Abstract
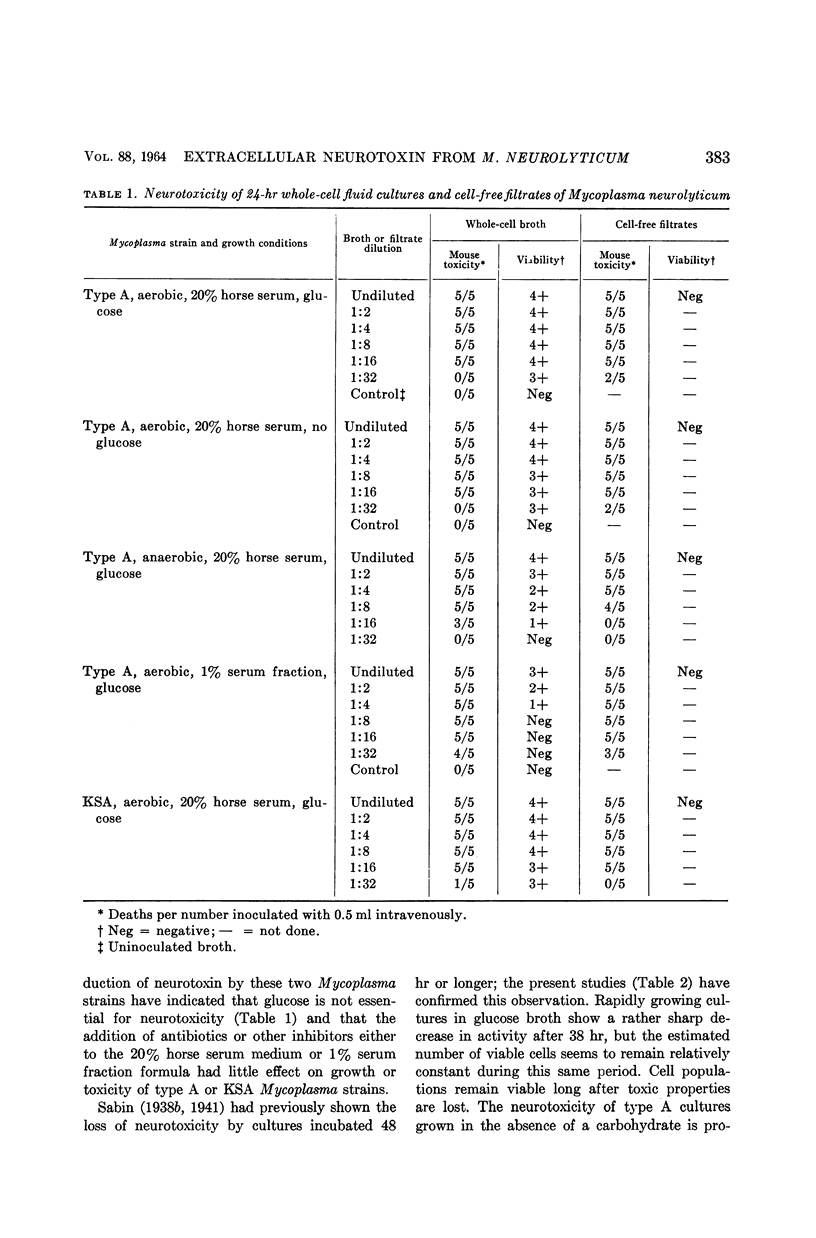
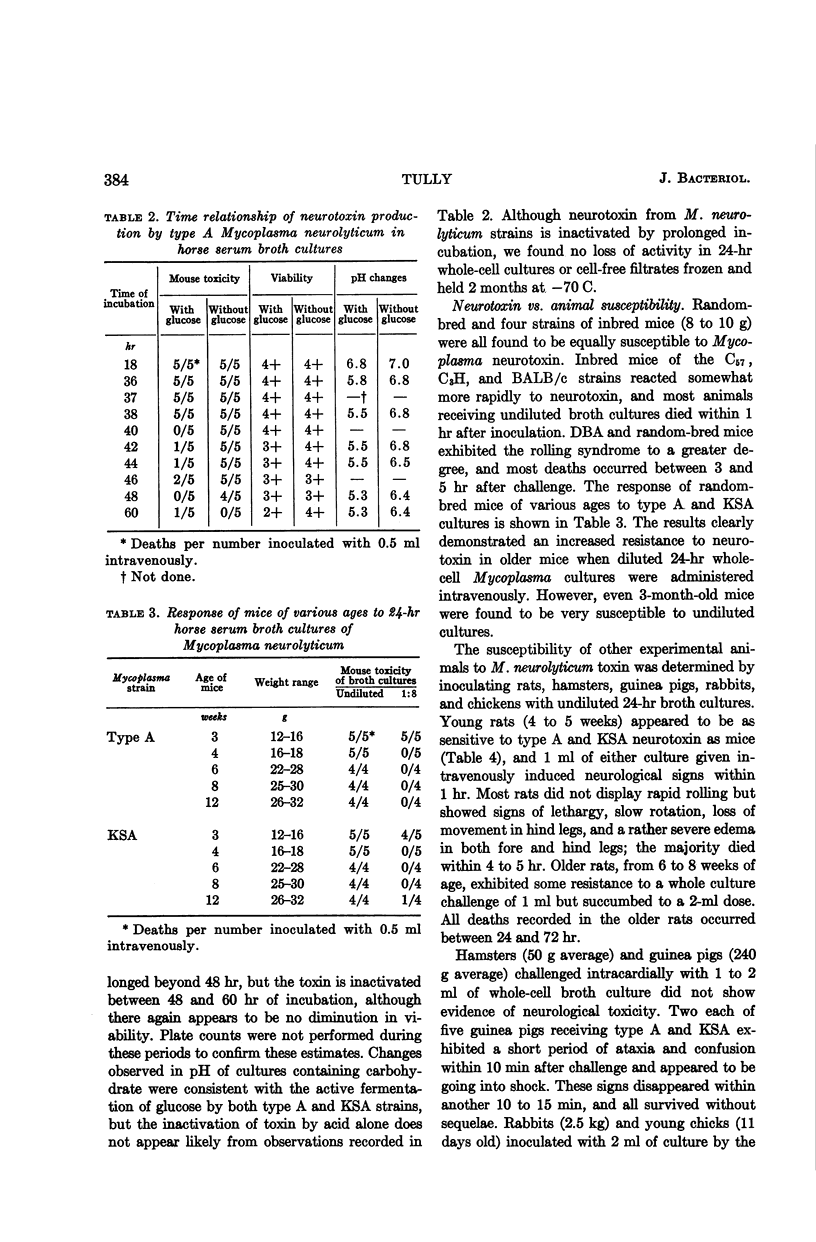
Tully, Joseph G. (National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, Bethesda, Md.). Production and biological characteristics of an extracellular neurotoxin from Mycoplasma neurolyticum. J. Bacteriol. 88:381–388. 1964.—Toxigenic strains of Mycoplasma neurolyticum were found to produce a potent extracellular neurotoxin for mice under a variety of cultural conditions. The observed biological characteristics of this toxin were quite similar to those originally described by Sabin. The toxin was again found to be readily inactivated by prolonged incubation and, when separated from Mycoplasma cells by filtration, possessed a greater heat resistance than whole cells. Young mice and rats were generally susceptible to neurotoxin, whereas most other experimental animals were resistant. Filtration results confirmed a minimal reproductive unit of 125 to 200 mμ for two neurotoxic Mycoplasma strains, with both cell-free filtrates reproducing the rolling disease syndrome in mice. Twice-washed Mycoplasma cells were also observed to be as neurotoxic as filtrates. Plate counting results revealed an intravenous ld50 of approximately 3 × 108 washed cells for young mice.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CHANOCK R. M., HAYFLICK L., BARILE M. F. Growth on artificial medium of an agent associated with atypical pneumonia and its identification as a PPLO. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Jan 15;48:41–49. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANOCK R. M., JAMES W. D., FOX H. H., TURNER H. C., MUFSON M. A., HAYFLICK L. Growth of Eaton PPLO in broth and preparation of complement fixing antigen. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1962 Aug-Sep;110:884–889. doi: 10.3181/00379727-110-27681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDWARD D. G., FREUNDT E. A. The classification and nomenclature of organisms of the pleuropneumonia group. J Gen Microbiol. 