61) | 15 (52) | 38 (47) | |
| PHD2 cytoplasmic | |||||
| Negative | 6 (17) | 3 (9) | 6 (12) | 15 (12) | 0.615 |
| Positive | 30 (83) | 30 (91) | 46 (88) | 106 (88) | |
| PHD3 cytoplasmic | |||||
| Negative | 20 (53) | 10 (30) | 15 (28) | 45 (36) | 0.037 |
| Positive | 18 (47) | 23 (70) | 39 (72) | 80 (64) | |
| PHD1 nuclear | |||||
| Negative | 28 (100) | 23 (100) | 29 (100) | 80 (100) | NA |
| Positive | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| PHD2 nuclear | |||||
| Negative | 34 (94) | 27 (81) | 44(84) | 105 (88) | 0.309 |
| Positive | 2 (6) | 6 (19) | 8 (16) | 16 (12) | |
| PHD3 nuclear | |||||
| Negative | 32 (85) | 25 (77) | 36 (67) | 93 (74) | 0.179 |
| Positive | 6 (15 | 8 (23) | 18 (33) | 32 (26) | |
| VEGF | |||||
| Negative | 4 (12) | 3 (9) | 11 (22) | 18 (16) | 0.228 |
| Positive | 31 (88) | 30 (91) | 40 (78) | 101 (84) | |
| FIH cytoplasmic | |||||
| Negative | 19 (53) | 10 (32) | 27 (53) | 56 (47) | 0.143 |
| Positive | 17 (47) | 21 (68) | 24 (47) | 62 (53) | |
| FIH nuclear | |||||
| Negative | 24 (75) | 15 (50) | 37 (73) | 76 (67) | 0.062 |
| Positive | 8 (25) | 15 (50) | 14 (28) | 37 (33) | |
Abbreviation: NA=not applicable.
When familial tumours were stratified by intrinsic phenotypes based on Nielsen et al (2004), cytoplasmic PHD3 negativity was significantly associated with a basal phenotype (19/37, 51%) compared with luminal phenotype (39/49, 80%) (P=0.037) (Table 4a). Similarly, nuclear FIH negativity was also associated with basal phenotype (30/36, 83%) compared with luminal phenotype (25/46, 59%) (P=0.011) (Table 4b). In contrast, HIF-1α positivity was significantly associated with basal (27/36, 75%) compared with luminal phenotype (14/47, 30%) (P=0.001) (Table 4c). Other hypoxia pathway members examined showed no significant differences in expression between the phenotypes (P>0.05).
Table 4. (A) Cytoplasmic PHD3 expression stratified by intrinsic phenotypes in familial breast cancer (P=0.037). (B) Nuclear FIH expression stratified by intrinsic phenotypes in familial breast cancer (P=0.011). (C) HIF-1α expression stratified by intrinsic phenotypes in familial breast cancer (P=0.001).
| Luminal n (%) | Basal n (%) | HER2 n (%) | Null n (%) | Total (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (A) | |||||
| Negative | 10 (20) | 18 (49) | 1 (17) | 2 (29) | 31 (31) |
| Positive | 39 (80) | 19 (51) | 5 (83) | 5 (71) | 68 (69) |
| Total | 49 | 37 | 6 | 7 | 99 |
| (B) | |||||
| Negative | 25 (54) | 30 (83) | 6 (100) | 4 (57) | 65 (68) |
| Positive | 21 (46) | 6 (17) | (0) | 3 (43) | 46 (30) |
| Total | 46 | 36 | 6 | 6 | 95 |
| (C) | |||||
| Negative | 33 (70) | 9 (25) | 4 (67) | 3 (50) | 49 (52) |
| Positive | 14 (30) | 27 (75) | 2 (33) | 3 (50) | 46 (48) |
| Total | 47 | 36 | 6 | 6 | 95 |
Expression of hypoxia factors between familial and sporadic breast cancers
The expression of cytoplasmic PHD2 (106/121, 88%), cytoplasmic PHD3 (80/125, 64%) and VEGF (101/119, 84%) was significantly associated with familial breast cancers as a combined group compared with sporadic cancers (cytoplasmic PHD2 (65/165, 39%), cytoplasmic PHD3 (65/165, 39%), VEGF (92/182, 51%)) (all P<0.001). In contrast both nuclear and cytoplasmic FIH expression were significantly correlated with sporadic (133/179, 74 and 114/179, 64%) compared with familial cancers (62/118, 53 and 39/118, 33%) (both P<0.001). There was no significant difference in HIF-1α, cytoplasmic PHD1 and nuclear PHD1-3 expression between familial and sporadic cancers (both P>0.05).
