Abstract
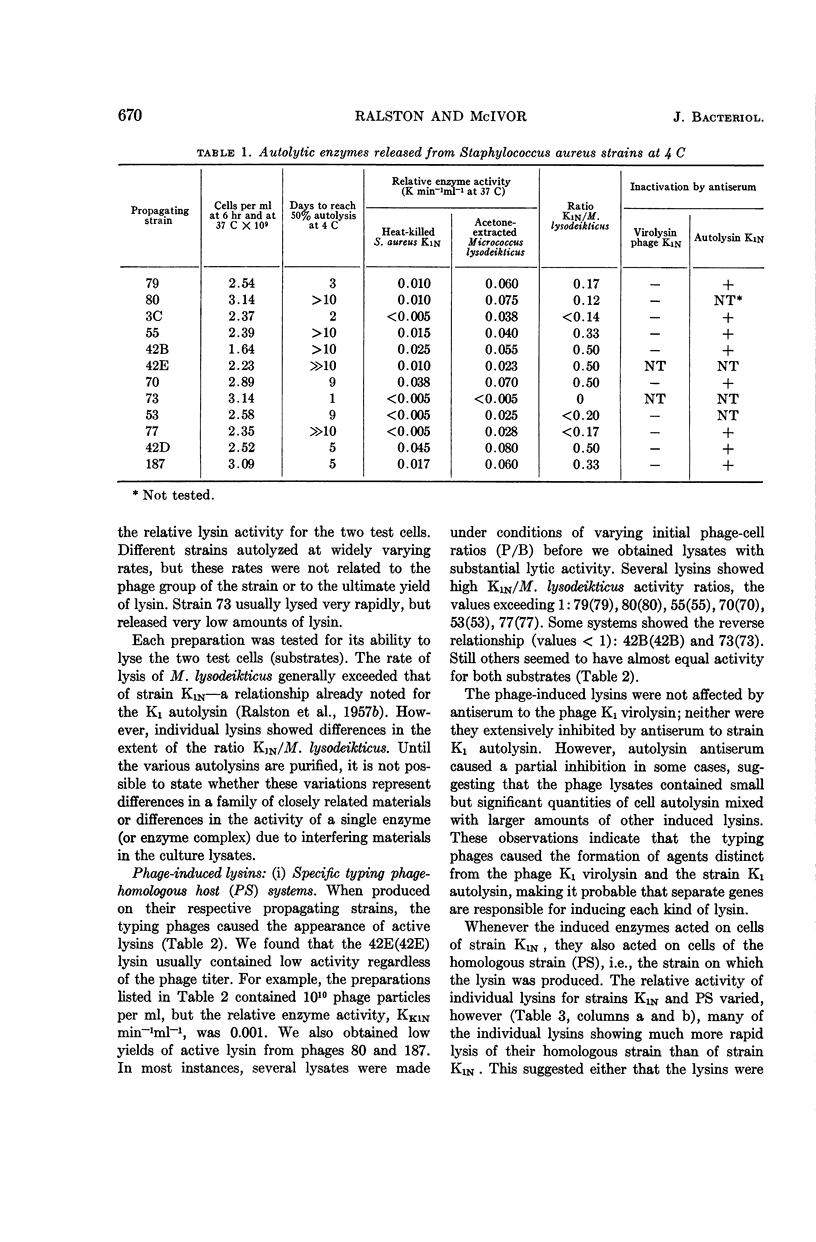
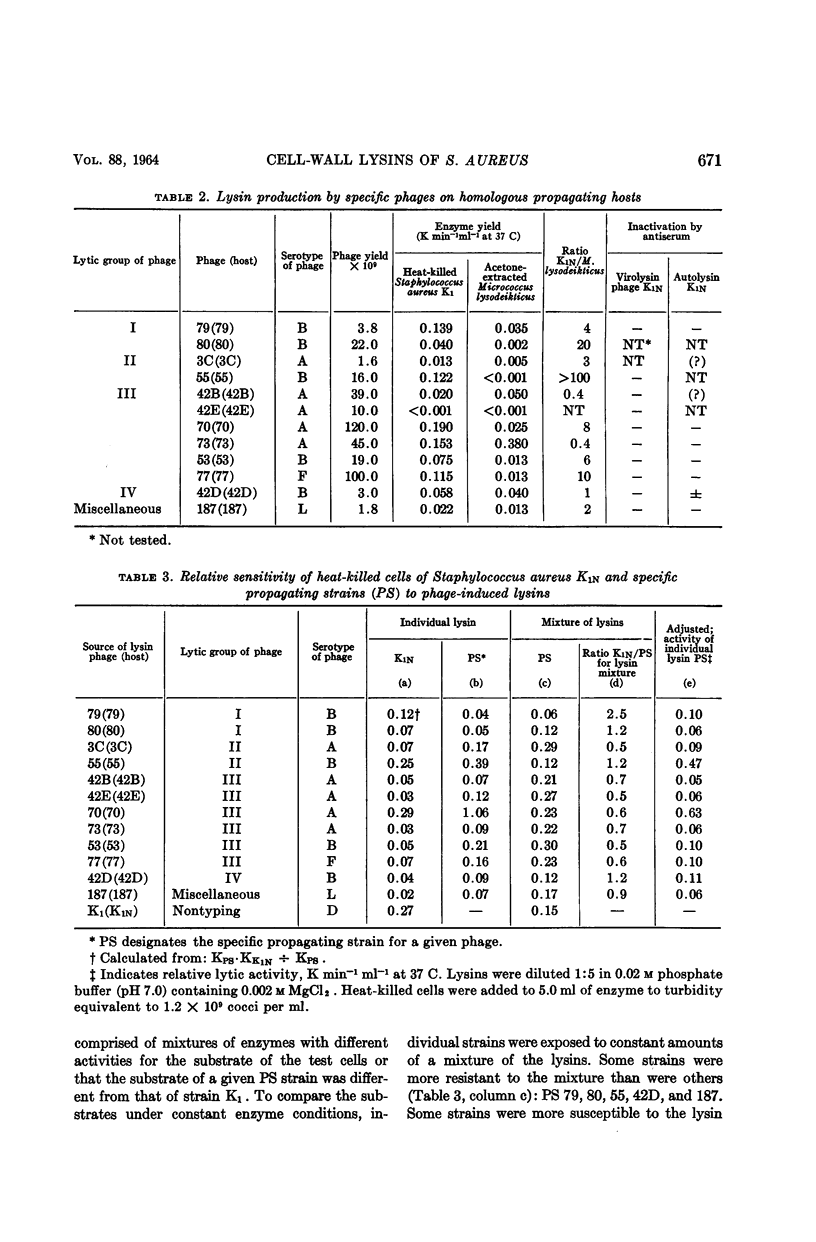
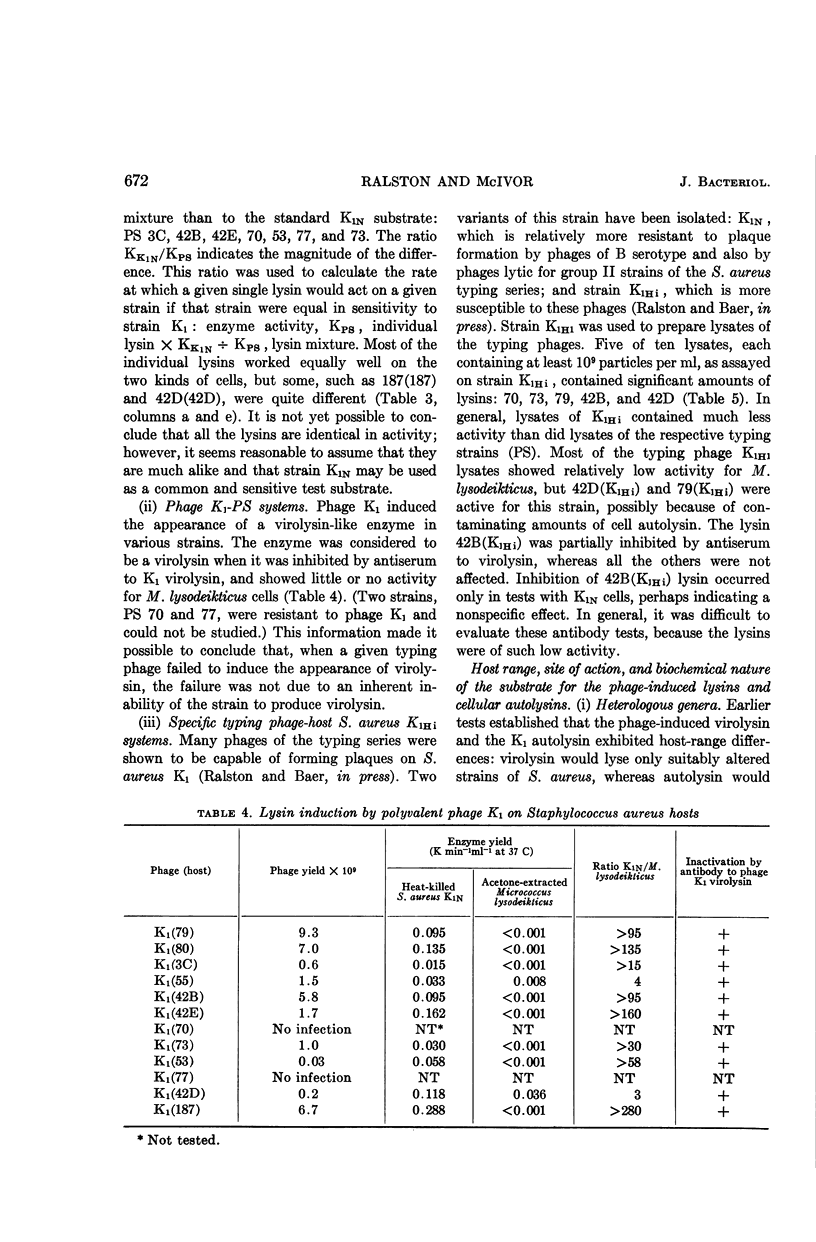
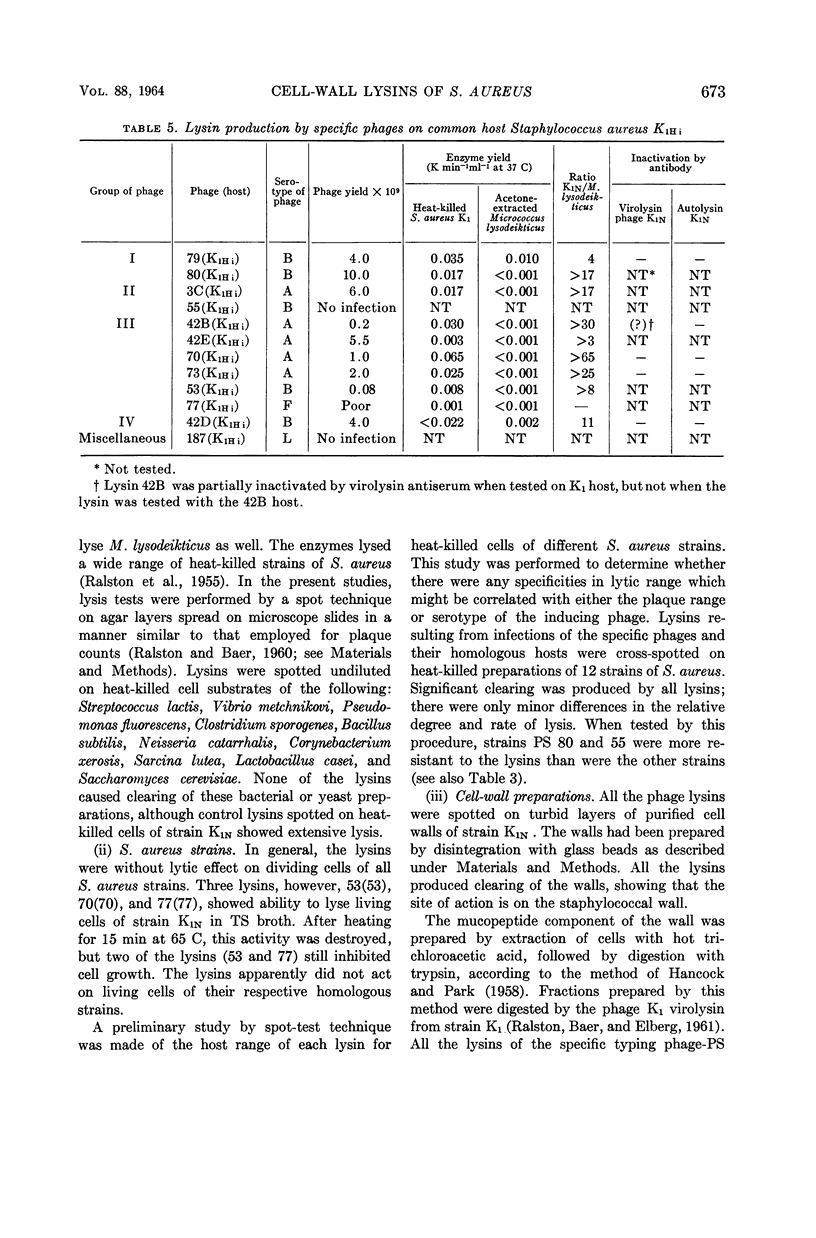
Ralston, Doris J. (University of California, Berkeley), and Mary McIvor. Cell-wall lysins of Staphylococcus aureus strains induced by specific typing phages. J. Bacteriol. 88:667–675. 1964.—At least 12 different phages induced the formation of soluble lysins (separable from the phages by ultracentrifugation). The lysins caused rapid clearing of heat-killed cells of all strains of Staphylococcus aureus tested, irrespective of the capacity of the phage to form plaques on living cells of the strain. The uninfected cells of the 12 strains contained a second lysin, an autolysin, released upon cellular autolysis. The autolysin preparations differed from the phage-induced lysins, in that they exhibited relatively high activity for lysing Micrococcus lysodeikticus and low activity for strain S. aureus K1N, and were each specifically inhibited by antiserum prepared