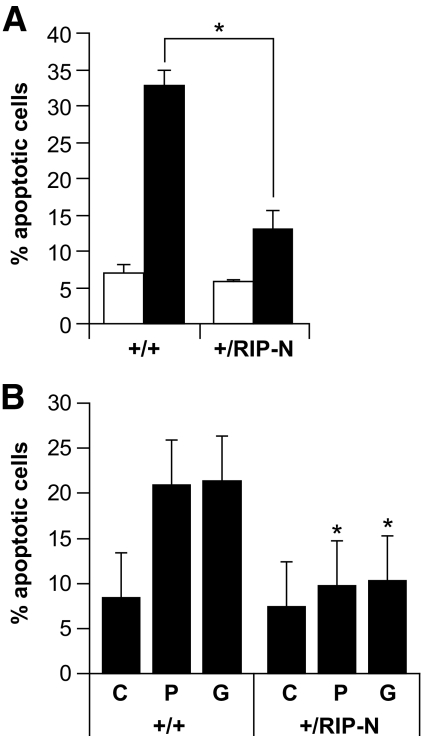
FIG. 4.
RIP-N islet cells are more resistant to stress-induced apoptosis. A: Freshly isolated islets were loosely dissociated (see research design and methods) and incubated or not with inflammatory cytokines (1,000 units/ml TNF-α, 1,000 units/ml interleukin-1β, and 50 units/ml interferon-γ) for an additional 24-h period. The islets were then stained with Hoechst 33342 and apoptosis scored. The results correspond to the means ± SD of three independent experiments (statistic analyses were performed for the control and stimulated conditions between wild-type and RIP-N mice [two comparisons]). □, Control; ■, cytokines. B: Freshly isolated islets were loosely dissociated and treated with vehicle (C; ethanol 1%) or incubated during 72 h with 1 mmol/l palmitate (P) or 33 mmol/l glucose (G). Apoptosis was then assessed as above. The results correspond to the means ± SD of three independent experiments (statistic analysis was performed for each condition between wild-type and RIP-N mice [three comparisons]). * indicates a statistically significant difference as described in the research design and methods section.