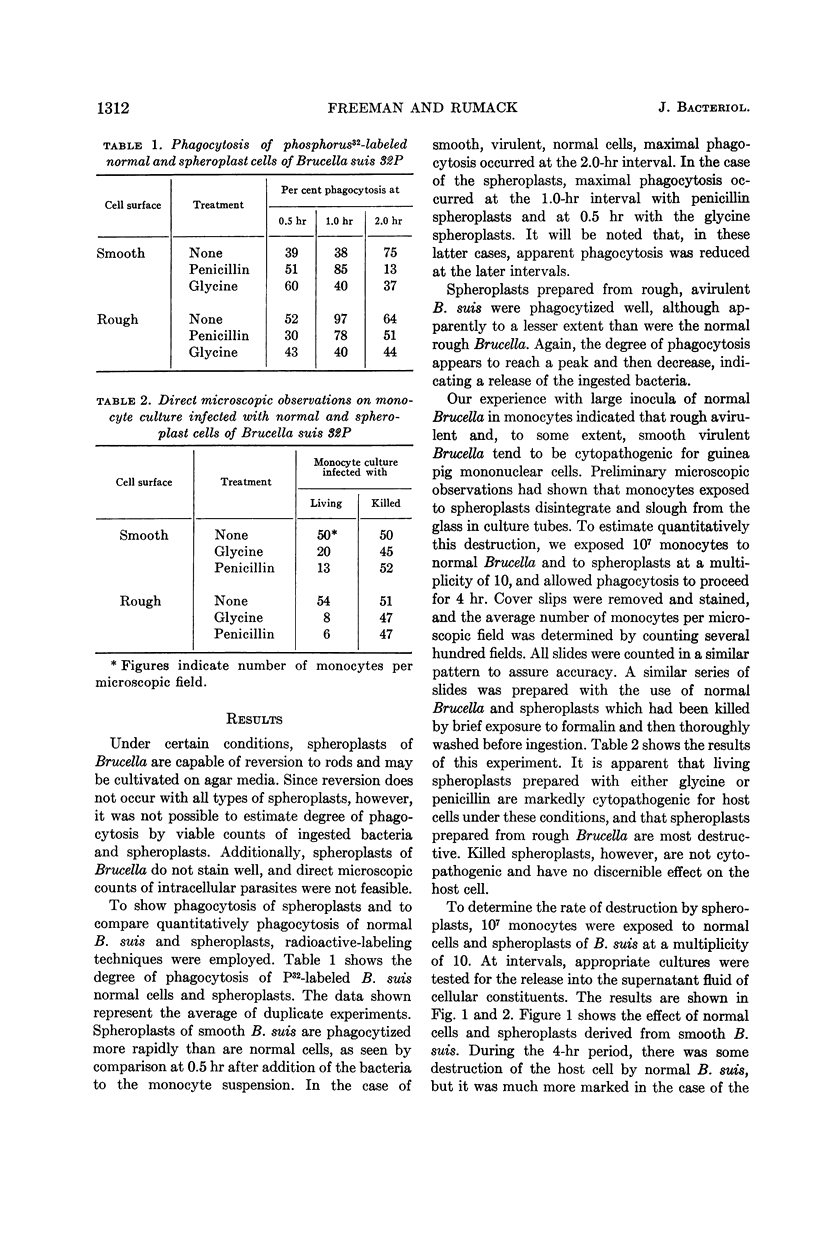
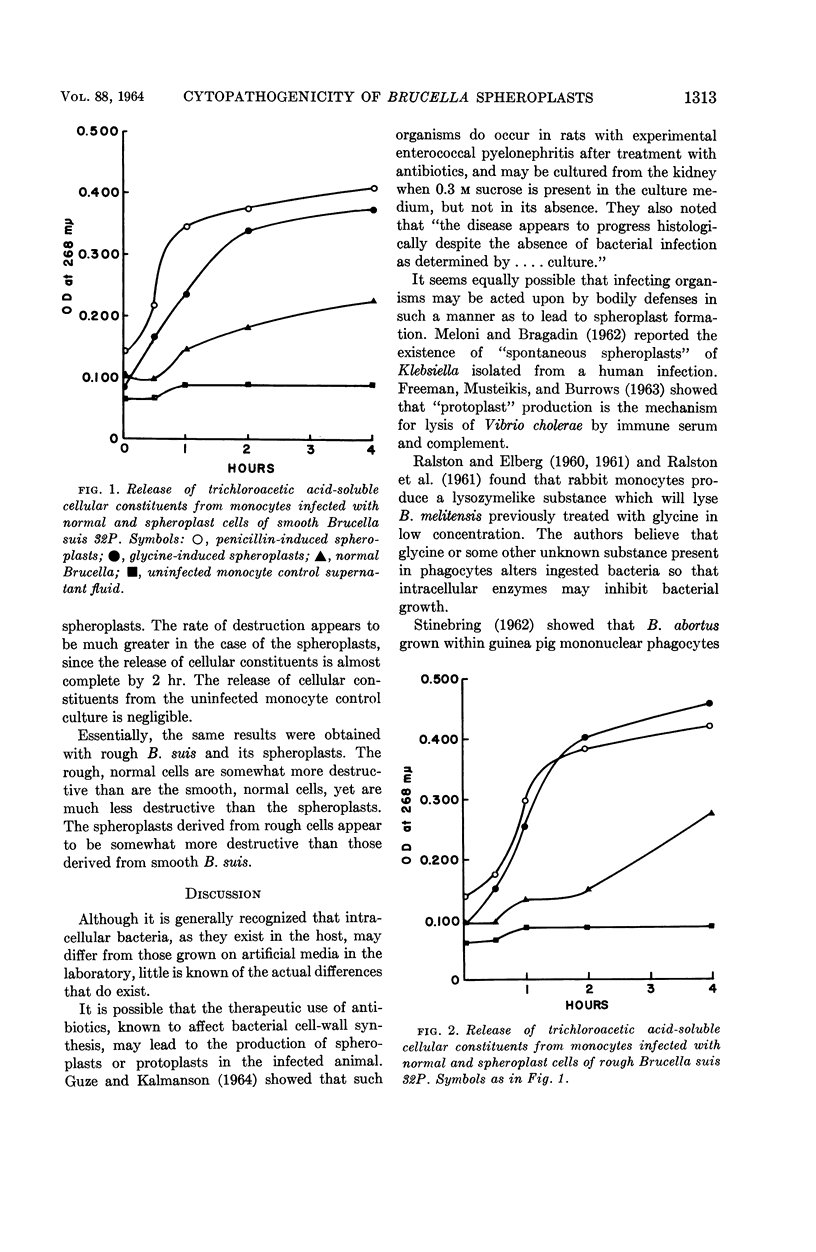
Abstract
Freeman, Bob A. (The University of Chicago, Chicago, Ill.), and Barry H. Rumack. Cytopathogenic effect of Brucella spheroplasts on monocytes in tissue culture. J. Bacteriol. 88:1310–1315. 1964.—Mononuclear phagocytes from guinea pig peritoneal exudates were shown to ingest both normal Brucella suis and spheroplasts prepared from B. suis by treatment with glycine and with penicillin. Quantitative ingestion studies with P32-labeled Brucella showed that rough normal Brucella are ingested at a greater rate than are smooth normal Brucella. Spheroplasts prepared from smooth cells were phagocytized at a greater rate than were the normal smooth cells, and spheroplasts prepared from rough Brucella were phagocytized well, although apparently to a lesser extent than from the normal rough Brucella. The degree of phagocytosis of all spheroplasts appeared to reach a peak and then decrease, indicating a release of ingested bacteria; this release of intracellular bacteria is believed to be due to the cytopathogenic effect exerted by the spheroplasts. Direct microscopic observations showed that infection with living spheroplasts prepared from either smooth or rough Brucella destroyed a major portion of the host cells within 4 hr, but that formalin-killed spheroplasts were no more destructive than were normal Brucella. When host cell destruction was assayed by the release of cellular constituents into the medium, it was apparent that host-cell destruction by spheroplasts reaches a significant level within 0.5 hr after ingestion begins, and is almost complete by 4 hr. The implications of these findings in studies on the nature of intracellular Brucella are discussed.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ELBERG S. S. Cellular immunity. Bacteriol Rev. 1960 Mar;24(1):67–95. doi: 10.1128/br.24.1.67-95.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREEMAN B. A., KROSS D. J., CIRCO R. Host-parasite relationships in brucellosis. II. Destruction of macrophage cultures by Brucella of different virulence. J. J Infect Dis. 1961 May-Jun;108:333–338. doi: 10.1093/infdis/108.3.333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREEMAN B. A., MUSTEIKIS G. M., BURROWS W. Protoplast formation as the mechanism for immune lysis of Vibrio cholerae. