Abstract
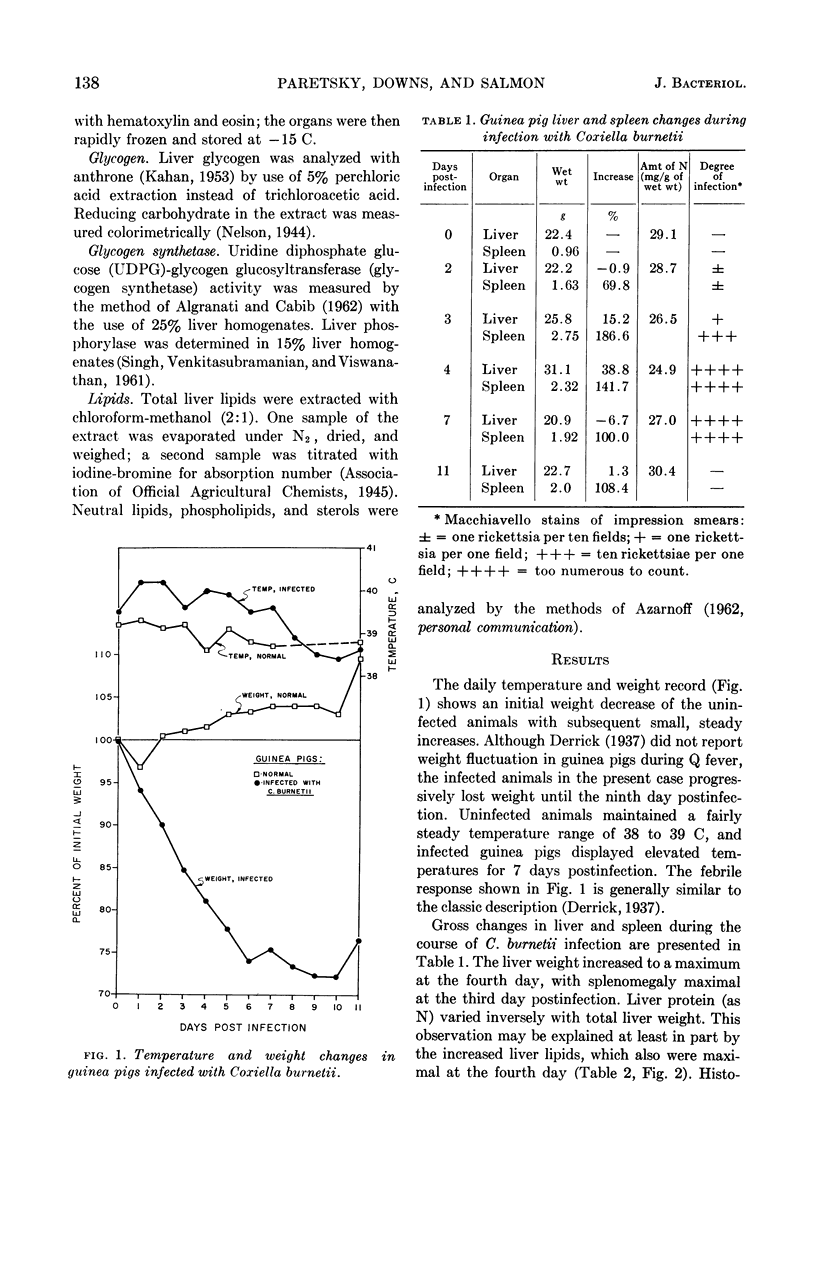
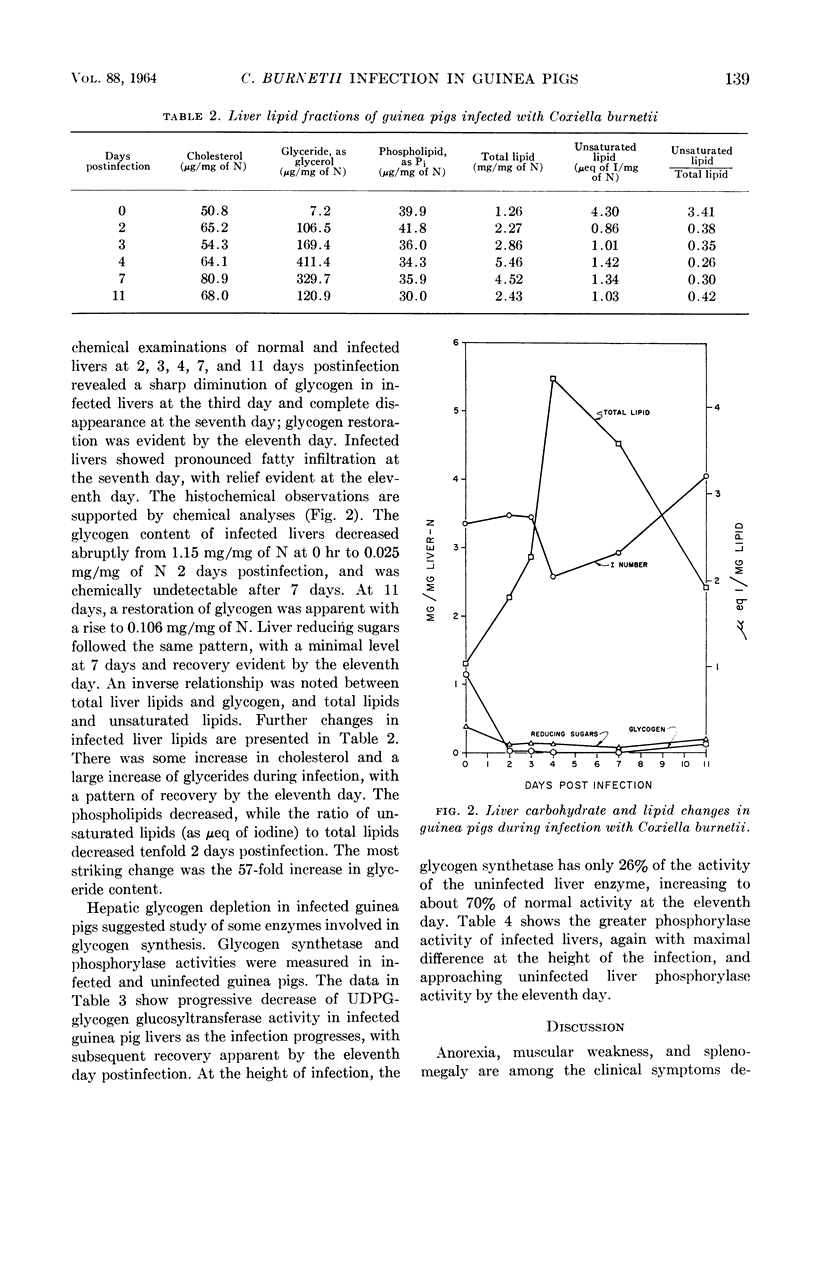
Paretsky, D. (University of Kansas, Lawrence), C. M. Downs, and C. W. Salmon. Some biochemical changes in the guinea pig during infection with Coxiella burnetii. J. Bacteriol. 88:137–142. 1964.—Guinea pigs infected with Coxiella burnetii, the rickettsial agent of Q fever, were studied for 11 days postinfection. Maximal changes in liver lipids, liver phosphorylase, and uridine diphosphate glucose (UDPG)-glycogen glucosyl-transferase activities occurred 3 to 4 days post-infection. In this period, total liver lipids increased from 1.26 to 5.46 mg/mg of N, with the largest increment in the glyceride fraction. Liver glycogen virtually disappeared by the second day, with no chemically detectable restoration until the eleventh day. A pattern of altered phosphorylase and UDPG-glycogen transglucosylase activities was observed, with maximal phosphorylase and minimal glucosyltransferase activities at the third and fourth days. Histochemical observations confirmed chemical analyses for lipids and glycogen.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALGRANATI I. D., CABIB E. Uridine diphosphate D-glucose-glycogen glucosyltransferase from yeast. J Biol Chem. 1962 Apr;237:1007–1013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AZARNOFF D. L. Micromethod for the determination of serum lipids. J Lab Clin Med. 1962 Aug;60:331–338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRADLEY S. G., LEDERBERG J. Heterokaryosis in Streptomyces. J Bacteriol. 1956 Aug;72(2):219–225. doi: 10.1128/jb.72.2.219-225.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONSIGLI R. A., PARETSKY D. Oxidation of glucose 6-phosphate and isocitrate by Coxiella burnetii. J Bacteriol. 1962 Jan;83:206–207. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.1.206-207.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CORI G. T., ILLINGWORTH B. The effect of epinephrine and other glycogenolytic agents on the phosphorylase A content of muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1956 Jul;21(1):105–110. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(56)90099-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAUSH C. R., YOUNGNER J. S. Studies on the lipids of virusinfected cells. I. Lipid analysis of a soluble hemagglutinin from chorioallantoic membranes infected with vaccinia virus. Virology. 1963 Apr;19:573–579. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90053-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAHAN J. A rapid photometric method for the determination of glycogen. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1953 Dec;47(2):408–418. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(53)90477-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KORDOVA N., REHACEK J. Experimental infection of ticks in vivo and their organs in vitro with filterable particles of Coxiella burneti. Acta Virol. 1959 Oct;3:201–209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MALLAVIA L., PARETSKY D. STUDIES ON THE PHYSIOLOGY OF RICKETTSIAE. V. METABOLISM OF CARBAMYL PHOSPHATE BY COXIELLA BURNETII. J Bacteriol. 1963 Aug;86:232–238. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.2.232-238.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATTHEIS M. S., SILVERMAN M., PARETSKY D. Studies on the physiology of Rickettsiae. IV. Folic acids of Coxiella burnetii. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jan;85:37–41. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.1.37-41.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MYERS W. F., PARETSKY D. Synthesis of serine by Coxiella burnetii. J Bacteriol. 1961 Nov;82:761–763. doi: 10.1128/jb.82.5.761-763.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARETSKY D., CONSIGLI R. A., DOWNS C. M. Studies on the physiology of rickettsiae. III. Glucose phosphorylation and hexokinase activity in Coxiella burnetii. J Bacteriol. 1962 Mar;83:538–543. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.3.538-543.