Correlation of hypoxia factors with clinicopathological parameters in familial breast cancers
HIF-1α expression correlated with high tumour grade (P=0.009), negative oestrogen receptor-α (ER) status (P=0.001) and the absence of lymph node metastasis (P=0.028) (Table 5). On multivariate analysis using binary logistic regression, including grade, size, lymph node, HER2 and ER status, only negative ER significantly correlated with HIF-1α expression (P=0.039, Hazard ratio=0.289, 95% CI for hazard ratio 0.089–0.941).
Table 5. Contingency table of hypoxia-induced factors and clinicopathological parameters in familial breast cancer.
|
HIF-1α
|
Cytoplasmic PHD1
|
Cytoplasmic PHD2
|
Cytoplasmic PHD3
|
VEGF
|
Cytoplasmic FIH
|
Nuclear FIH
|
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neg (%) | Pos (%) | Neg (%) | Pos (%) | Neg (%) | Pos (%) | Neg (%) | Pos (%) | Neg (%) | Pos (%) | Neg (%) | Pos (%) | Neg (%) | Pos (%) | |
| Size (mm) | ||||||||||||||
| <20 | 31 (61%) | 33 (61%) | 26 (67%) | 13 (36%) | 9(60%) | 57 (59%) | 30 (73%) | 40 (53%) | 13 (81%) | 56 (59%) | 34 (67%) | 29 (50) | 43 (59%) | 21 (61%) |
| ⩾20 | 20 (39%) | 21 (39%) | 13 (33%) | 23 (64%) | 6 (40%) | 40 (41%) | 11 (27%) | 35 (47%) | 3 (19%) | 26 (39%) | 17 (33%) | 29 (50) | 30 (41%) | 11 (34%) |
| P-value | 0.973 | 0.008 | 0.928 | 0.037 | 0.089 | 0.079 | 0.516 | |||||||
| Grade | ||||||||||||||
| 1/2 | 23 (48%) | 11 (22%) | 9 (25%) | 13 (41%) | 4 (31%) | 32 (36%) | 9 (24%) | 28 (41%) | 3 (25%) | 32 (36%) | 10 (22%) | 22 (41.5) | 20 (31%) | 13 (42%) |
| 3 | 25 (52%) | 38 (78%) | 27 (75%) | 19 (59%) | 9 (69%) | 58 (64%) | 28 (76%) | 41 (595) | 9 (75%) | 57 (64%) | 36 (78%) | 31 (58.5) | 45 (69%) | 18 (58%) |
| P-value | 0.009 | 0.169 | 0.735 | 0.094 | 0.454 | 0.036 | 0.281 | |||||||
| ER | ||||||||||||||
| Neg | 14 (26%) | 31 (62%) | 20 (54%) | 12 (35%) | 6 (55%) | 40 (41%) | 22 (58%) | 27 (37%) | 6 (38%) | 38 (43%) | 27 (55%) | 19 (33.9) | 36 (53%) | 10 (29%) |
| Pos | 39 (74%) | 19 (38%) | 17 (46%) | 22 (65%) | 5 (45%) | 57 (59%) | 16 (42%) | 46 (63%) | 10 (62%) | 51 (57%) | 22 (45%) | 37 (66.1) | 32 (47%) | 24 (71%) |
| P-value | 0.001 | 0.112 | 0.398 | 0.035 | 0.698 | 0.029 | 0.024 | |||||||
| Lymph nodes | ||||||||||||||
| Neg | 38 (66%) | 46 (84%) | 35 (83%) | 25 (66%) | 10 (67%) | 81 (76%) | 37 (82%) | 55 (69%) | 44 (80%) | 16 (89%) | 73 (72%) | 44 (71.0) | 55 (72%) | 30 (82%) |
| Pos | 20 (35%) | 9 (16%) | 7 (17%) | 13 (34%) | 5 (33%) | 25 (24%) | 8 (18%) | 25 (31%) | 11 (20%) | 2 (11%) | 28 (28%) | 18 (29.0) | 21 (28%) | 7 (19%) |
| P-value | 0.028 | 0.070 | 0.413 | 0.101 | 0.135 | 0.344 | 0.314 | |||||||
Abbreviations: ER=estrogen receptor; Neg=negative; Pos=positive.
