Abstract
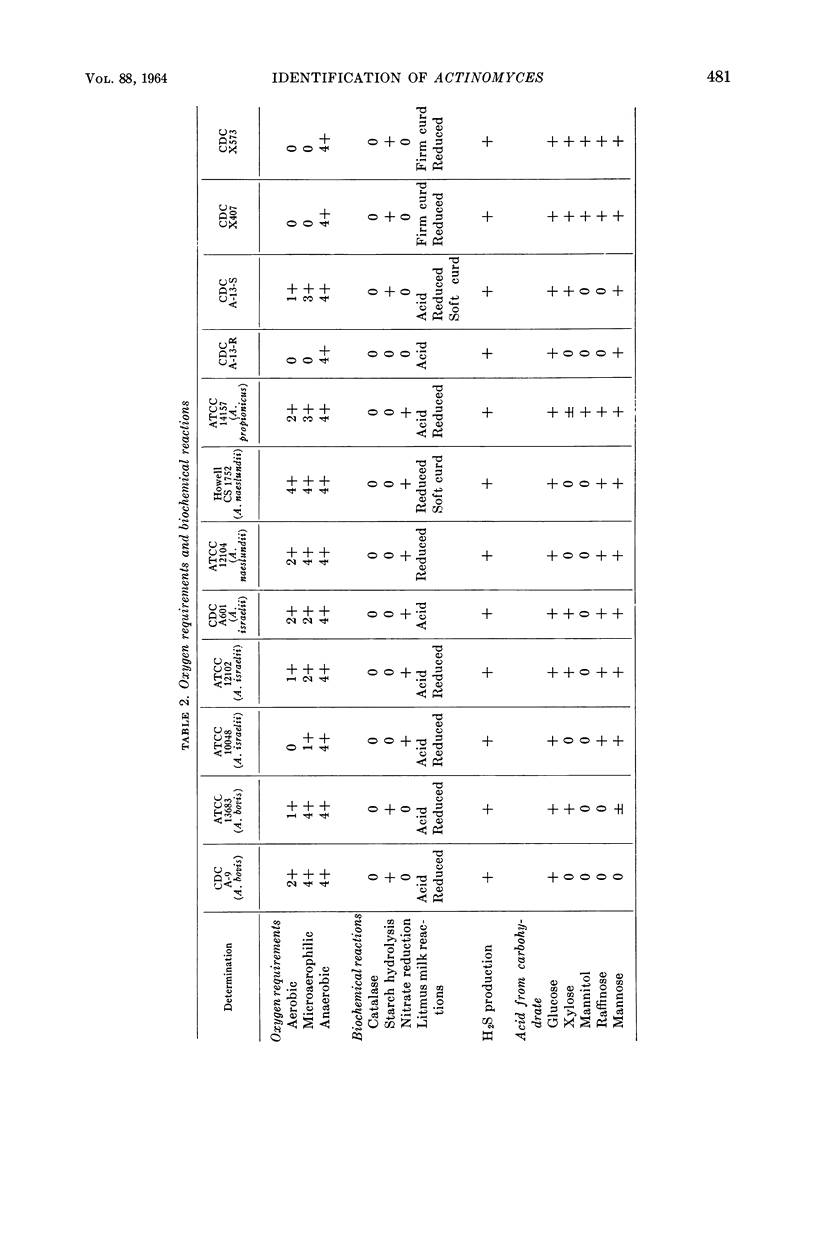
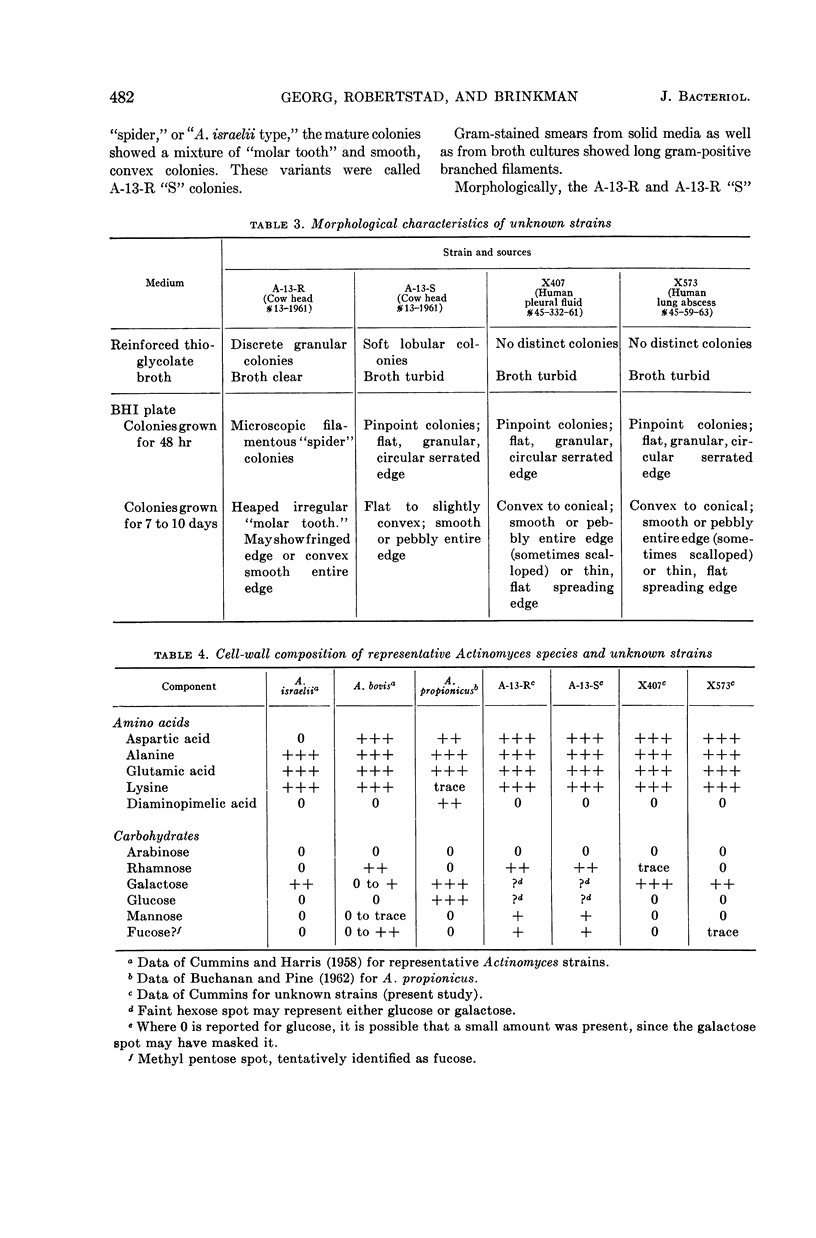
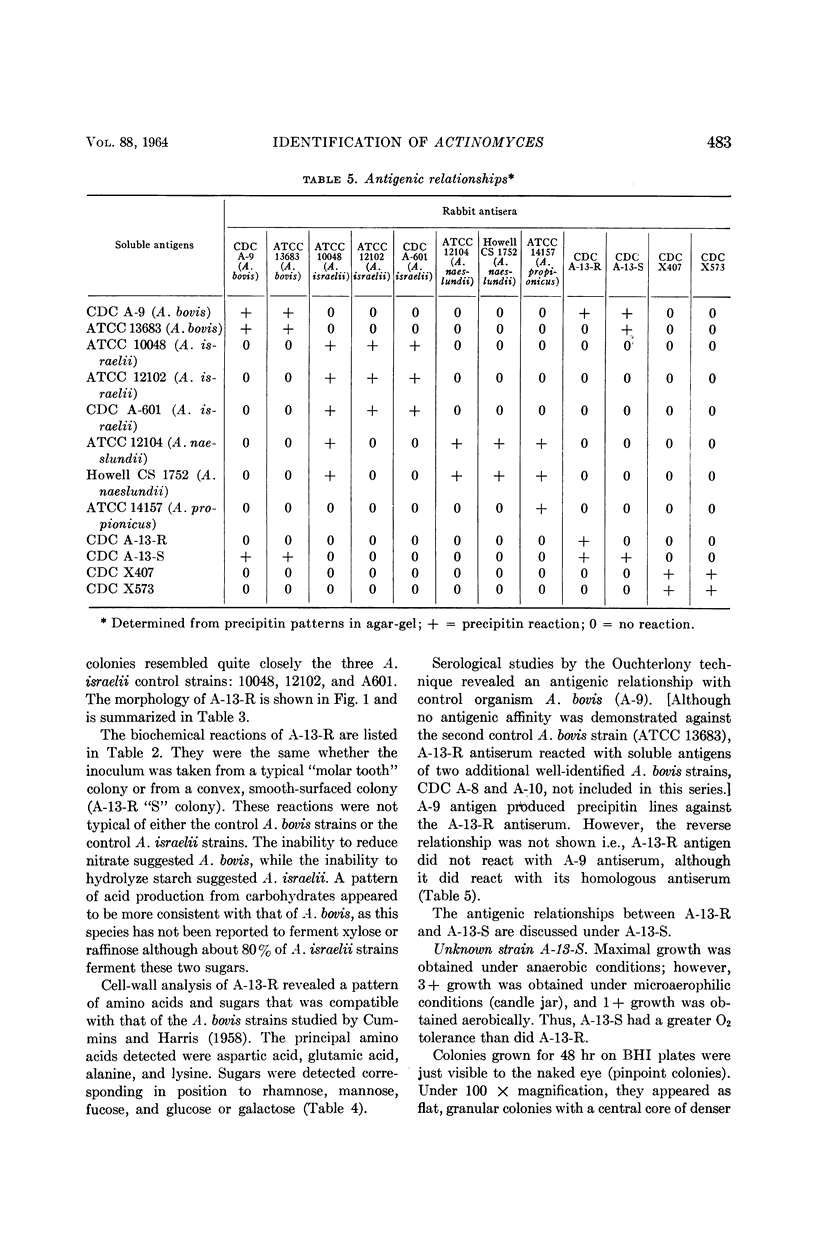
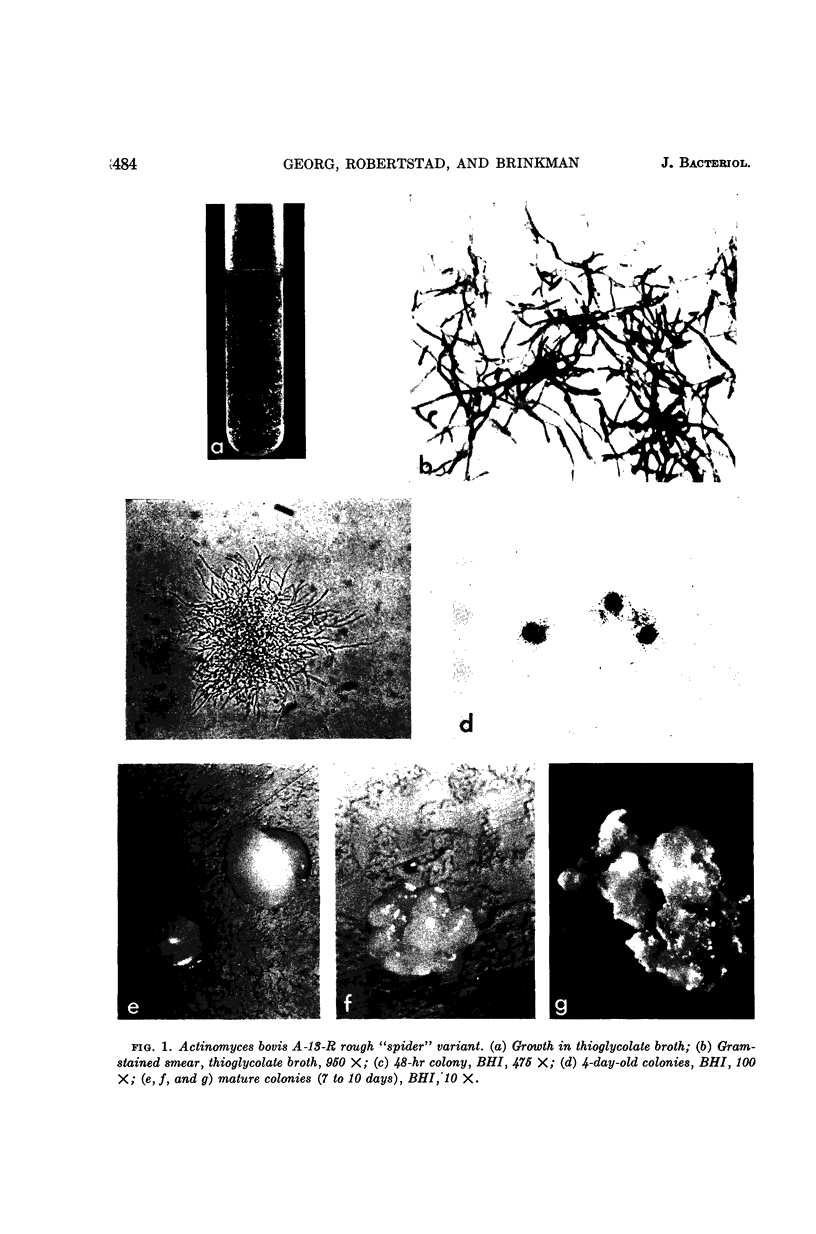
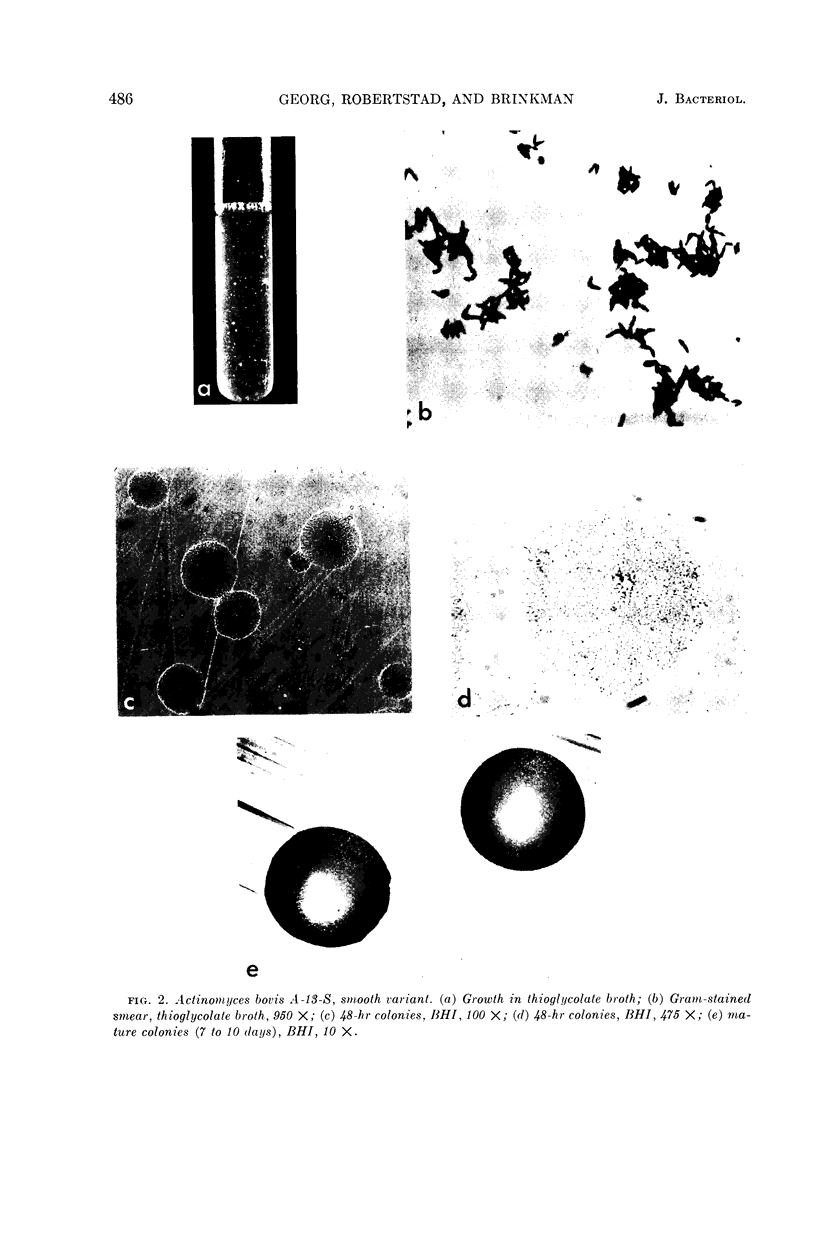
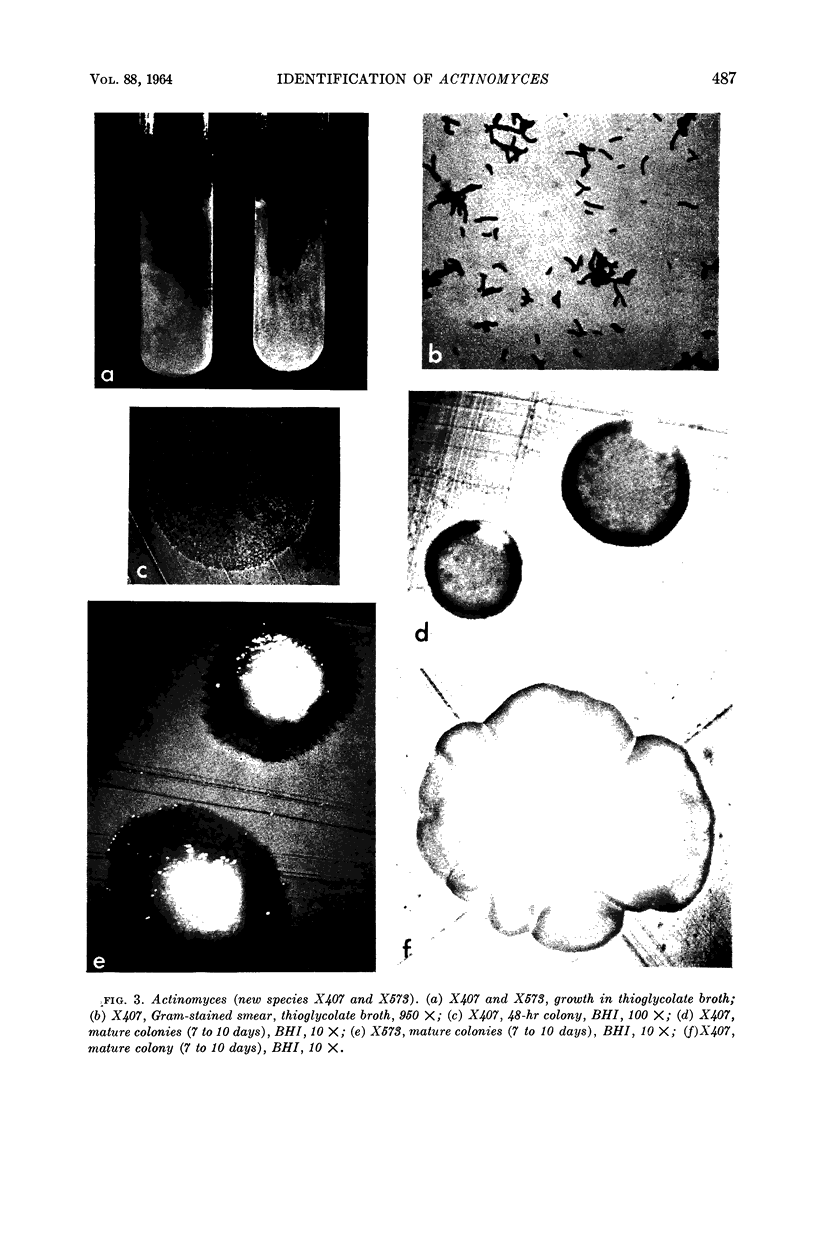
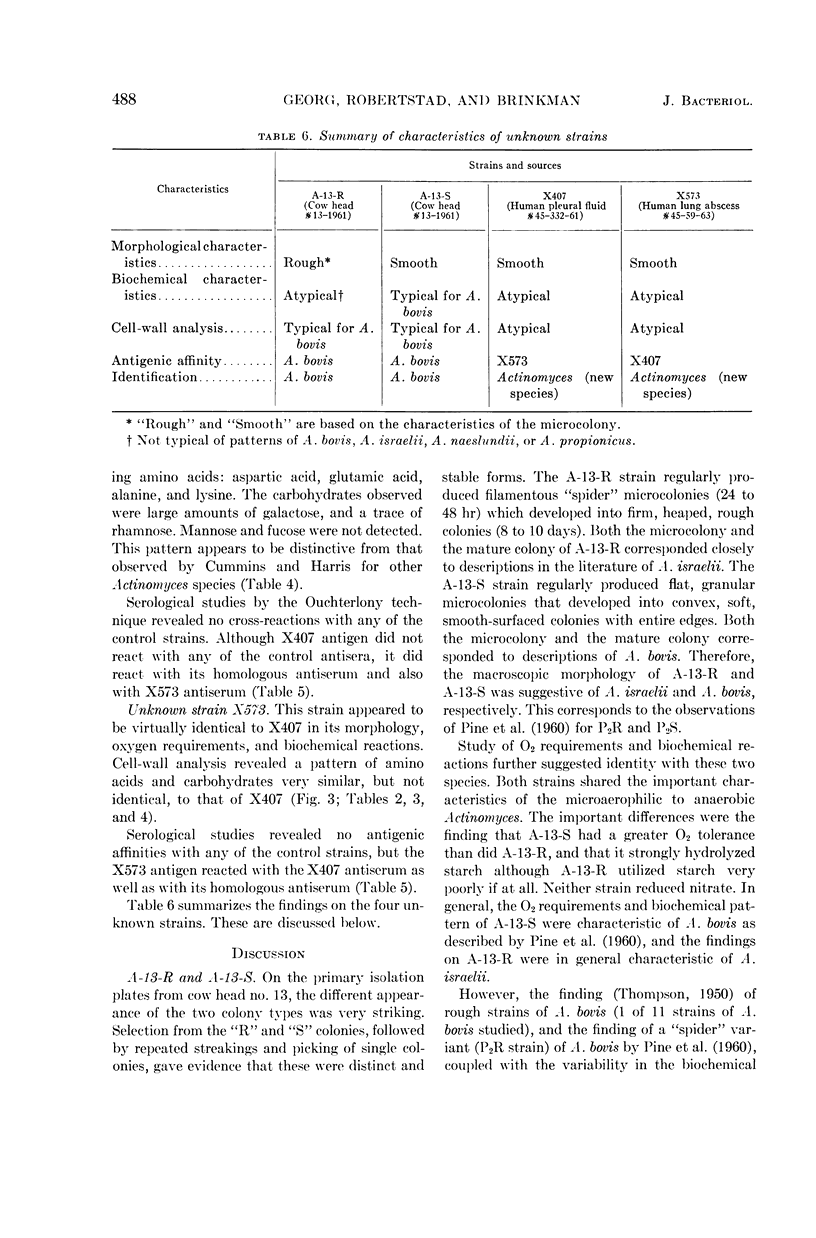
Georg, Lucille K. (Communicable Disease Center, Atlanta, Ga.), Gordon W. Robertstad, and Sherry A. Brinkman. Identification of species of Actinomyces. J. Bacteriol. 88:477–490. 1964.—Four unusual isolates of Actinomyces species were compared with six control strains of well-identified Actinomyces species. Their oxygen requirements and