1956 Feb;14(1):197–207. doi: 10.1099/00221287-14-1-197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDWARD D. G. The pleuropneumonia group of organisms: a review, together with some new observations. J Gen Microbiol. 1954 Feb;10(1):27–64. doi: 10.1099/00221287-10-1-27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRAEMER P. M., DEFENDI V., HAYFLICK L., MANSON L. A. Mycoplasma (PPLO) strains with lytic activity for murine lymphoma cells in vitro. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1963 Feb;112:381–387. doi: 10.3181/00379727-112-28052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRAEMER P. M. INTERACTION OF MYCOPLASMA (PPLO) AND MURINE LYMPHOMA CELL CULTURES: PREVENTION OF CELL LYSIS BY ARGININE. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Jan;115:206–212. doi: 10.3181/00379727-115-28871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morowitz H. J., Tourtellotte M. E., Pollack M. E. USE OF POROUS CELLULOSE ESTER MEMBRANES IN THE PRIMARY ISOLATION AND SIZE DETERMINATION OF PLEUROPNEUMONIA-LIKE ORGANISMS. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jan;85(1):134–136. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.1.134-136.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROTH W. Isolierung von Pleuropneumonie-Virus aus dem Gehirn weisser Mäuse. Schweiz Z Pathol Bakteriol. 1951;14(5):578–582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabin A. B. EXPERIMENTAL PROLIFERATIVE ARTHRITIS IN MICE PRODUCED BY FILTRABLE, PLEUROPNEUMONIA-LIKE MICROORGANISMS. Science. 1939 Mar 10;89(2306):228–229. doi: 10.1126/science.89.2306.228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabin A. B. IDENTIFICATION OF THE FILTRABLE, TRANSMISSIBLE NEUROLYTIC AGENT ISOLATED FROM TOXOPLASMA-INFECTED TISSUE AS A NEW PLEUROPNEUMONIA-LIKE MICROBE. Science. 