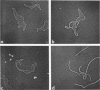
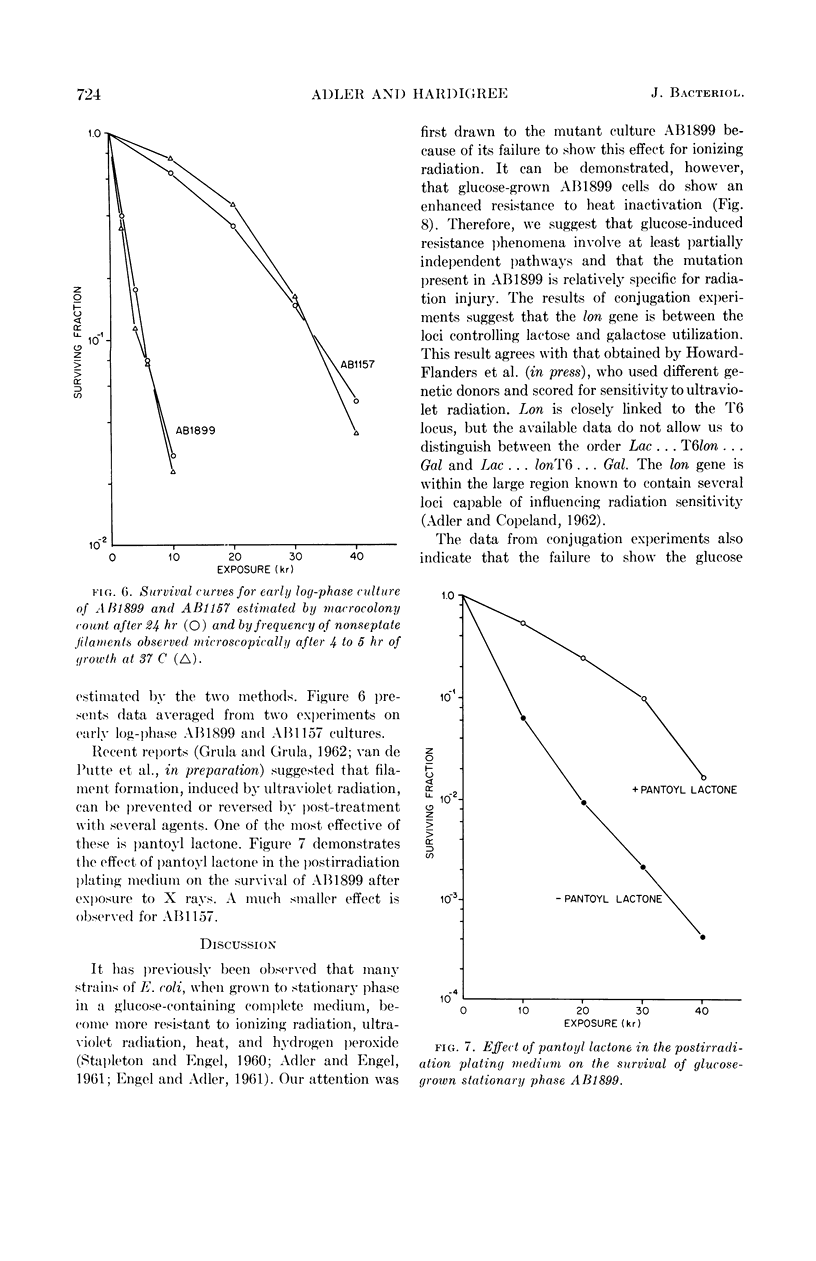
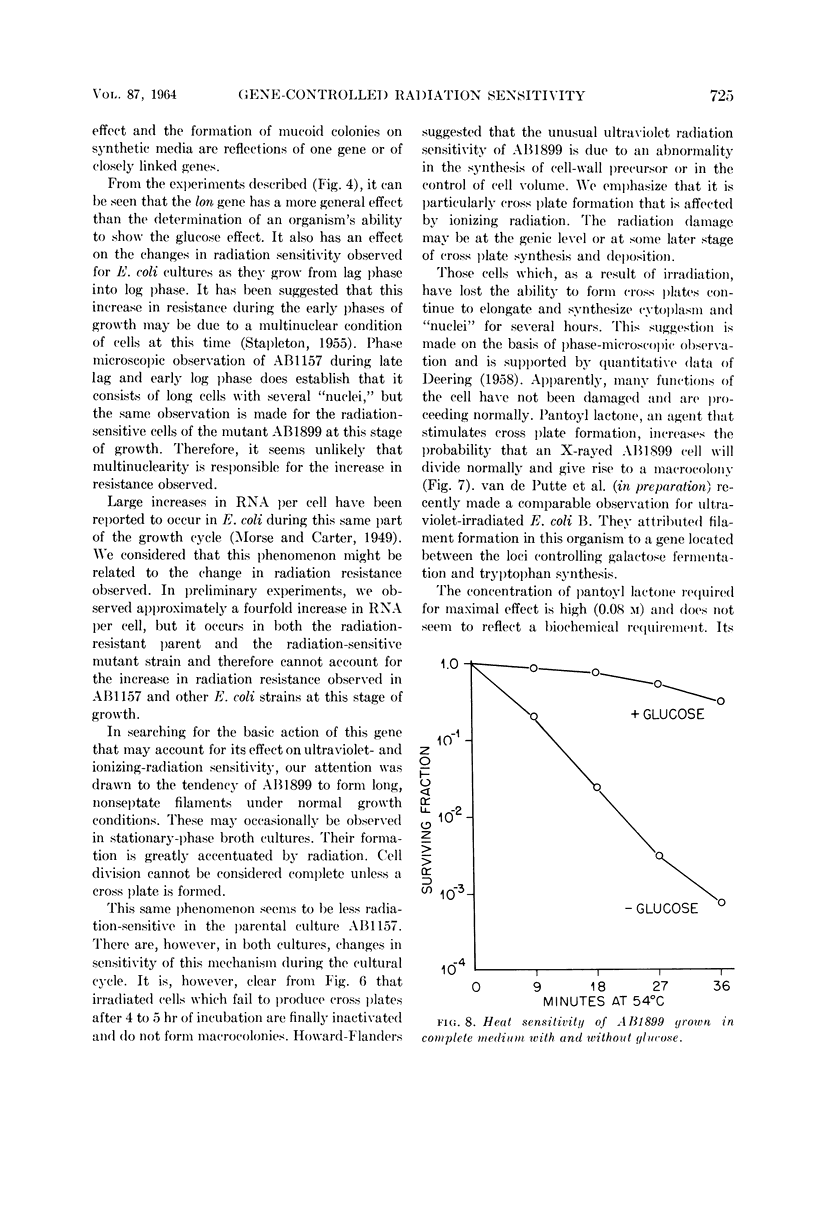
Abstract
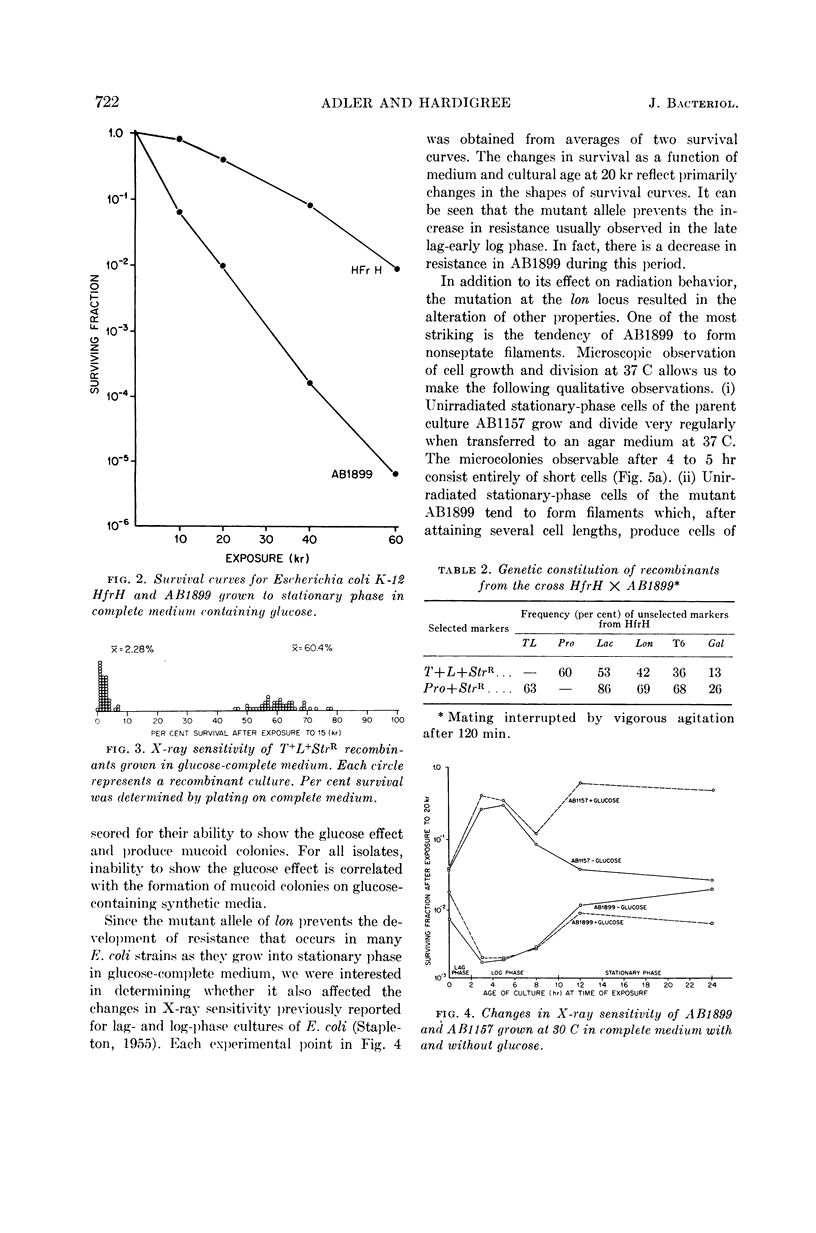
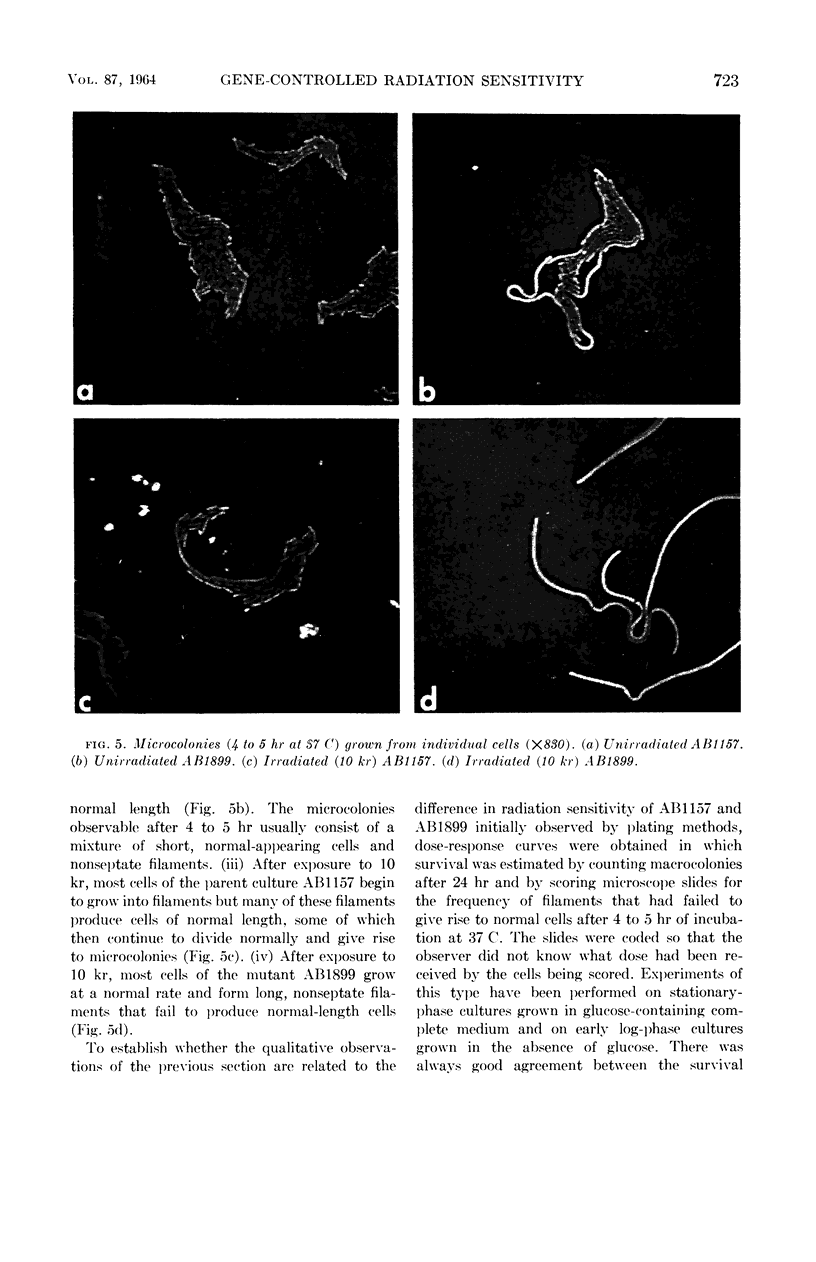
Adler, Howard I. (Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, Tenn.), and Alice A. Hardigree. Analysis of a genetic locus controlling cell division and sensitivity to radiation in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 87:720–726. 1964.—Radiation sensitivity in Escherichia coli is under control of genes that are transferred during conjugation between donor and recipient strains. Conjugation experiments establish that one of these genes occupies a locus on the E. coli K-12 linkage map between the genes controlling ability to utilize lactose and galactose. It affects sensitivity to both ionizing and ultraviolet (2,537 A) radiation. A strain