Abstract
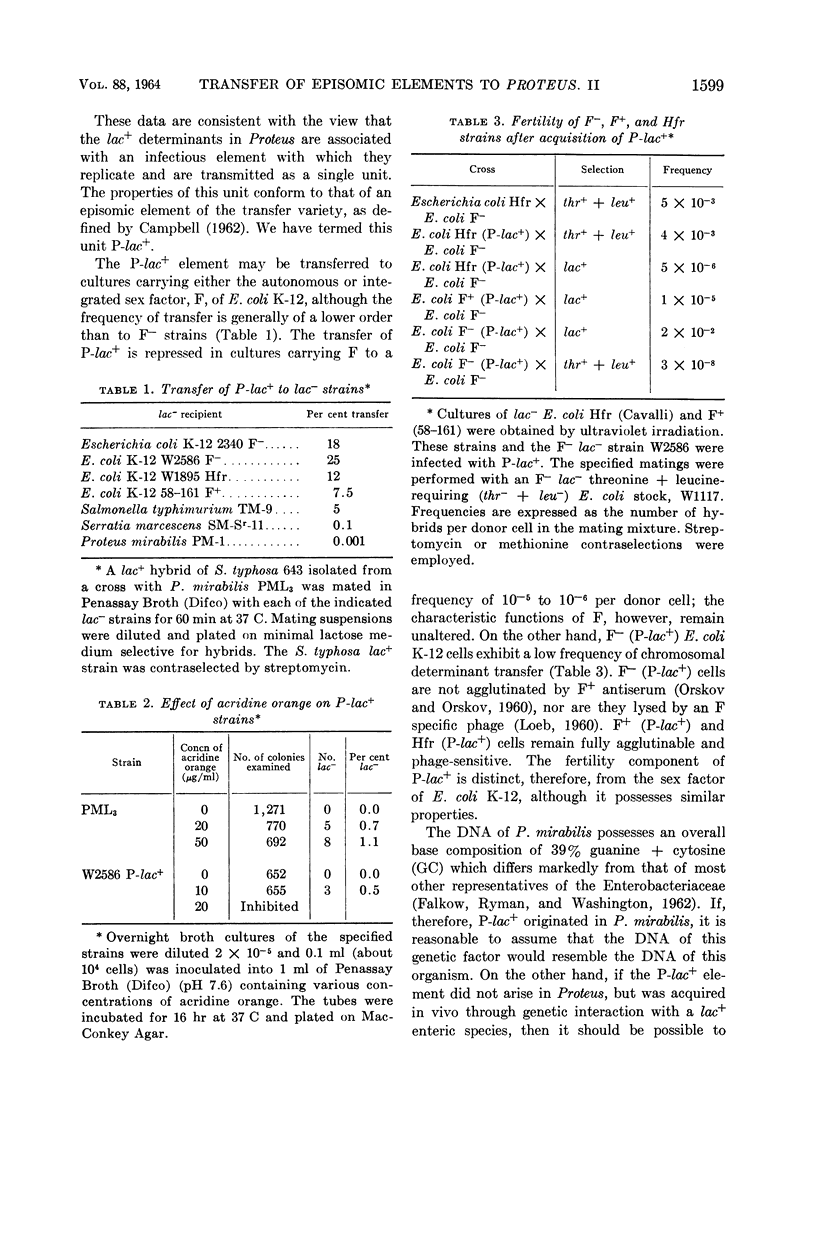
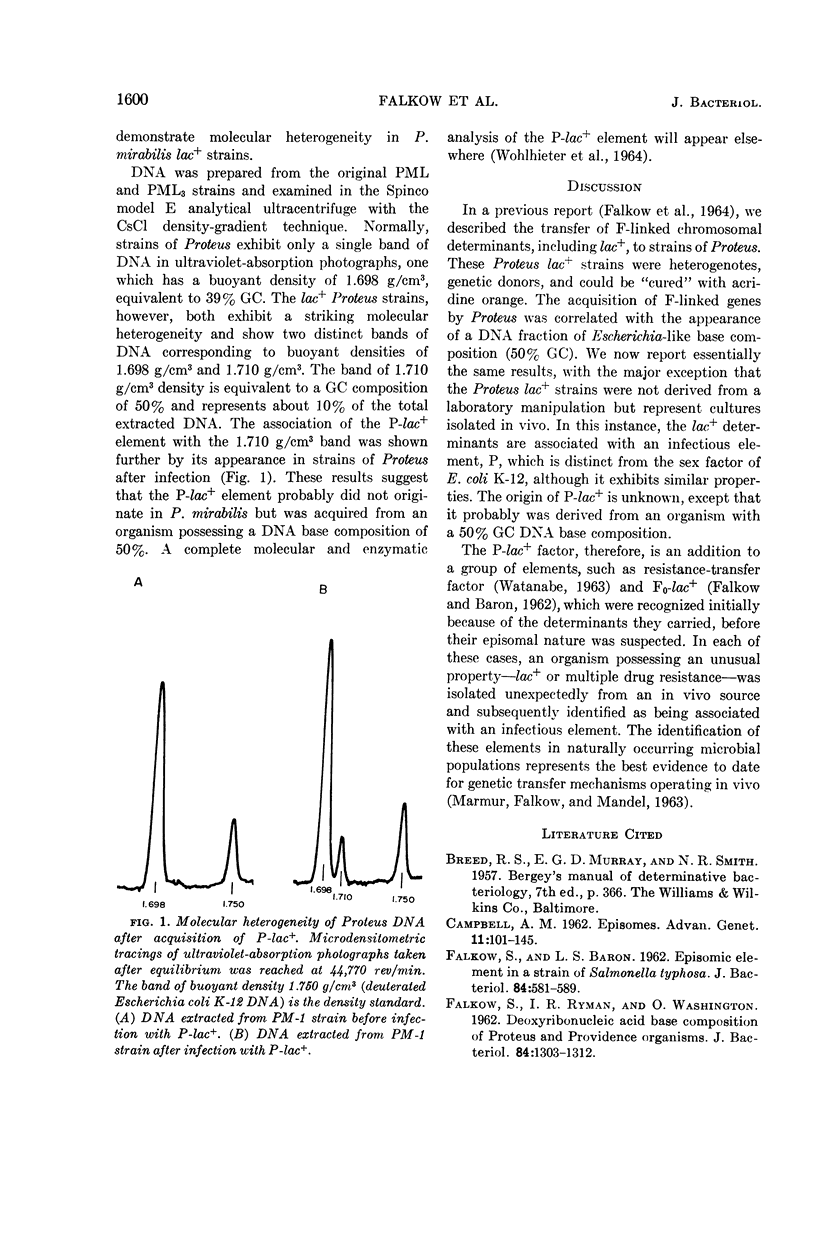
Falkow, Stanley (Walter Reed Army Institute of Research, Washington, D.C.), J. A. Wohlhieter, R. V. Citarella, and L. S. Baron. Transfer of episomic elements to Proteus. II. Nature of lac+Proteus strains isolated from clinical specimens. J. Bacteriol. 88:1598–1601. 1964.—Strains of Proteus mirabilis exhibiting the unusual property of utilizing lactose (lac+) have been reported in clinical material. A genetic examination discloses that the lac+ determinants in these Proteus strains are associated with an infectious element, P, which is distinct from the sex factor of Escherichia coli K-12. The composite genetic element, P-lac, is readily transmissible to other enteric species and possesses properties which conform to those of an episomic element of the transfer variety. CsCl density-gradient studies of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) extracted from lac+P. mirabilis indicate that the P-lac+ element did not arise in this species, but was acquired from an organism possessing a markedly different DNA base composition.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- FALKOW S., WOHLHIETER J. A., CITARELLA R. V., BARON L. S. TRANSFER OF EPISOMIC ELEMENTS TO PROTEUS. I. TRANSFER OF F-LINKED CHROMOSOMAL DETERMINANTS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Jan;87:209–219. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.1.209-219.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkow S., Baron L. S. EPISOMIC ELEMENT IN A STRAIN OF SALMONELLA TYPHOSA. J Bacteriol. 1962 Sep;84(3):581–589. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.3.581-589.