Cytoplasmic FIH expression correlated with positive ER (P=0.029) and lower tumour grade (P=0.036) (Table 5). The correlation between cytoplasmic FIH expression and lower grade was confirmed on multivariate analysis including size, lymph node, HER2 and ER status (P=0.024, Hazard ratio=0.273 and 95% CI for hazard ratio 0.089–0.840). Nuclear FIH also correlated with positive ER (P=0.024).
Cytoplasmic PHD1 correlated with tumour size (P=0.008), whereas cytoplasmic PHD3 correlated with tumour size (P=0.037) and ER expression (P=0.035). Cytoplasmic PHD2, nuclear PHD1-3 and VEGF did not show any significant association with any of the clinicopathological parameters.
Survival analysis in familial breast cancers
When familial cancers were assessed as a combined group, there was no significant correlation in relapse-free or overall survival with hypoxia factors HIF-1α, FIH, VEGF and all PHDs (P>0.05).
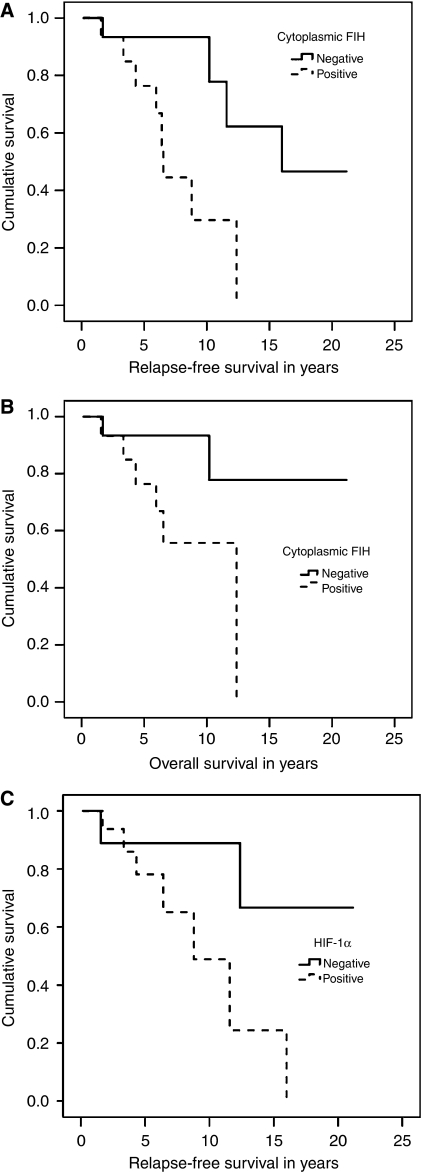
However, when BRCA1 cancers were assessed as a separate group, cytoplasmic FIH correlated with shorter relapse-free (P=0.007) (Figure 1A) and overall survival (P=0.026) (Figure 1B). No such differences in disease-free or overall survival were seen for nuclear FIH (P>0.05). BRCA1 tumours with HIF-1α expression was associated with a shorter relapse-free (P=0.049) (Figure 1C) but not overall survival (P=0.764). There was a trend for cytoplasmic PHD1-positive tumours with BRCAX mutation to be associated with a shorter relapse-free survival, although this did not reach statistical significance (P=0.058). For BRCA2 tumours there was no significant correlation present between survival and expression of hypoxia-induced factors (P>0.05).
Figure 1.
(A) Kaplan–Meier curve of relapse-free survival of BRCA1 tumours stratified by cytoplasmic FIH (P=0.007, n=35). (B) Kaplan–Meier curve of overall survival of BRCA1 tumours stratified by cytoplasmic FIH (P=0.026, n=35). (C) Kaplan–Meier curve of relapse-free survival of BRCA1 tumours stratified by HIF-1α (P=0.049, n=31).