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARETSKY D., DOWNS C. M., CONSIGLI R. A., JOYCE B. K. Studies on the physiology of rickettsiae. I. Some enzyme systems of Coxiella burnetii. J Infect Dis. 1958 Jul-Aug;103(1):6–11. doi: 10.1093/infdis/103.1.6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBERTS A. N., DOWNS C. M. Study on the growth of Coxiella burnetii in the L strain mouse fibroblast and the chick fibroblast. J Bacteriol. 1959 Feb;77(2):194–204. doi: 10.1128/jb.77.2.194-204.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SINGH V. N., BHARGAVA U., VENKITASUBRAMANIAN T. A., VISWANATHAN R. Study of glycogen synthesizing and degrading enzymes of guinea pig liver in experimental tuberculosis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1963 May;101:234–238. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(63)80008-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SINGH V. N., VENKITASUBRAMANIAN T. A., VISWANATHAN R. Study of glucose tolerance and synthesis of hepatic glycogen from glucose and glycine-1-C-14 in tuberculous guinea pigs. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1963 May;101:229–233. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(63)80007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUTHERLAND E. W., RALL T. W. Fractionation and characterization of a cyclic adenine ribonucleotide formed by tissue particles. J Biol Chem. 1958 Jun;232(2):1077–1091. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SZENTIVANYI A., FISHEL C. W., TALMAGE D. W. ADRENALINE MEDIATION OF HISTAMINE AND SEROTONIN HYPERGLYCEMIA IN NORMAL MICE AND THE ABSENCE OF ADRENALINE-INDUCED HYPERGLYCEMIA IN PERTUSSIS-SENSITIZED MICE. J Infect Dis. 1963 Sep-Oct;113:86–98. doi: 10.1093/infdis/113.2.86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh V. N., Venkitasubramanian T. A., Viswanathan R. The glycolytic enzymes of guinea-pig lung in experimental bagassosis. Biochem J. 1961 Apr;78(4):728–732. doi: 10.1042/bj0780728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VILLAR-PALASI C., LARNER J. Insulin treatment and increased UDPG-glycogen transglucosylase activity in muscle. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1961 Sep;94:436–442. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(61)90071-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