possessing a mutation at this locus fails to show increases in resistance to ionizing radiation during late lag and early log phases, and increases in resistance when grown to stationary phase in a glucose-containing complete medium. The primary effect of the mutation at this locus may be an interference with the mechanism by which cells form cross plates. Cells of the mutant form long, nonseptate filaments when grown after exposure to ionizing radiation. The filaments do not give rise to macrocolonies. Pantoyl lactone, an agent that initiates cross plate formation, allows the filaments to divide normally and produce macrocolonies. When plated after irradiation on complete medium containing pantoyl lactone, the survival of the mutant is greatly increased.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADLER H. I., COPELAND J. C. Genetic analysis of radiation response in Escherichia coli. Genetics. 1962 Jun;47:701–712. doi: 10.1093/genetics/47.6.701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
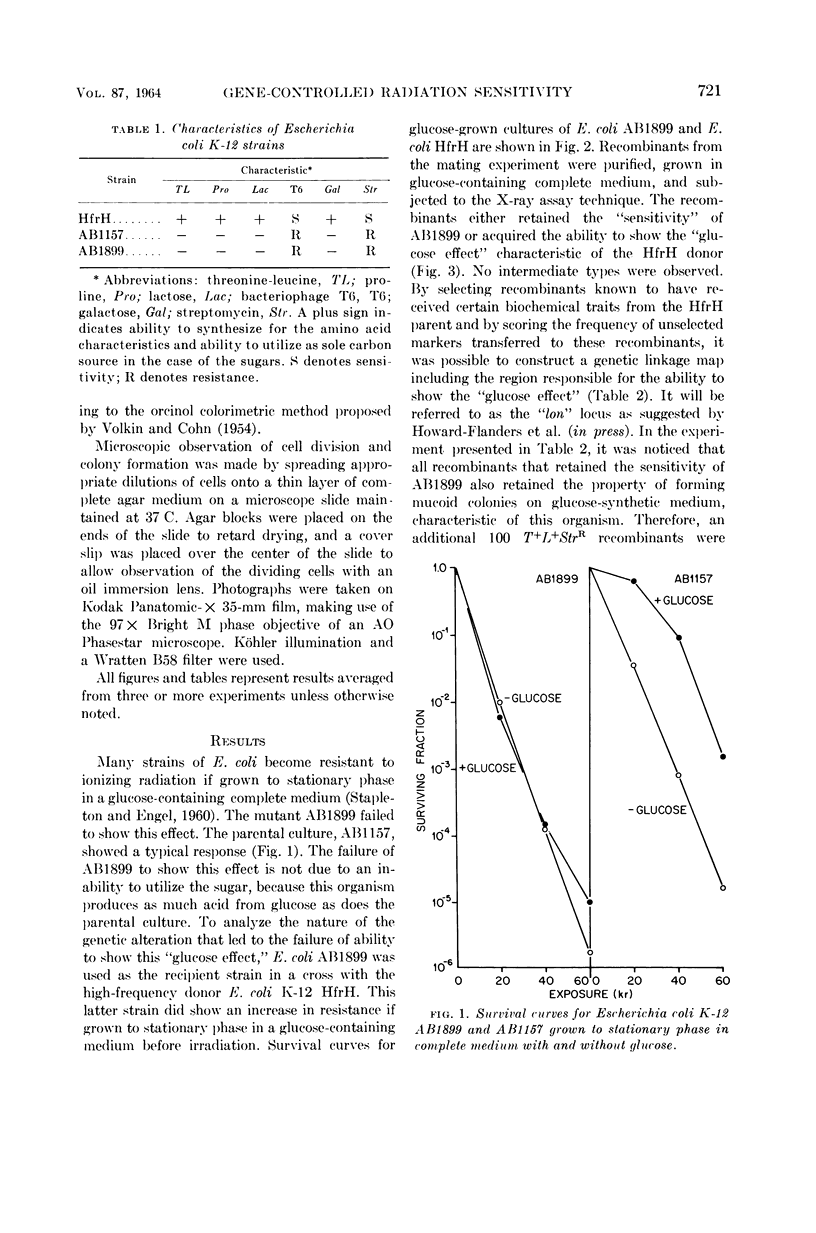
- ADLER H. I., ENGEL M. S. Factors influencing the survival of bacteria after exposure to ionizing radiation. J Cell Comp Physiol. 1961 Dec;58(3):95–105. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030580410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENGEL M. S., ADLER H. I. Catalase activity, sensitivity to hydrogen peroxide, and radiation response in the genus Escherichia. Radiat Res. 1961 Sep;15:269–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRULA E. A., GRULA M. M. Cell division in a species of Erwinia III. Reversal of inhibition of cell division caused by D-amino acids, penicillin, and ultraviolet light. J Bacteriol. 1962 May;83:981–988. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.5.981-988.