Abstract
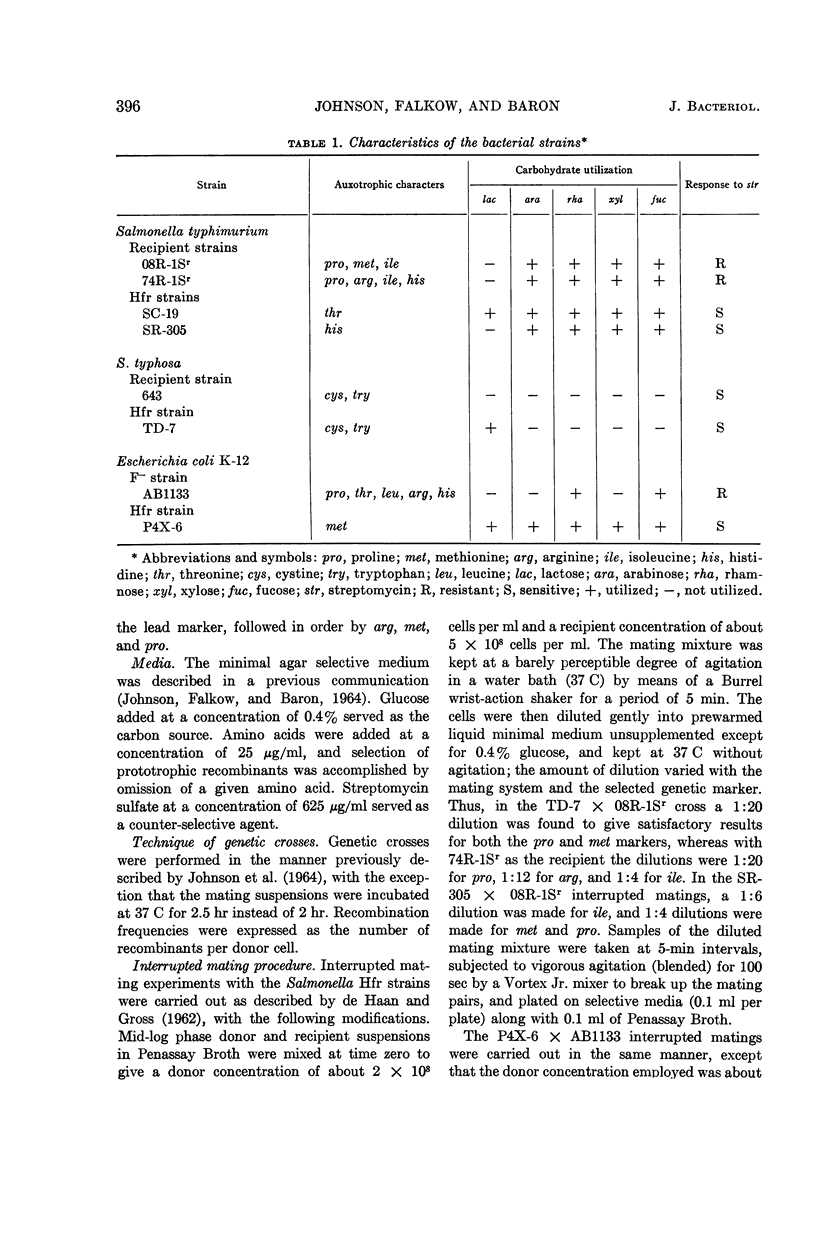
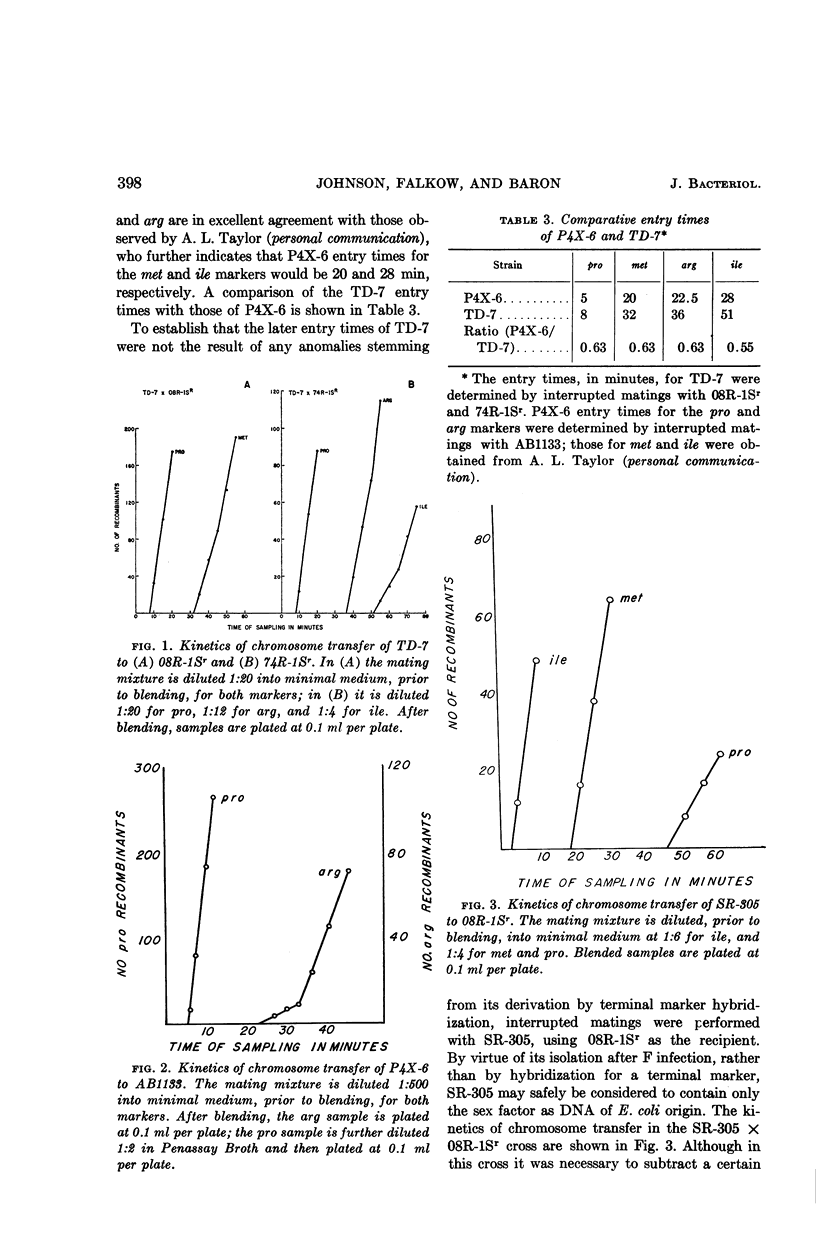
Johnson, E. M. (Walter Reed Army Institute of Research, Washington, D.C.), Stanley Falkow, and L. S. Baron. Chromosome transfer kinetics of Salmonella Hfr strains. J. Bacteriol. 88:395–400. 1964.—The kinetics of chromosome transfer of an Hfr strain of Salmonella typhosa and an Hfr strain of S. typhimurium were examined in interrupted matings with multiply auxotrophic S. typhimurium recipients. The S. typhosa Hfr, TD-7, was found to transfer the pro-A, met-A, arg (A, C, F, or H), and ile markers at 8, 32, 36, and 51 min, respectively, after contact with the recipient strain. Comparison of these entry times with those of the analogous Escherichia coli Hfr P4X-6 for the same markers showed the gene order to be identical. However, the TD-7 entry times were considerably extended over those of P4X-6, which transfers these markers of E. coli F− strains at, respectively, 5, 20, 22.5, and 28 min. A similar extension of the entry times was noted with the S. typhimurium Hfr, SR-305, which transfers the markers in the reverse order, ile-met-A-pro-A, at 3 to 4, 18, and 46 min, respectively. Examination of P4X-6/Salmonella Hfr entry time ratios showed them to be constant at 0.63 for the earlier markers transferred by both TD-7 and SR-305. These data suggest that the physical length of the Salmonella chromosome is the same as that of E. coli, and that the rate of chromosome transfer of the Salmonella Hfr strains to S. typhimurium recipients is only 0.63 that of P4X-6 to E. coli F− strains under the same physical conditions.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- JACOB F., WOLLMAN E. L. Analyse des groupes de liaison génétique de différentes souches donatrices d'Escherichia coli K 12. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1957 Nov 18;245(21):1840–1843. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNSON E. M., FALKOW S., BARON L. S. RECIPIENT ABILITY OF SALMONELLA TYPHOSA IN GENETIC CROSSES WITH ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Bacteriol. 1964 Jan;87:54–60. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.1.54-60.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAKELA P. H. HFR males in Salmonella abony. Genetics. 1963 Mar;48:423–429. doi: 10.1093/genetics/48.3.423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyake T. Exchange of Genetic Material between Salmonella Typhimurium and Escherichia Coli K-12. Genetics. 1962 Aug;47(8):1043–1052. doi: 10.1093/genetics/47.8.1043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZINDER N. D. Hybrids of Escherichia and Salmonella. Science. 1960 Mar 18;131(3403):813–815. doi: 10.1126/science.131.3403.813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZINDER N. D. Sexuality and mating in salmonella. Science. 1960 Mar 25;131(3404):924–926. doi: 10.1126/science.131.3404.924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