their morphological and biochemical characteristics were determined. Final identifications were confirmed by cell-wall analyses for amino acid and carbohydrate composition and by agar-gel techniques. Two strains, A-13-R and A-13-S, isolated from the same cow head were shown to represent rough and smooth variants of A. bovis. The strains were not only morphologically distinct, but had different biochemical reactions and antigenic makeup. The two other strains, X407 and X573, isolated from human pleural fluid and a lung abscess, respectively, were shown to represent a new Actinomyces species.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BUCHANAN B. B., PINE L. Characterization of a propionic acid producing actinomycete, Actinomyces propionicus, sp. nov. J Gen Microbiol. 1962 Jun;28:305–323. doi: 10.1099/00221287-28-2-305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CUMMINS C. S. Chemical composition and antigenic structure of cell walls of Corynebacterium, Mycobacterium, Nocardia, Actinomyces and Arthrobacter. J Gen Microbiol. 1962 Apr;28:35–50. doi: 10.1099/00221287-28-1-35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CUMMINS C. S., HARRIS H. Studies on the cell-wall composition and taxonomy of Actinomycetales and related groups. J Gen Microbiol. 1958 Feb;18(1):173–189. doi: 10.1099/00221287-18-1-173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOWELL A., Jr, MURPHY W. C., 3rd, PAUL F., STEPHAN R. M. Oral strains of Actinomyces. J Bacteriol. 1959 Jul;78(1):82–95. doi: 10.1128/jb.78.1.82-95.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOWELL A., Jr, PINE L. Studies on the growth of species of Actinomyces. I. Cultivation in a synthetic medium with starch. J Bacteriol. 1956 Jan;71(1):47–53. doi: 10.1128/jb.71.1.47-53.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOWELL A., Jr, STEPHAN R. M., PAUL F. Prevalence of Actin-omyces