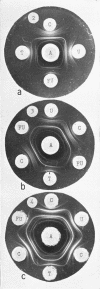
Abstract
De Repentigny, J. (University of Montreal, Montreal, Quebec, Canada), S. Sonea, and A. Frappier. Differentiation by immunodiffusion and by quantitative immunofluorescence between 5-fluorouracil-treated and normal cells from a toxinogenic Staphylococcus aureus strain. J. Bacteriol. 88:444–448. 1964.—Immunodiffusion and quantitative immunofluorescence can both detect antigenic changes produced by 5-fluorouracil (FU) in Staphylococcus aureus Wood 46 strain. When FU is added to the cultures in their logarithmic phase of growth, a number of bacterial antigens are no longer detectable by immuno-diffusion and the intensity of the total immuno-fluorescence of bacteria is diminished; thus, these antigens are either profoundly modified or no longer synthesized. Uracil and, less effectively, thymine can reverse the FU inhibitory effect on the synthesis of antigens, and the number of precipitin lines remains closer to controls. The immunochemical approach provides a new way of obtaining information on the action of this pyrimidine analogue on metabolic processes in pathogenic bacteria. Microscopic quantitative immunofluorescence seems to be adaptable to give indirect information on changes in the metabolism or synthesis or antigens of a single bacterial cell.
Full text
PDF
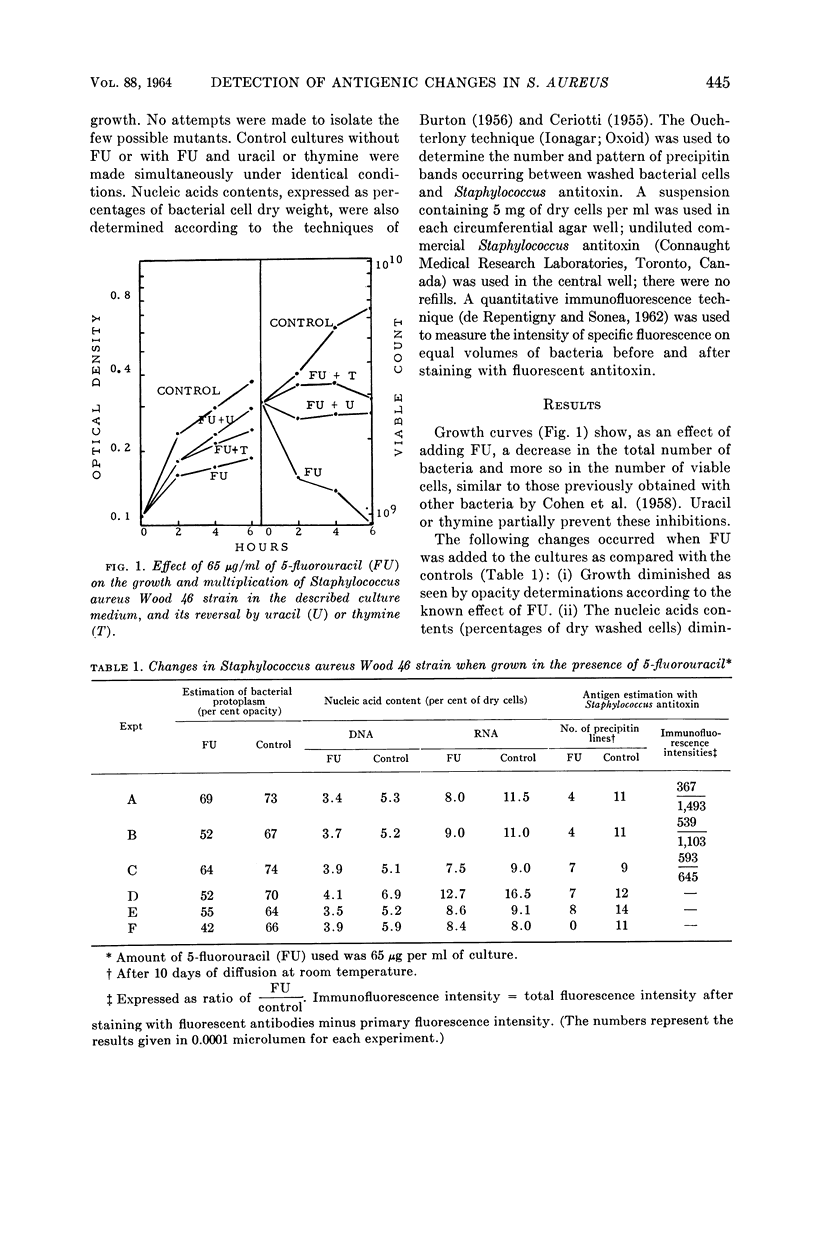
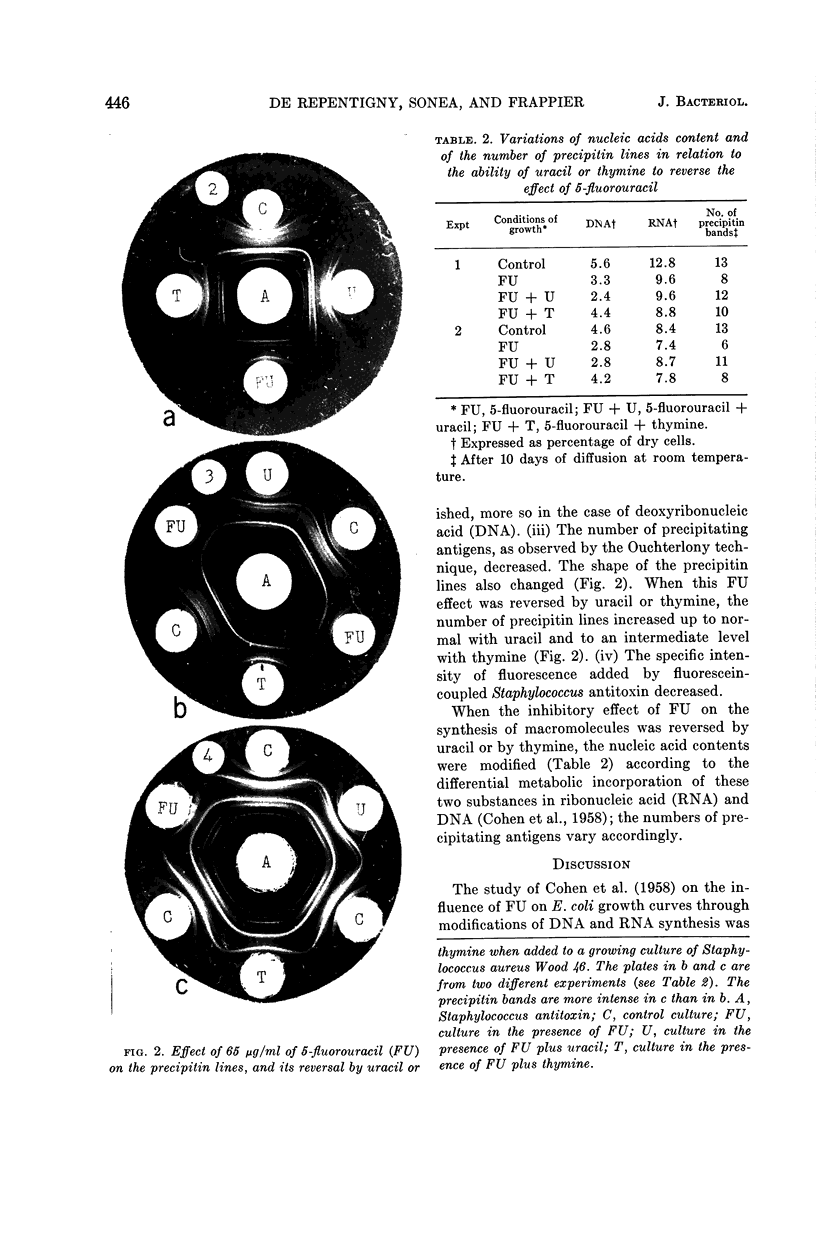


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CERIOTTI G. Determination of nucleic acids in animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1955 May;214(1):59–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. S., Flaks J. G., Barner H. D., Loeb M. R., Lichtenstein J. THE MODE OF ACTION OF 5-FLUOROURACIL AND ITS DERIVATIVES. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1958 Oct 15;44(10):1004–1012. doi: 10.1073/pnas.44.10.1004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEREPENTIGNY J., SONEA S., FRAPPIER A. COMPARISON OF QUANTITATIVE IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE AND IMMUNODIFFUSION FOR THE EVALUATION OF ANTIGENIC MATERIALS FROM STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. J Bacteriol. 