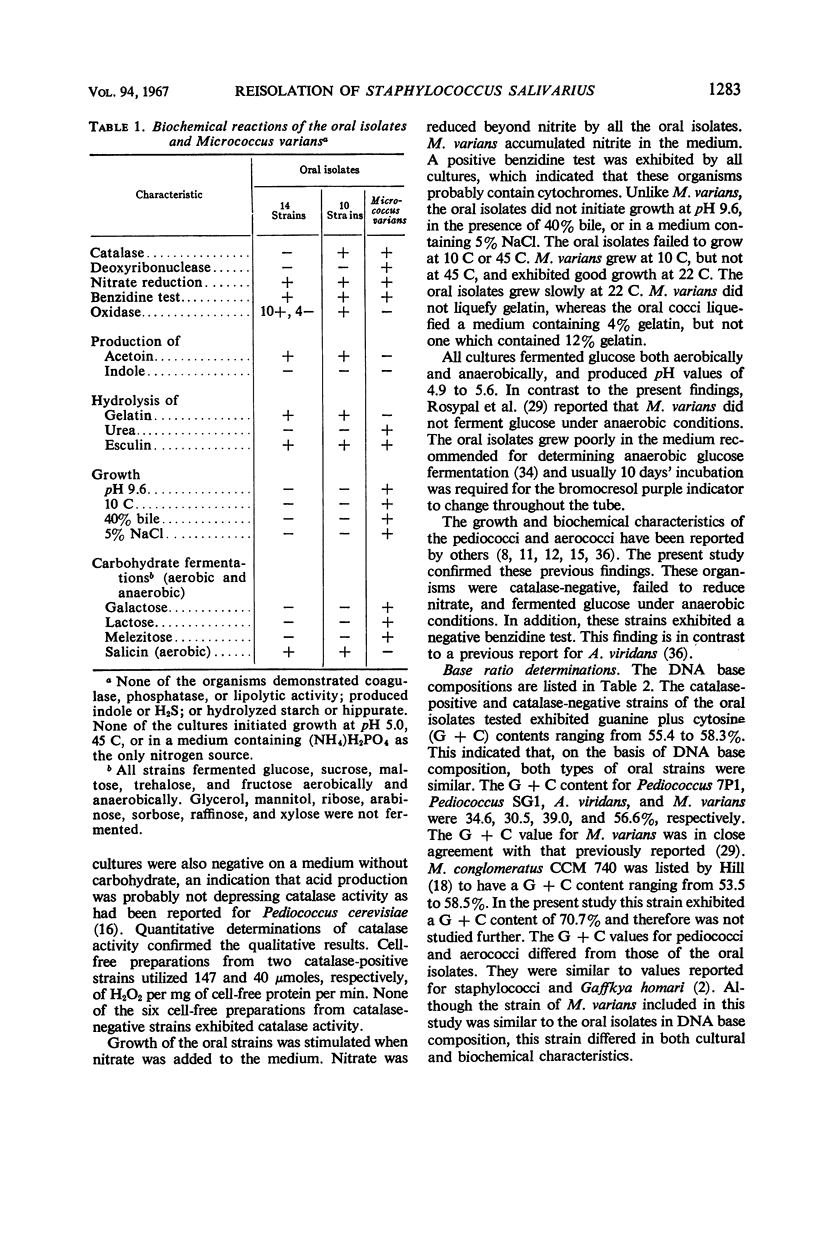
Abstract
Twenty-four strains of gram-positive facultative cocci, arranged primarily in small clusters, were isolated from the surface of the human tongue. With the exception of 14 catalase-negative isolates, these strains were identical in cultural and biochemical characteristics and in deoxyribonucleic acid base composition. All cultures produced viscous growth in both liquid and agar media. They fermented glucose anaerobically, reduced nitrate beyond nitrite, were benzidine-positive, and failed to grow in the presence of 5% NaCl or at 45 C. In addition, they exhibited guanine plus cytosine (G + C) contents of 55.4 to 58.3%. These isolates differed from strains of pediococci, aerococci, and micrococci which were included for comparison. On the basis of G + C content, these organisms appear to be intermediate between micrococci and staphylococci; however, on the basis of anaerobic glucose fermentation, it is suggested that they be placed in the genus Staphylococcus. It is proposed that they be recognized as S. salivarius.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auletta A. E., Kennedy E. R. Deoxyribonucleic acid base composition of some members of the Micrococcaceae. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jul;92(1):28–34. doi: 10.1002/path.1700920103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAIRD-PARKER A. C. A classification of micrococci and staphylococci based on physiological and biochemical tests. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Mar;30:409–427. doi: 10.1099/00221287-30-3-409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAIRD-PARKER A. C. THE CLASSIFICATION OF STAPHYLOCOCCI AND MICROCOCCI FROM WORLD-WIDE SOURCES. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Mar;38:363–387. doi: 10.1099/00221287-38-3-363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLAUSEN O. G. THE DISCOVERY, ISOLATION, AND CLASSIFICATION OF VARIOUS ALPHA-HAEMOLYTIC MICROCOCCI WHICH RESEMBLE AEROCOCCI. J Gen Microbiol. 1964 Apr;35:1–8. doi: 10.1099/00221287-35-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COWAN S. T., STEEL K. L. COMPARISON OF DIFFERENTIATING CRITERIA FOR STAPHYLOCOCCI AND MICROCOCCI. J Bacteriol. 1964 Sep;88:804–805. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.3.804-805.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEIBEL R. H., EVANS J. B. Modified benzidine test for the detection of cytochrome-containing respiratory systems in microorganisms. J Bacteriol. 1960 Mar;79:356–360. doi: 10.1128/jb.79.3.356-360.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEIBEL R. H., NIVEN C. F., Jr Comparative study of Gaffkya homari, Aerococcus viridans, tetrad-forming cocci from meat curing brines, and the genus Pediococcus. J Bacteriol. 1960 Feb;79:175–180. doi: 10.1128/jb.79.2.175-180.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEIBEL R. H., SILLIKER J. H., FAGAN P. T. SOME CHARACTERISTICS OF AN OLEATE-REQUIRING, HEMOLYTIC PEDIOCOCCUS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Oct;88:1078–1083. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.4.1078-1083.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUNTHER H. L., WHITE H. R. The cultural and physiological characters of the Pediococci. J Gen Microbiol. 1961 Oct;26:185–197. doi: 10.1099/00221287-26-2-185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUTEKUNST R. R., DELWICHE E. A., SEELEY H. W. Catalase activity in Pediococcus cerevisiae as related to hydrogen ion activity. J Bacteriol. 1957 Nov;74(5):693–695. doi: 10.1128/jb.74.5.693-695.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon D. F., Jr, Gibbons R. J. Studies of the predominant cultivable micro-organisms from the human tongue. Arch Oral Biol. 1966 Jun;11(6):627–632. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(66)90229-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill L. R. An index to deoxyribonucleic acid base compositions of bacterial species. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 Sep;44(3):419–437. doi: 10.1099/00221287-44-3-419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JONES D., DEIBEL R. H., NIVEN C. F., Jr Identity of Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jan;85:62–67. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.1.62-67.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOVACS N. Identification of Pseudomonas pyocyanea by the oxidase reaction. Nature. 1956 Sep 29;178(4535):703–703. doi: 10.1038/178703a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARMUR J., DOTY P. Determination of the base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid from its thermal denaturation temperature. J Mol Biol. 1962 Jul;5:109–118. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosypal S., Rosypalová A., Horejs J. The classification of micrococci and staphylococci based on their DNA base composition and adansonian analysis. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 Aug;44(2):281–292. doi: 10.1099/00221287-44-2-281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silvestri L. G., Hill L. R. Agreement Between Deoxyribonucleic Acid Base Composition and Taxometric Classification of Gram-Positive Cocci. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jul;90(1):136–140. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.1.136-140.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims W. The isolation of pediococci from human saliva. Arch Oral Biol. 1966 Oct;11(10):967–972. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(66)90198-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAPLIN J., GOLDSWORTHY N. E. A study of 225 strains of Staphylococcus isolated from the mouth. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1958 Aug;36(4):289–304. doi: 10.1038/icb.1958.32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMS R. E., HIRCH A., COWAN S. T. Aerococcus, a new bacterial genus. J Gen Microbiol. 1953 Jun;8(3):475–480. doi: 10.1099/00221287-8-3-475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