israelii, A. naeslundii, Bacterionema matruchotii, and Candida albicans in selected areas of the oral cavity and saliva. J Dent Res. 1962 Sep-Oct;41:1050–1059. doi: 10.1177/00220345620410050701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KING S., MEYER E. Gel diffusion technique in antigen-antibody reactions of Actinomyces species and "anaerobic diphtheroids". J Bacteriol. 1963 Jan;85:186–190. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.1.186-190.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OVERMAN J. R., PINE L. ELECTRON MICROSCOPY OF CYTOPLASMIC STRUCTURES IN FACULTATIVE AND ANAEROBIC ACTINOMYCES. J Bacteriol. 1963 Oct;86:656–665. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.4.656-665.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PINE L., HARDIN H. Actinomyces israelii, a cause of lacrimal canaliculitis in man. J Bacteriol. 1959 Aug;78:164–170. doi: 10.1128/jb.78.2.164-170.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PINE L., HOWELL A., Jr, WATSON S. J. Studies of the morphological, physiological, and biochemical characters of Actinomyces bovis. J Gen Microbiol. 1960 Dec;23:403–424. doi: 10.1099/00221287-23-3-403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHUBERT J. H., LYNCH H. J., Jr, AJELLO L. Evaluation of the agar-plate precipitin test for histoplasmosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1961 Dec;84:845–849. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1961.84.6.845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMPSON L. Isolation and comparison of Actinomyces from human and bovine infections. Proc Staff Meet Mayo Clin. 1950 Feb 15;25(4):81–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMPSON L., LOVESTEDT S. A. An Actinomyces-like organism obtained from the human mouth. Proc Staff Meet Mayo Clin. 1951 May 9;26(10):169–175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]