Discussion
Hypoxia is the result of an imbalance between oxygen delivery and oxygen consumption resulting in the reduction of oxygen tension below the normal level for a specific tissue (Lundgren et al, 2007). Hypoxia occurs in many disease processes, and it is widespread in solid tumours because of the tumour outgrowing the existing vasculature. Hypoxia is associated with aggressive behaviour, metastasis and lower survival (Harris, 2002). Central to the hypoxic response is the transcription factor HIF. We have therefore examined the role of the key pathway members regulating HIF-mediated transcription including HIF-1α, PHD1, PHD2, PHD3, VEGF and FIH in a series of familial breast cancers stratified by BRCA status and intrinsic phenotypes.
In this study, we have shown frequent expression of HIF-1α in the neoplastic cells of BRCA1-related breast cancer and basal-like cancers (72 and 75%, respectively) of tumours being positive. This is in accordance with 90% positivity in a small series of 30 patients with BRCA1 mutation (van der Groep et al, 2008) and our previous findings where basal-like breast cancers have an enhanced hypoxic drive and aggressive behaviour (Tan, 2008). The observation in this study of a positive association of HIF-1α with high tumour grade and relapse-free survival supports a similarly upregulated hypoxic response in BRCA1/basal like cancers. Furthermore, it may also partly account for the increased genomic instability described in BRCA1-associated tumours (Cheng and Loeb, 1993; Sutherland, 1998; Semenza, 2000; Chan et al, 2008).
Our findings also support the role of hypoxia and HIF-1α in the downregulation of ERα expression in familial cancers. In a multivariate analysis, HIF-1α was the only independent variable, which predicted ERα negativity. This is consistent with cell culture studies where intermittent hypoxia induces proteasome-dependent downregulation of ERα (Kurebayashi et al, 2001; Cooper et al, 2004; Yi et al, 2009). This is also supported by immunohistochemical studies on ERα-positive tumours where the geographic distribution of CAIX, a surrogate marker of hypoxia, corresponds to areas of tumour negative for ERα (Cooper et al, 2004). This sequence may enhance the proposed role of BRCA1 in regulating ERα expression in BRCA1 and basal like cancers (Gorski et al, 2009).
One potential mechanism of retaining elevated HIF-1α in both BRCA1 and basal-like may be the relative paucity of PHD3, which showed significantly lower expression in BRCA1 tumours. Under normal conditions, BRCA1 interacts with STAT1 to activate the transcription of IFN-γ target genes (Ouchi et al, 2000). In the hypoxic state, this pathway selectively induces PHD3, but not PHD1 or PHD2 mRNA and protein expression (Gerber et al, 2009). Thus, the loss of PHD3 expression induced by the BRCA1/STAT dysfunction may be a mechanism specific to BRCA1 tumours. Furthermore, hypoxia in basal type/BRCA1 tumours may lead to the preferential degradation of PHD3. The lack of an N-terminal extension in PHD3, which is found in PHD1 and PHD2, renders it more susceptible to degradation by RING finger E3 ligase Siah2 in low oxygen tensions (Nakayama et al, 2007). The absence of a prolyl hyrdoxylase may allow the escape of HIF degradation even in the presence of molecular oxygen. This is because significant effects on HIF occur even when the impact of suppression of a single PHD on the total level of PHD protein is only modest (Appelhoff et al, 2004). Indeed, PHD3 has been shown to have major effects on HIF, with its loss substantially prolonging the half-life of HIF-1α (Appelhoff et al, 2004).
In the normoxic state PHD2 is the main cellular oxygen sensor (Berra et al, 2003; Berchner-Pfannschmidt et al, 2008). Berra et al (2003) showed that under normoxic conditions, siRNA inhibition of PHD2, but not PHD1 or PHD3 resulted in the stabilisation of HIF-1α. Interestingly, the same author found PHD2 was upregulated by hypoxia, suggesting changes in PHD2 levels were not responsible for HIF-1α stabilisation under low oxygen tensions. This is supported by our study of BRCA1 tumours, where upregulation of HIF-1α was not associated with changes in PHD2 expression.