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOWARD-FLANDERS P., BOYCE R. P., SIMSON E., THERIOT L. A genetic locus in E. coli K12 that controls the reactivation of UV-photoproducts associated with thymine in DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Dec 15;48:2109–2115. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.12.2109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse M. L., Carter C. E. THE SYNTHESIS OF NUCLEIC ACIDS IN CULTURES OF ESCHERICHIA COLI, STRAINS B AND B/R. J Bacteriol. 1949 Sep;58(3):317–326. doi: 10.1128/jb.58.3.317-326.1949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RORSCH A., EDELMAN A., COHEN J. A. The gene-controlled radiation sensitivity in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Feb 26;68:263–270. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90141-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STAPLETON G. E. Variations in the sensitivity of escherichia coli to ionizing radiations during the growth cycle. J Bacteriol. 1955 Oct;70(4):357–362. doi: 10.1128/jb.70.4.357-362.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman J. M., Albus W. R. Physiological Youth in Bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1923 Mar;8(2):127–139. doi: 10.1128/jb.8.2.127-139.1923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stapleton G. E., Engel M. S. CULTURAL CONDITIONS AS DETERMINANTS OF SENSITIVITY OF ESCHERICHIA COLI TO DAMAGING AGENTS. J Bacteriol. 1960 Oct;80(4):544–551. doi: 10.1128/jb.80.4.544-551.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOLKIN E., COHN W. E. Estimation of nucleic acids. Methods Biochem Anal. 1954;1:287–305. doi: 10.1002/9780470110171.ch11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]