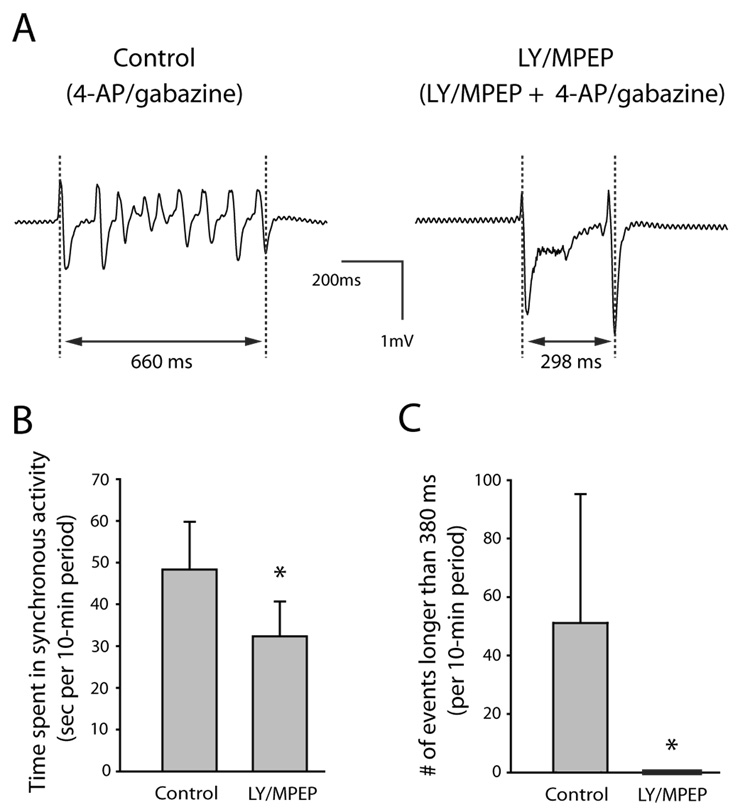
Fig. 5. Group I mGluR antagonists LY 367385 and MPEP reduced epileptiform activity induced by co-application of 4-AP and the GABAA antagonist gabazine. Slices from the same animal were paired (n = 7 pairs). The control group of slices was exposed only to 4-AP/gabazine. The experimental group of slices was first exposed to LY/MPEP alone for 30–40 min and then to 4-AP/gabazine in the continued presence of LY/MPEP.
A: Extracellular voltage traces showing a single epileptiform event recorded from control slice exposed only to 4-AP/gabazine (left) and experimental slice exposed to LY/MPEP and 4-AP/gabazine (right). Electrode was placed at stratum lacunosum-moleculare /stratum radiatum border in CA3. Each synchronous event was measured from the first peak of the initial deflection to the final peak of the last deflection as indicated in the figure. B: The slices exposed to LY/MPEP spent significantly less time in synchronous activity than control slices. In both control and experimental slices, all synchronous events occurring in the 10-minute period between 30 and 40 minutes of 4-AP/gabazine exposure were measured and the lengths were added together as a measure of time spent in synchronous activity per 10-min period. C: There were significantly more synchronous events longer than 380 ms in the control slices than in those exposed to LY/MPEP. Error bars are SD. * indicates statistically significant.