In the present study, the intracellular location of FIH appears to have an important role in HIF-1α regulation and prognosis, with BRCA1 and familial basal type cancers being negative for nuclear FIH and positive for HIF-1α. In addition, cytoplasmic FIH appears as a prognostic marker in BRCA1 breast tumours conferring a shorter relapse-free and overall survival, despite its association with a lower grade, whereas no such differences are seen for nuclear FIH. This is in keeping with our previous studies where cytoplasmic FIH expression correlated with a poorer prognosis (Tan et al, 2007). These findings do not appear to be due to nuclear staining being more difficult to appreciate in the presence of strong cytoplasmic staining, as there was a positive correlation between nuclear and cytoplasmic FIH (Spearman r=0.318, P<0.001). FIH inhibits HIF-1α activity by hydroxylating the asparagine residue 803, thereby preventing HIF-1α from interacting with co-factor p300 (Lando et al, 2002). This effect may be exclusively mediated by FIH located in the nucleus. Translocation of FIH into the cytoplasm may be a mechanism by which BRCA1 and basal-type tumours escape inhibition of HIF-1α activity.
Our findings suggest the aggressive nature of BRCA1, basal-type tumours may be partly explained by an enhanced hypoxic drive and hypoxia-driven ER degradation, due to suppressed PHD and aberrantly located FIH expression. This may have important treatment implications, as these aggressive tumours may respond to compounds directed against HIF-1α or its downstream targets (Lundgren et al, 2007; Milani and Harris, 2008). Of particular interest include agents targeting FIH because, unlike the prolyl hydroxlases, it retains its activity across a wide range of oxygen tensions (Stolze et al, 2004; Dayan et al, 2006). This is supported by studies suggesting hypoxic tumours may respond to Bortezomib (Shin et al, 2008) and Amphotericin B (Yeo et al, 2006), which suppress HIF-1α activity by re-enforcing FIH-mediated inhibition of p300 recruitment.
Acknowledgments
We thank Heather Thorne, Eveline Niedermayr, all the kConFab research nurses and staff, the heads and staff of the Family Cancer Clinics, and the Clinical Follow Up Study (funded by NHMRC Grants 145684, 288704 and 454508) for their contributions to this resource, and the many families who contribute to kConFab. kConFab is supported by grants from the National Breast Cancer Foundation, the National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC) and by the Queensland Cancer Fund, the Cancer Councils of New South Wales, Victoria, Tasmania and South Australia, and the Cancer Foundation of Western Australia. This study was partly funded by the Victorian Breast Research Consortium and the Victorian Cancer Biobank, Australia.
Footnotes
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on British Journal of Cancer website (http://www.nature.com/bjc)
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Supplementary Material
References
- Antoniou A, Pharoah PD, Narod S, Risch HA, Eyfjord JE, Hopper JL, Loman N, Olsson H, Johannsson O, Borg A, Pasini B, Radice P, Manoukian S, Eccles DM, Tang N, Olah E, Anton-Culver H, Warner E, Lubinski J, Gronwald J, Gorski B, Tulinius H, Thorlacius S, Eerola H, Nevanlinna H, Syrjakoski K, Kallioniemi OP, Thompson D, Evans C, Peto J, Lalloo F, Evans DG, Easton DF (2003) Average risks of breast and ovarian cancer associated with BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations detected in case Series unselected for family history: a combined analysis of 22 studies. Am J Hum Genet 72: 1117–1130 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appelhoff RJ, Tian YM, Raval RR, Turley H, Harris AL, Pugh CW, Ratcliffe PJ, Gleadle JM (2004) Differential function of the prolyl hydroxylases PHD1, PHD2, and PHD3 in the regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor. J Biol Chem 279: 38458–38465 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armes JE, Egan AJ, Southey MC, Dite GS, McCredie MR, Giles GG, Hopper JL, Venter DJ (1998) The histologic phenotypes of breast carcinoma occurring before age 40 years in women with and without BRCA1 or BRCA2 germline mutations: a population-based study. Cancer 83: 2335–2345 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berchner-Pfannschmidt U, Tug S, Trinidad B, Oehme F, Yamac H, Wotzlaw C, Flamme I, Fandrey J (2008) Nuclear oxygen