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1963 Jul;113:675–680. doi: 10.3181/00379727-113-28459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUZE L. B., KALMANSON G. M. PERSISTENCE OF BACTERIA IN "PROTOPLAST" FORM AFTER APPARENT CURE OF PYELONEPHRITIS IN RATS. Science. 1964 Mar 20;143(3612):1340–1341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEILMAN D. H., HOWARD D. H., CARPENTER C. M. Tissue culture studies on bacterial allergy in experimental brucellosis. I. The effect of Brucella suis whole antigen on cultures of spleen from normal and brucella-infected guinea pigs. J Exp Med. 1958 Feb 1;107(2):319–332. doi: 10.1084/jem.107.2.319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEILMAN D. H., RICE E., HOWARD D. H., WEIMER H. E., CARPENTER C. M. Tissue culture studies on bacterial allergy in experimental brucellosis. II. The cytotoxicity of nucleoprotein fractions of brucellae. J Immunol. 1960 Sep;85:258–267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HINES W. D., FREEMAN B. A., PEARSON G. R. PRODUCTION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF BRUCELLA SPHEROPLASTS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Feb;87:438–445. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.2.438-445.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RALSTON D. J., BAER B. S., ELBERG S. S. Lysis of brucellae by the combined action of glycine and a lysozyme-like agent from rabbit monocytes. J Bacteriol. 1961 Sep;82:342–353. doi: 10.1128/jb.82.3.342-353.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RALSTON D. J., ELBERG S. S. Action of glycine and a lysozymelike agent from rabbit monocytes in destruction of Brucella. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1960 Jul;104:464–467. doi: 10.3181/00379727-104-25874. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RALSTON D. J., ELBERG S. S. Intramonocytic destruction of Brucella: potentiating effect of glycine on intracellular lysozyme activity. J Infect Dis. 1961 Jul-Aug;109:71–80. doi: 10.1093/infdis/109.1.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STINEBRING W. R. Characteristics of intracellularly grown Brucella abortus. J Infect Dis. 1962 Jul-Aug;111:17–24. doi: 10.1093/infdis/111.1.17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