against purified autolysin from strain K1. A third kind of lysin, virolysin, induced by polyvalent phage K, was differentiated from the lysins of the specific phages on the basis of its antigenic specificity and lack of action on M. lysodeikticus. All three kinds of lysins digested the mucopeptide portion of staphylococcal cell walls. No evidence was found that any of these lysins possessed specific host ranges which could be correlated with the lytic host range of the inducing phage.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- HANCOCK R., PARK J. T. Cell-wall synthesis by Staphylococcus aureus in the presence of chloramphenicol. Nature. 1958 Apr 12;181(4615):1050–1052. doi: 10.1038/1811050a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RALSTON D. J., BAER B. S., ELBERG S. S. Lysis of brucellae by the combined action of glycine and a lysozyme-like agent from rabbit monocytes. J Bacteriol. 1961 Sep;82:342–353. doi: 10.1128/jb.82.3.342-353.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RALSTON D. J., BAER B. S., LIEBERMAN M., KRUEGER A. P. Lysis from without of S. aureus K1 by the combined action of phage and virolysin. J Gen Physiol. 1957 Nov 20;41(2):343–358. doi: 10.1085/jgp.41.2.343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RALSTON D. J., BAER B. S., LIEBERMAN M., KRUEGER A. P. Virolysin: a virus-induced lysin from staphylococcal phage lysates. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1955 Aug;89(4):502–507. doi: 10.3181/00379727-89-21859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RALSTON D. J., BAER B., LIEBERMAN M., KRUEGER A. P. Virolysin, a virus-induced lysin: its appearance and function in phage-infected staphylococci. J Gen Microbiol. 1961 Mar;24:313–325. doi: 10.1099/00221287-24-3-313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RALSTON D. J., LIEBERMAN M., BAER B., KRUEGER A. P. Staphylococcal virolysin, a phage-induced lysin; its differentiation from the autolysis of normal cells. J Gen Physiol. 1957 May 20;40(5):791–807. doi: 10.1085/jgp.40.5.791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RALSTON D. J., MCIVOR M. LYSIS-FROM-WITHOUT OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS STRAINS BY COMBINATIONS OF SPECIFIC PHAGES AND PHAGE-INDUCED LYTIC ENZYMES. J Bacteriol. 1964 Sep;88:676–681. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.3.676-681.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHMOND M. H. Lytic enzymes of Staphylococcus aureus 524. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Feb;31(2):564–565. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90041-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RIPPON J. E. The classification of bacteriophages lysing staphylococci. J Hyg (Lond) 1956 Jun;54(2):213–226. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400044478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralston D. J., Baer B. IMPROVED METHOD OF PHAGE ASSAY BY A PLAQUE COUNT METHOD ON MICROSCOPE SLIDES IN TRAYS. J Bacteriol. 1960 May;79(5):758–759. doi: 10.1128/jb.79.5.758-759.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