sensing: induction of endogenous prolyl-hydroxylase 2 activity by hypoxia and nitric oxide. J Biol Chem 283: 31745–31753 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berra E, Benizri E, Ginouves A, Volmat V, Roux D, Pouyssegur J (2003) HIF prolyl-hydroxylase 2 is the key oxygen sensor setting low steady-state levels of HIF-1alpha in normoxia. EMBO J 22: 4082–4090 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boddy JL, Fox SB, Han C, Campo L, Turley H, Kanga S, Malone PR, Harris AL (2005) The androgen receptor is significantly associated with vascular endothelial growth factor and hypoxia sensing via hypoxia-inducible factors HIF-1a, HIF-2a, and the prolyl hydroxylases in human prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res 11: 7658–7663 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bos R, van der Groep P, Greijer AE, Shvarts A, Meijer S, Pinedo HM, Semenza GL, van Diest PJ, van der Wall E (2003) Levels of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha independently predict prognosis in patients with lymph node negative breast carcinoma. Cancer 97: 1573–1581 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan N, Koritzinsky M, Zhao H, Bindra R, Glazer PM, Powell S, Belmaaza A, Wouters B, Bristow RG (2008) Chronic hypoxia decreases synthesis of homologous recombination proteins to offset chemoresistance and radioresistance. Cancer Res 68: 605–614 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng KC, Loeb LA (1993) Genomic instability and tumor progression: mechanistic considerations. Adv Cancer Res 60: 121–156 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper C, Liu GY, Niu YL, Santos S, Murphy LC, Watson PH (2004) Intermittent hypoxia induces proteasome-dependent down-regulation of estrogen receptor alpha in human breast carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 10: 8720–8727 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couvelard A, Deschamps L, Rebours V, Sauvanet A, Gatter K, Pezzella F, Ruszniewski P, Bedossa P (2008) Overexpression of the oxygen sensors PHD-1, PHD-2, PHD-3, and FIH Is associated with tumor aggressiveness in pancreatic endocrine tumors. Clin Cancer Res 14: 6634–6639 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayan F, Roux D, Brahimi-Horn MC, Pouyssegur J, Mazure NM (2006) The oxygen sensor factor-inhibiting hypoxia-inducible factor-1 controls expression of distinct genes through the bifunctional transcriptional character of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha. Cancer Res 66: 3688–3698 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Generali D, Berruti A, Brizzi MP, Campo L, Bonardi S, Wigfield S, Bersiga A, Allevi G, Milani M, Aguggini S, Gandolfi V, Dogliotti L, Bottini A, Harris AL, Fox SB (2006) Hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha expression predicts a poor response to primary chemoendocrine therapy and disease-free survival in primary human breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 12: 4562–4568 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber SA, Yatsula B, Maier CL, Sadler TJ, Whittaker LW, Pober JS (2009) Interferon-gamma induces Prolyl Hydroxylase (PHD)3 through a STAT1-dependent mechanism in human endothelial cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol published online Jul; 2: 2009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorski JJ, Kennedy RD, Hosey AM, Harkin DP (2009) The complex relationship between BRCA1 and ER{alpha} in hereditary breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 15: 1514–1518 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris AL (2002) Hypoxia--a key regulatory factor in tumour growth. Nat Rev Cancer 2: 38–47 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang LE, Gu J, Schau M, Bunn HF (1998) Regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha is mediated by an O2-dependent degradation domain via the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 7987–7992 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacquemier J, Padovani L, Rabayrol L, Lakhani SR, Penault-Llorca F, Denoux Y, Fiche M, Figueiro P, Maisongrosse V, Ledoussal V, Martinez Penuela J, Udvarhely N, El Makdissi G, Ginestier C, Geneix J, Charafe-Jauffret E, Xerri L, Eisinger F, Birnbaum D, Sobol H (2005) Typical medullary breast carcinomas have a basal/myoepithelial phenotype. J Pathol 207: 260–268 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonsson G, Naylor TL, Vallon-Christersson J, Staaf J, Huang J, Ward MR, Greshock JD, Luts L, Olsson H, Rahman N, Stratton M, Ringner M, Borg A, Weber BL (2005) Distinct genomic profiles in hereditary breast tumors identified by array-based comparative genomic hybridization. Cancer Res 65: 7612–7621 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurebayashi J, Otsuki T, Moriya T, Sonoo H (2001) Hypoxia reduces hormone responsiveness of human breast cancer cells. Jpn J Cancer Res 92: 1093–1101 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laakso M, Loman N, Borg A, Isola J (2005) Cytokeratin 5/14-positive breast cancer: true basal phenotype confined to BRCA1 tumors. Mod Pathol 18: 1321–1328 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lakhani SR, Gusterson BA, Jacquemier J, Sloane JP, Anderson TJ, van de Vijver MJ, Venter D, Freeman A, Antoniou A, McGuffog L, Smyth E, Steel CM, Haites N, Scott RJ, Goldgar D, Neuhausen S, Daly PA, Ormiston W, McManus R, Scherneck S, Ponder BA, Futreal PA, Peto J, Stoppa-Lyonnet D, Bignon YJ, Stratton MR (2000) The pathology of familial breast cancer: histological features of cancers in families not attributable to mutations in BRCA1 or BRCA2. Clin Cancer Res 6: 782–789 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lakhani SR, Reis-Filho JS, Fulford L, Penault-Llorca F, van der Vijver M, Parry S, Bishop T, Benitez J, Rivas C, Bignon YJ, Chang-Claude J, Hamann U, Cornelisse CJ, Devilee P, Beckmann MW, Nestle-Kramling C, Daly PA, Haites N, Varley J, Lalloo F, Evans G, Maugard C, Meijers-Heijboer H, Klijn JG, Olah E, Gusterson BA, Pilotti S, Radice P, Scherneck S, Sobol H, Jacquemier J, Wagner T, Peto J, Stratton MR, McGuffog L, Easton DF (2005) Prediction of BRCA1 status in patients with breast cancer using estrogen receptor and basal phenotype. Clin Cancer Res 11: 5175–5180 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lando D, Peet DJ, Gorman JJ, Whelan DA, Whitelaw ML, Bruick RK (2002) FIH-1 is an asparaginyl hydroxylase enzyme that regulates the transcriptional activity of hypoxia-inducible factor. Genes Dev 16: 1466–1471 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundgren K, Holm C, Landberg G (2007) Hypoxia and breast cancer: prognostic and therapeutic implications. Cell Mol Life Sci 64: 3233–3247 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin SG, Orridge C, Mukherjee A, Morgan DA (2007) Vascular endothelial growth factor expression predicts outcome after primary radiotherapy for head and neck squamous cell cancer. Clin Oncol (Royal College of Radiologists (Great Britain)) 19: 71–76 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McShane LM, Altman DG, Sauerbrei W, Taube SE, Gion M, Clark GM (2005) Reporting Recommendations for Tumor Marker Prognostic Studies. J Clin Oncol 23: 9067–9072 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milani M, Harris AL (2008) Targeting tumour hypoxia in breast cancer. Eur J Cancer 44: 2766–2773 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama K, Gazdoiu S, Abraham R, Pan ZQ, Ronai Z (2007) Hypoxia-induced assembly of prolyl hydroxylase PHD3 into complexes: implications for its activity and susceptibility for degradation by the E3 ligase Siah2. Biochem J 401: 217–226 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen TO, Hsu FD, Jensen K, Cheang M, Karaca G, Hu Z, Hernandez-Boussard T, Livasy C, Cowan D, Dressler L, Akslen LA, Ragaz J, Gown AM, Gilks CB, van de Rijn M, Perou CM (2004) Immunohistochemical and clinical characterization of the basal-like subtype of invasive breast carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 10: 5367–5374 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noike T, Miwa S, Soeda J, Kobayashi A, Miyagawa S (2008) Increased expression of thioredoxin-1, vascular endothelial growth factor, and redox factor-1 is associated with poor prognosis in patients with liver metastasis from colorectal cancer. Hum Pathol 39: 201–208 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ouchi T, Lee SW, Ouchi M, Aaronson SA, Horvath CM (2000) Collaboration of signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 (STAT1) and BRCA1 in differential regulation of IFN-gamma target genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97: 5208–5213 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palacios J, Honrado E, Osorio A, Cazorla A, Sarrio D, Barroso A, Rodriguez S, Cigudosa