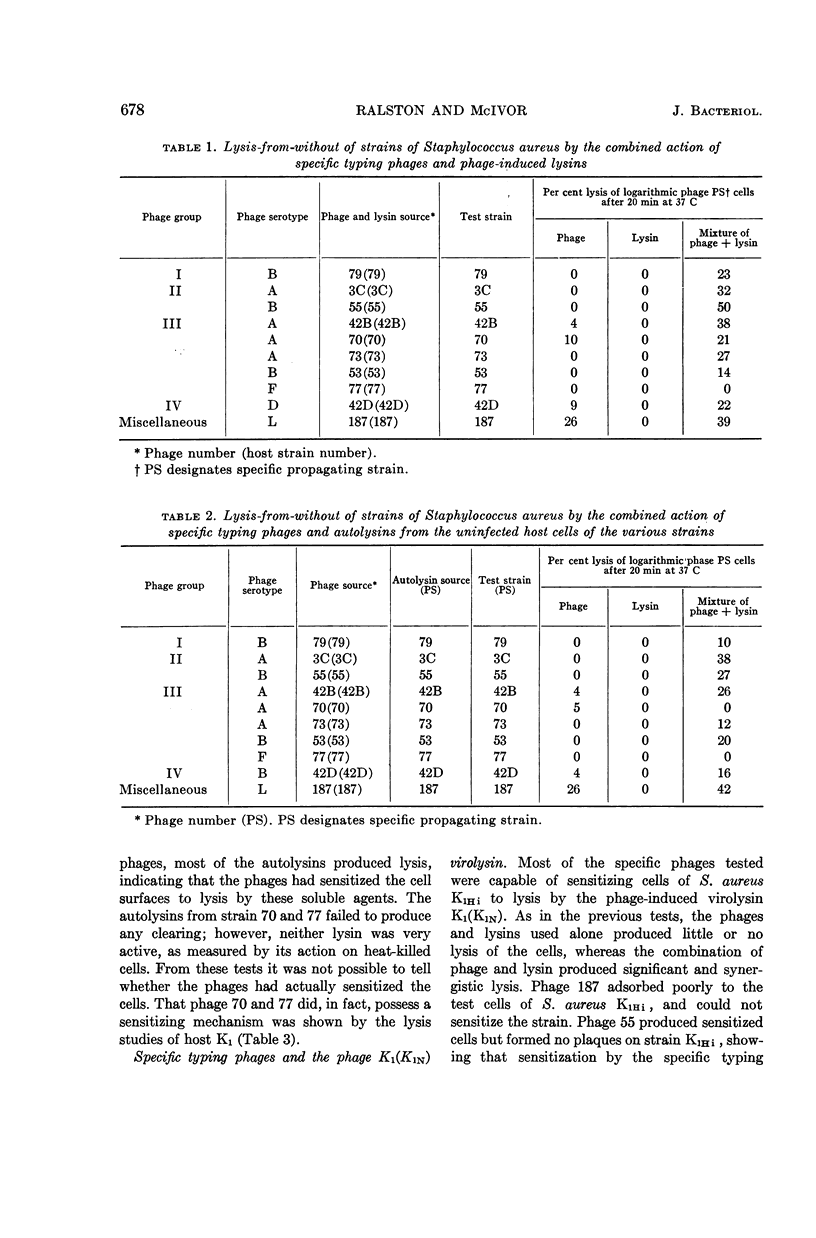
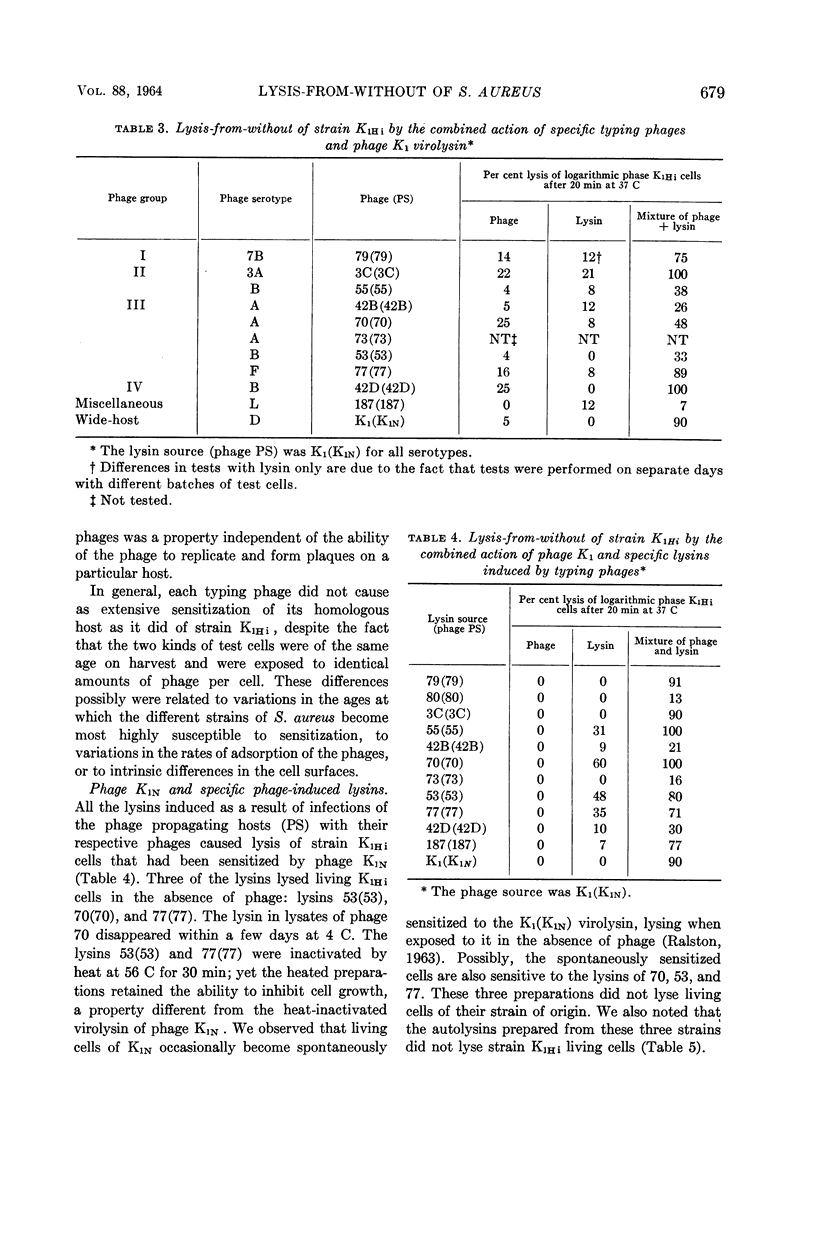
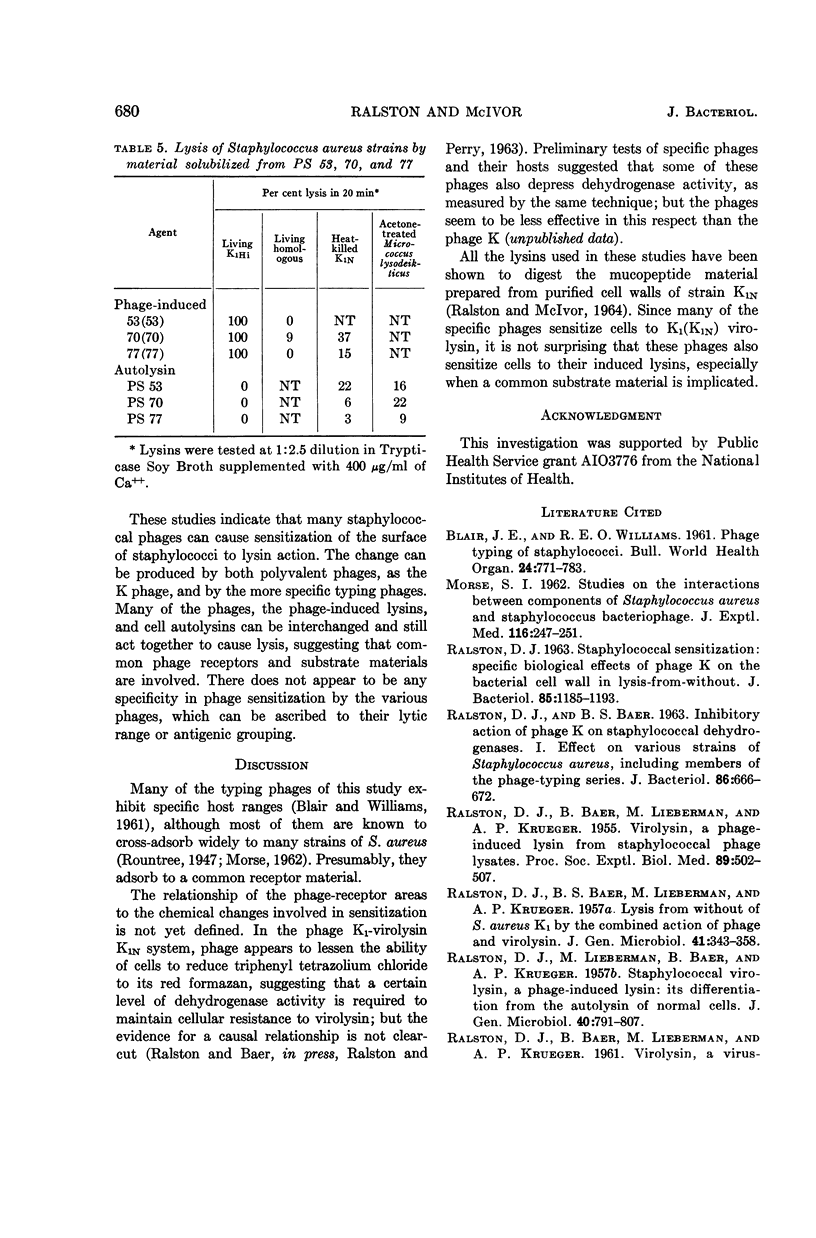
Abstract
Ralston, Doris J. (University of California, Berkeley) and Mary McIvor. Lysis-from-without of Staphylococcus aureus strains by combinations of specific phages and phage-induced lytic enzymes. J. Bacteriol. 88:676–681. 1964—Several typing phages, adsorbed in sufficient concentrations to their homologous propagating strains, altered the cell surface so as to render the cells sensitive to rapid and synergistic lysis by extra-cellular additions of wall lysins. Lysis was effected both by lysins induced by the individual phages and by phage K1 virolysin. Phage K1 also rendered cells sensitive to the lysins of the typing phages. With the exception of lysins from PS 53, 70, and 77, none of the lysins nor purified phages tested separately caused significant lysis of living cells. Lysis-from-without in Staphylococcus aureus appears to be a stepwise process: sensitization by phage followed by digestion of the wall by lysin.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- MORSE S. I. Studies on the interactions between components of Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus bacteriophage. J Exp Med. 1962 Aug 1;116:247–251. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.2.247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RALSTON D. J., BAER B. S. INHIBITORY ACTION OF PHAGE K ON STAPHYLOCOCCAL DEHYDROGENASES. I. EFFECT ON VARIOUS STRAINS OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS, INCLUDING MEMBERS OF THE PHAGE-TYPING SERIES. J Bacteriol. 1963 Oct;86:666–672. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.4.666-672.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RALSTON D. J., BAER B. S., LIEBERMAN M., KRUEGER A. P. Lysis from without of S. aureus K1 by the combined action of phage and virolysin. J Gen Physiol. 1957 Nov 20;41(2):343–358. doi: 10.1085/jgp.41.2.343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RALSTON D. J., BAER B. S., LIEBERMAN M., KRUEGER A. P. Virolysin: a virus-induced lysin from staphylococcal phage lysates. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1955 Aug;89(4):502–507. doi: 10.3181/00379727-89-21859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RALSTON D. J., LIEBERMAN M., BAER B., KRUEGER A. P. Staphylococcal virolysin, a phage-induced lysin; its differentiation from the autolysis of normal cells. J Gen Physiol. 1957 May 20;40(5):791–807. doi: 10.1085/jgp.40.5.791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RALSTON D. J., MCIVOR M. CELL-WALL LYSINS OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS STRAINS INDUCED BY SPECIFIC TYPING PHAGES. J Bacteriol. 1964 Sep;88:667–675. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.3.667-675.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RALSTON D. J., PERRY M. D. INHIBITORY ACTION OF PHAGE K ON STAPHYLOCOCCAL DEHYDROGENASES. II. ITS POSSIBLE RELATIONSHIP TO SENSITIZATION AND CELL LYSIS. J Bacteriol. 1963 Oct;86:740–748. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.4.740-748.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RALSTON D. J. STAPHYLOCOCCAL SENSITIZATION: SPECIFIC BIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF PHAGE K ON THE BACTERIAL CELL WALL IN LYSIS-FROM-WITHOUT. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jun;85:1185–1193. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.6.1185-1193.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