1963 Dec;86:1348–1349. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.6.1348-1349.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANEK F., RIHA I., STERZL J. Characteristics of gamma-globulin, lacking antibody properties, in new-born pigs. Nature. 1961 Mar 25;189:1020–1022. doi: 10.1038/1891020a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAUSE G. F., KOCHETKOVA G. V. Vulnerability of nucleic acids in mutant staphylococci with impaired respiration. J Gen Microbiol. 1962 Oct;29:317–323. doi: 10.1099/00221287-29-2-317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOWARD J. G. Diffusible antigens in relation to the virulence to mice of Staphylococcus aureus. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1954 Jul;68(1):177–186. doi: 10.1002/path.1700680122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OEDING P., HAUKENES G. IDENTIFICATION OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS ANTIGENS AND ANTIBODIES BY MEANS OF THE GEL PRECIPITATION TECHNIQUE. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1963;57:438–450. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1963.tb05112.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROGERS H. J., PERKINS H. R. 5-Fluorouracil and mucopeptide biosynthesis by Staphylococcus aureus. Biochem J. 1960 Dec;77:448–459. doi: 10.1042/bj0770448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SONEA S., de REPENTIGNY, FRAPPIER A. Changes in immunodiffusion patterns and in nucleic acid content of Staphylococcus aureus grown in the presence of a nucleic acid fluorochrome. J Bacteriol. 1962 Nov;84:1056–1060. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.5.1056-1060.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de REPENTIGNY, SONEA S. [A microfluorometric study of micro-organisms. III. Secondary fluorescence added by fluorescent antibodies]. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1962 Feb;102:182–191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]