1938 Dec 16;88(2294):575–576. doi: 10.1126/science.88.2294.575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabin A. B. ISOLATION OF A FILTRABLE, TRANSMISSIBLE AGENT WITH "NEUROLYTI" PROPERTIES FROM TOXOPLASMA-INFECTED TISSUES. Science. 1938 Aug 26;88(2278):189–191. doi: 10.1126/science.88.2278.189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabin A. B. MICE AS CARRIERS OF PATHOGENIC PLEUROPNEUMONIA-LIKE MICROORGANISMS. Science. 1939 Jul 7;90(2323):18–19. doi: 10.1126/science.90.2323.18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabin A. B. THE FILTRABLE MICROORGANISMS OF THE PLEUROPNEUMONIA GROUP. Bacteriol Rev. 1941 Mar;5(1):1–67. doi: 10.1128/br.5.1.1-67.1941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR-ROBINSON D., SOMERSON N. L., TURNER H. C., CHANOCK R. M. SEROLOGICAL RELATIONSHIPS AMONG HUMAN MYCOPLASMAS AS SHOWN BY COMPLEMENT-FIXATION AND GEL DIFFUSION. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jun;85:1261–1273. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.6.1261-1273.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TULLY J. G., RUCHMAN I. RECOVERY, IDENTIFICATION, AND NEUROTOXICITY OF SABIN'S TYPE A AND C MOUSE MYCOPLASMA (PPLO) FROM LYOPHILIZED CULTURES. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Feb;115:554–558. doi: 10.3181/00379727-115-28966. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VILLEMOT J. M., PROVOST A., QUEVAL R. Endotoxin from Mycoplasma mycoides. Nature. 1962 Mar 3;193:906–907. doi: 10.1038/193906a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIBULL C., LUNDIN B. M. Size and shape of pleuropneumonia-like organisms grown in liquid media. J Bacteriol. 1962 Sep;84:513–519. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.3.513-519.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


