Abstract
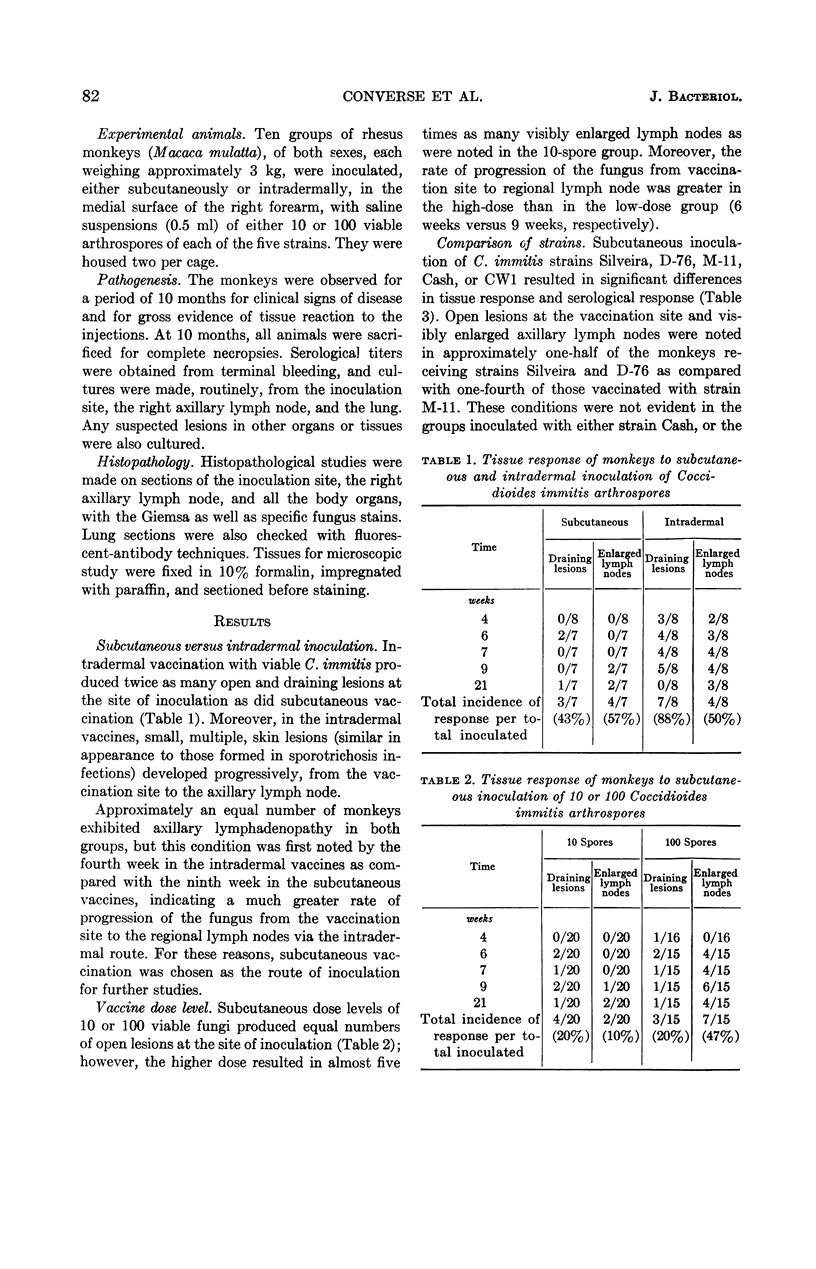
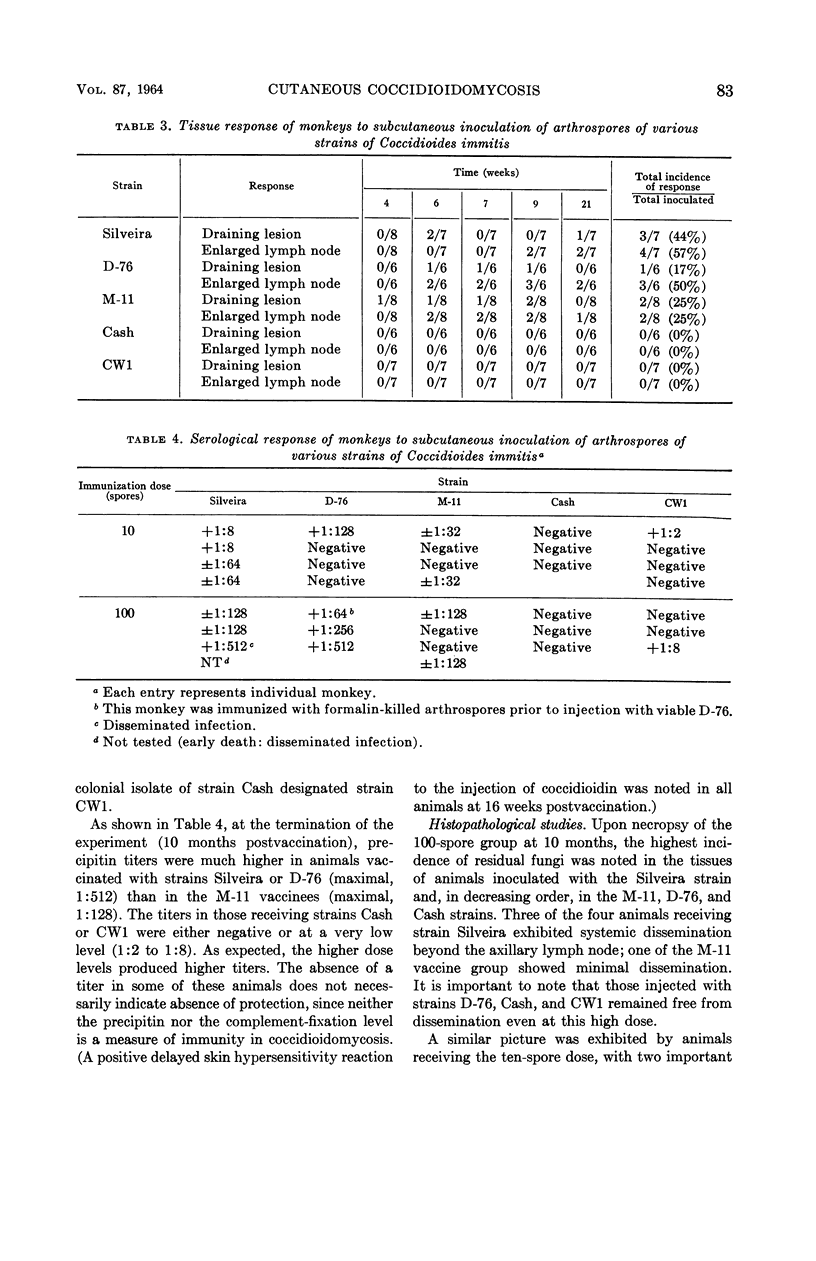
Converse, John L. (U.S. Army Biological Laboratories, Fort Detrick, Frederick, Md.), Steven P. Pakes, Ernest M. Snyder, and Merida W. Castleberry. Experimental primary cutaneous coccidioidomycosis in the monkey. J. Bacteriol. 87:81–85. 1964.—Primary cutaneous coccidioidomycosis was studied in the monkey (Macaca mulatta) to find a suitable strain of Coccidioides immitis for use as a viable vaccine. Intradermal inoculation (medial surface of the right forearm) produced more severe vaccination reactions (draining vaccination site and axillary lymph node hypertrophy) than did subcutaneous injection. A subcutaneous vaccine dose of 10 arthrospores resulted in less reaction than a 100-spore dose. Moreover, dissemination beyond the regional lymph nodes did not occur after injection of ten spores of even the most virulent strains of C. immitis. Two of the five strains tested (Silveira, M-11, D-76, Cash, and a colonial isolate from Cash designated CW1) exhibited very mild vaccination reactions and appeared to have been cleared from the tissues upon necropsy at 10 months postvaccination. These two strains (Cash and CW1) appear promising for further immunological studies with a viable vaccine.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- WILSON J. W., SMITH C. E., PLUNKETT O. A. Primary cutaneous coccidioidomycosis; the criteria for diagnosis and a report of a case. Calif Med. 1953 Sep;79(3):233–239. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