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkow S., Rownd R., Baron L. S. GENETIC HOMOLOGY BETWEEN ESCHERICHIA COLI K-12 AND SALMONELLA. J Bacteriol. 1962 Dec;84(6):1303–1312. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.6.1303-1312.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOEB T. Isolation of a bacteriophage specific for the F plus and Hfr mating types of Escherichia coli K-12. Science. 1960 Mar 25;131(3404):932–933. doi: 10.1126/science.131.3404.932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARMUR J., FALKOW S., MANDEL M. NEW APPROACHES TO BACTERIAL TAXONOMY. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1963;17:329–372. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.17.100163.001553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORSKOV I., ORSKOV F. An antigen termed f-plus occurring in F-plus E. coli strains. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1960;48:37–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUTTER V. L., FOECKING F. J. Biochemical characteristics of lactose-fermenting Proteus rettgeri from clinical specimens. J Bacteriol. 1962 Apr;83:933–935. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.4.933-935.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATANABE T. Infective heredity of multiple drug resistance in bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1963 Mar;27:87–115. doi: 10.1128/br.27.1.87-115.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOHLHIETER J. A., FALKOW S., CITARELLA R. V., BARON L. S. CHARACTERIZATION OF DNA FROM A PROTEUS STRAIN HARBORING AN EPISOME. J Mol Biol. 1964 Aug;9:576–588. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80228-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



