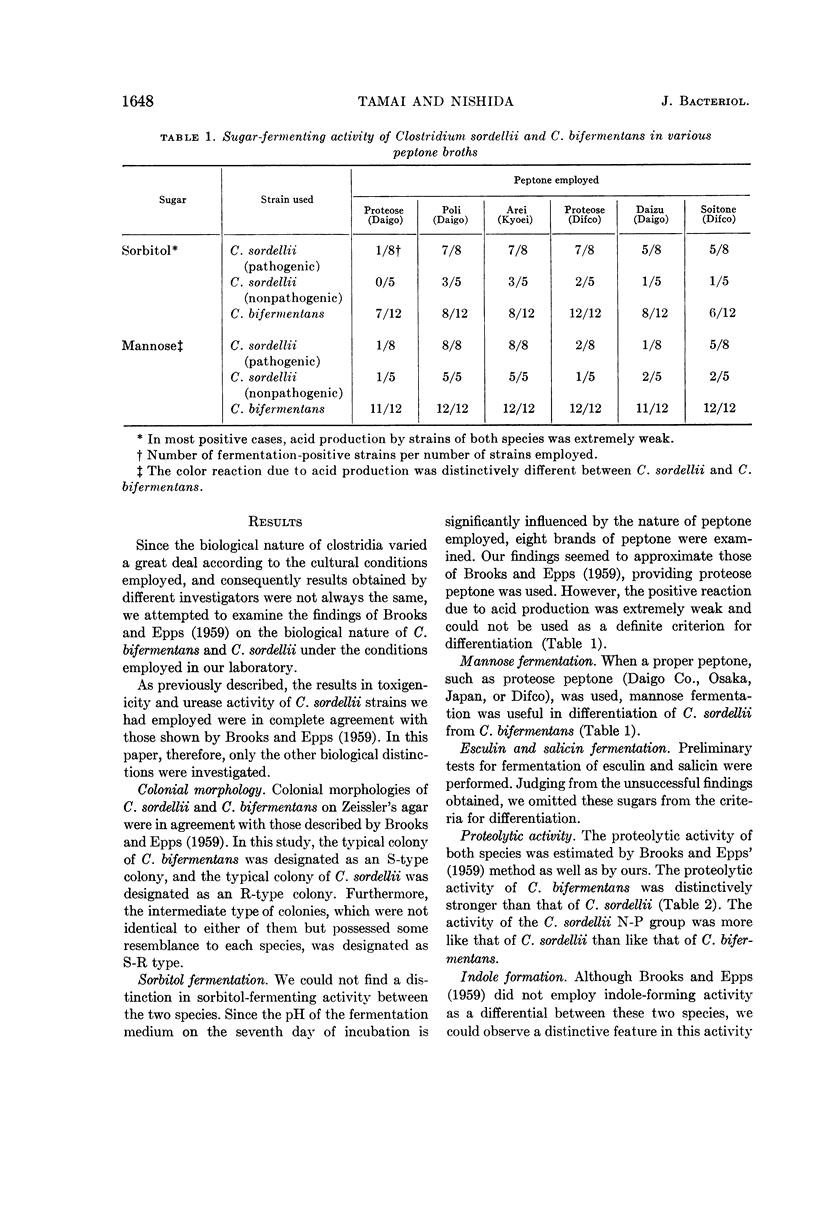
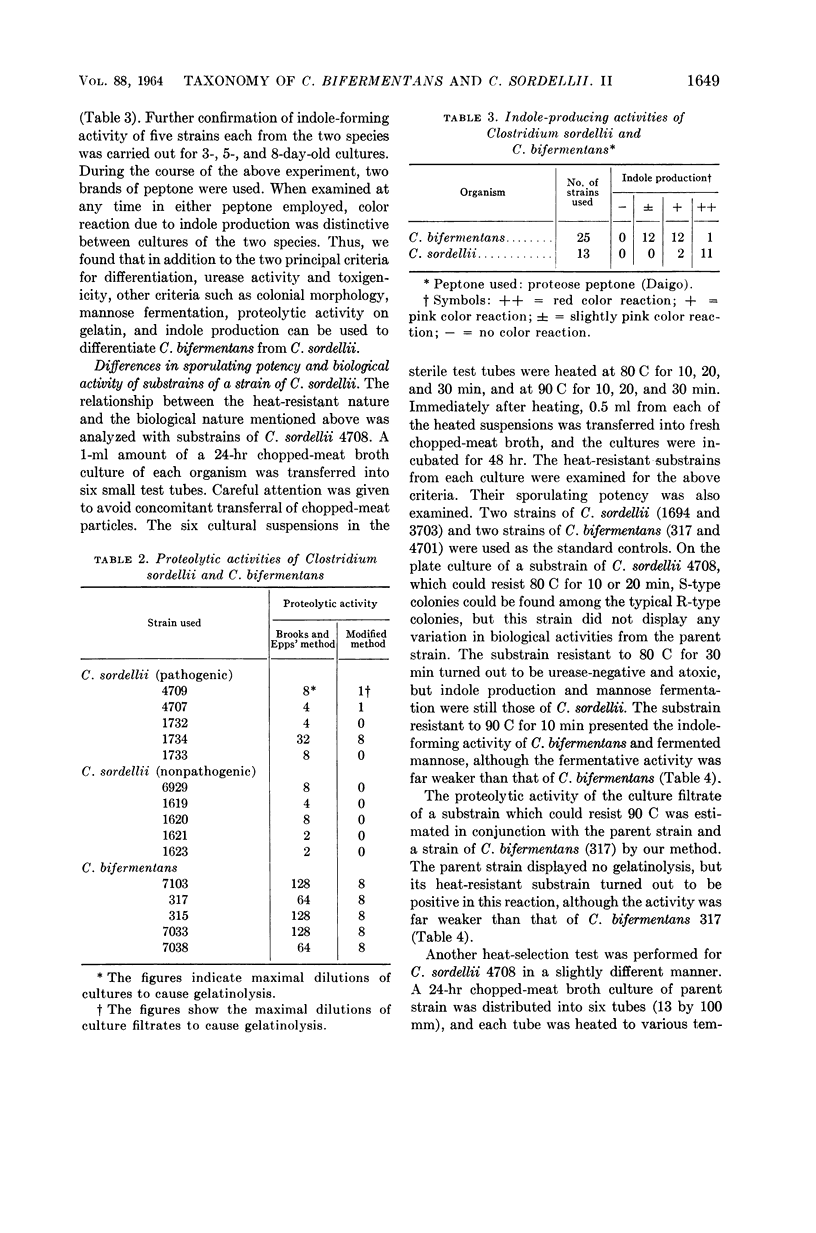
Abstract
Tamai, Kenzo (Kanazawa University, Kanazawa, Japan), and Shoki Nishida. Taxonomy of Clostridium bifermentans and Clostridium sordellii. II. Toxigenic and sporulating potencies in substrains of a Clostridium sordellii strain. J. Bacteriol. 88:1647–1651. 1964.—The existence of six biological criteria for distinction of Clostridium bifermentans and C. sordellii was confirmed. The difference in the six criteria gradually disappeared as the sporulating potency of the substrains of C. sordellii 4708 was strengthened. The substrains which could resist heating at 90 C for 10, 20, or 30 min were found to have lost all six criteria for distinction and were biologically in agreement with C. bifermentans. We further demonstrated that all newly isolated strains of C. bifermentans examined possessed extremely strong sporulating potency.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BROOKS M. E., EPPS H. B. Taxonomic studies of the genus Clostridium: Clostrididum bifermentans and C. sordellii. J Gen Microbiol. 1959 Aug;21:144–155. doi: 10.1099/00221287-21-1-144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NISIDA S., TAMAI K., YAMAGISHI T. TAXONOMY OF CLOSTRIDIUM BIFERMENTANS AND CLOSTRIDIUM SORDELLII. I. THEIR TOXIGENICITY, UREASE ACTIVITY, AND SPORULATING POTENCY. J Bacteriol. 1964 Dec;88:1641–1646. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.6.1641-1646.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YAMAGISHI T., ISHIDA S., NISHIDA S. ISOLATION OF TOXIGENIC STRAINS OF CLOSTRIDIUM PERFRINGENS FROM SOIL. J Bacteriol. 1964 Sep;88:646–652. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.3.646-652.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


