Abstract
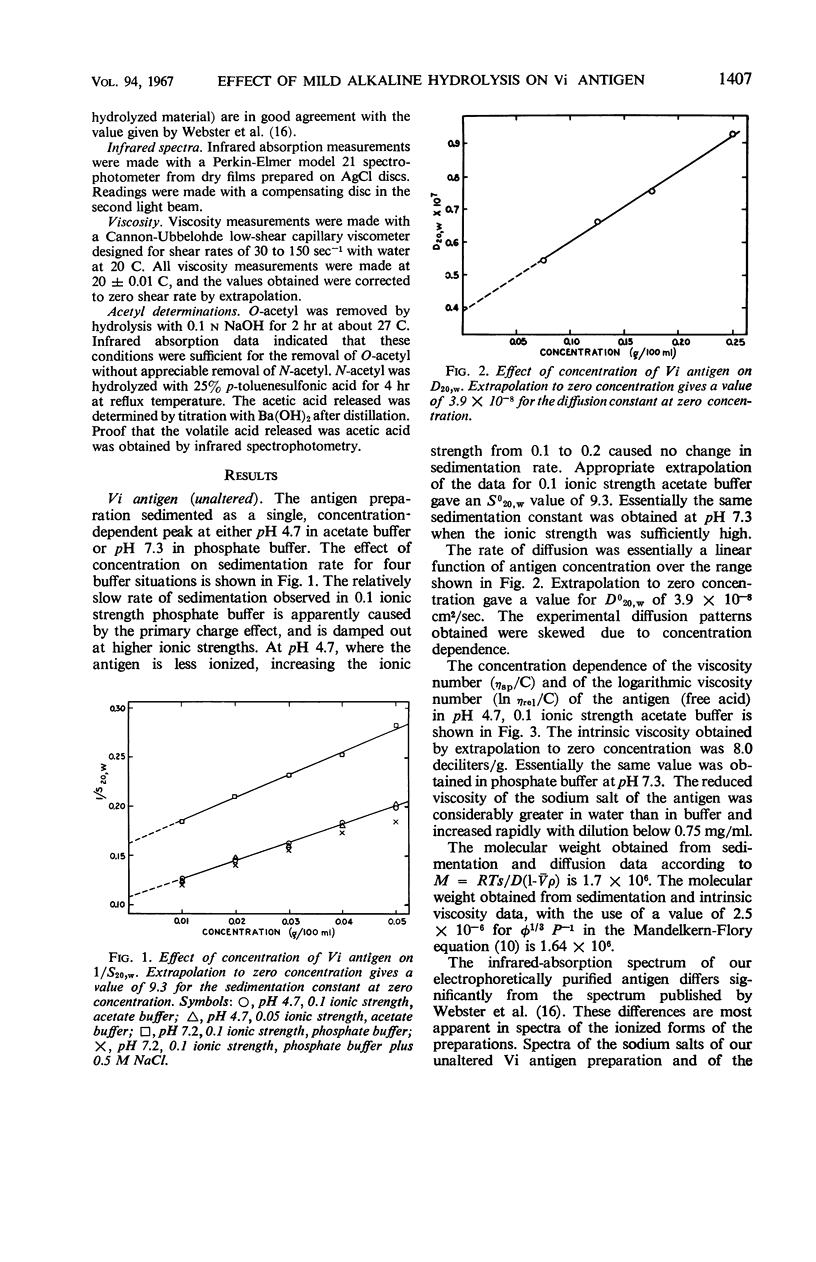
Sedimentation and diffusion constants were determined for electrophoretically purified Vi antigen before and after mild alkaline hydrolysis. The molecular weight of the intact antigen was found to be 1.7 × 106. Mild alkaline hydrolysis completely removed O-acetyl, reduced the molecular weight to 1.0 × 105, and lowered the intrinsic viscosity from 8.0 deciliters/g to approximately 0.5 deciliter/g. Infrared spectra of the two antigen preparations were also compared.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASHIDA T. Studies on the antigenic substances of Eberthella typhosa. Jpn J Exp Med. 1949 Sep;20(2):181–209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAKER E. E., WHITESIDE R. E., BASCH R., DEROW M. A. The VI antigens of the Enterobacteriaceae. I. Purification and chemical properties. J Immunol. 1959 Dec;83:680–696. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARK W. R., McLAUGHLIN J., WEBSTER M. E. An aminohexuronic acid as the principal hydrolytic component of the Vi antigen. J Biol Chem. 1958 Jan;230(1):81–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JARVIS F. G., MESENKO M. T., KYLE J. E. Electrophoretic purification of the Vi antigen. J Bacteriol. 1960 Nov;80:677–682. doi: 10.1128/jb.80.5.677-682.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JARVIS F. G., MESENKO M. T., TIBBS K. E. Production of Vi antigen on a chemically defined medium by a coliform bacterium. J Bacteriol. 1960 Nov;80:673–676. doi: 10.1128/jb.80.5.673-676.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANDY M., JOHNSON A. G., WEBSTER M. E. Studies on Vi antigen. VIII. Role of acetyl in antigenic activity. Am J Hyg. 1961 Jan;73:55–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANDY M., TRAPANI R. J., WEBSTER M. E., JAVIS F. G. Immunological properties of Vi antigen isolated by chemical fractionation and by electrophoresis. Tex Rep Biol Med. 1963;21:214–229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin D. G., Jarvis F. G., Milner K. C. Physicochemical and biological properties of sonically treated Vi antigen. J Bacteriol. 1967 Nov;94(5):1411–1416. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.5.1411-1416.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEBSTER M. E., CLARK W. R., FREEMAN M. E. Evidence for an aminohexuronic acid as hydrolytic product of Vi antigen. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1954 May;50(1):223–224. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(54)90028-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEBSTER M. E., LANDY M., FREEMAN M. E. Studies on Vi antigen. II. Purification of Vi antigen from Escherichia coli 5395/38. J Immunol. 1952 Aug;69(2):135–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEBSTER M. E., SAGIN J. F., ANDERSON P. R., BREESE S. S., FREEMAN M. E., LANDY M. Studies on Vi antigen. IV. Physicochemical characterization of Vi antigens isolated from V form Enterobacteriaceae. J Immunol. 1954 Jul;73(1):16–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