JC, Diez O, Alonso C, Lerma E, Dopazo J, Rivas C, Benitez J (2005) Phenotypic characterization of BRCA1 and BRCA2 tumors based in a tissue microarray study with 37 immunohistochemical markers. Breast Cancer Res Treat 90: 5–14 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palacios J, Honrado E, Osorio A, Cazorla A, Sarrio D, Barroso A, Rodriguez S, Cigudosa JC, Diez O, Alonso C, Lerma E, Sanchez L, Rivas C, Benitez J (2003) Immunohistochemical characteristics defined by tissue microarray of hereditary breast cancer not attributable to BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations: differences from breast carcinomas arising in BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation carriers. Clin Cancer Res 9: 3606–3614 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salceda S, Caro J (1997) Hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha (HIF-1alpha) protein is rapidly degraded by the ubiquitin-proteasome system under normoxic conditions. Its stabilization by hypoxia depends on redox-induced changes. J Biol Chem 272: 22642–22647 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semenza GL (2000) Hypoxia, clonal selection, and the role of HIF-1 in tumor progression. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 35: 71–103 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sensi E, Tancredi M, Aretini P, Cipollini G, Naccarato AG, Viacava P, Bevilacqua G, Caligo MA (2003) p53 inactivation is a rare event in familial breast tumors negative for BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations. Breast Cancer Res Treat 82: 1–9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shin DH, Chun YS, Lee DS, Huang LE, Park JW (2008) Bortezomib inhibits tumor adaptation to hypoxia by stimulating the FIH-mediated repression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1. Blood 111: 3131–3136 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soilleux EJ, Turley H, Tian YM, Pugh CW, Gatter KC, Harris AL (2005) Use of novel monoclonal antibodies to determine the expression and distribution of the hypoxia regulatory factors PHD-1, PHD-2, PHD-3 and FIH in normal and neoplastic human tissues. Histopathology 47: 602–610 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stolze IP, Tian YM, Appelhoff RJ, Turley H, Wykoff CC, Gleadle JM, Ratcliffe PJ (2004) Genetic analysis of the role of the asparaginyl hydroxylase factor inhibiting hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) in regulating HIF transcriptional target genes. J Biol Chem 279: 42719–42725 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland RM (1998) Tumor hypoxia and gene expression--implications for malignant progression and therapy. Acta Oncol (Stockholm, Sweden) 37: 567–574 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan EY, Campo L, Han C, Turley H, Pezzella F, Gatter KC, Harris AL, Fox SB (2007) Cytoplasmic location of factor-inhibiting hypoxia-inducible factor is associated with an enhanced hypoxic response and a shorter survival in invasive breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res 9: R89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan EY, Yan M, Campo L, Han C, Takano E, Turley H, Candiloro I, Pezzella F, Gatter KC, Millar EK, O'Toole SA, McNeil CM, Crea P, Segara D, Sutherland RL, Harris AL, Fox SB (2008) The key hypoxia regulated gene CAIX is upregulated in basal-like breast tumours and is associated with resistance to chemotherapy. Br J Cancer 2009; 100: 405–411 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Groep P, Bouter A, Menko FH, van der Wall E, van Diest PJ (2008) High frequency of HIF-1alpha overexpression in BRCA1 related breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 111: 475–480 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaupel P (2004) The role of hypoxia-induced factors in tumor progression. Oncologist 9(Suppl 5): 10–17 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeo EJ, Ryu JH, Cho YS, Chun YS, Huang LE, Kim MS, Park JW (2006) Amphotericin B blunts erythropoietin response to hypoxia by reinforcing FIH-mediated repression of HIF-1. Blood 107: 916–923 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yi JM, Kwon HY, Cho JY, Lee YJ (2009) Estrogen and hypoxia regulate estrogen receptor alpha in a synergistic manner. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 378: 842–846 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.