Abstract
Galasso, G. J. (University of North Carolina School of Medicine, Chapel Hill), and D. G. Sharp. Effects of heat on the infecting, antibody-absorbing, and interfering powers of vaccinia virus. J. Bacteriol. 89:611–616. 1965.—At 56 C the infectivity of vaccinia virus particles is destroyed rapidly, but even when it is reduced by a factor of 106 the particles are capable of producing strong interference in L cells. The rate constant K for thermal inactivation of plaque-forming power is greater than that for interfering power by the factor e3.8 or about 45 times. At 37 C both properties of the virus decline more slowly and at equal rates. The temperature coefficient of K is discontinuous in the region of 40 C, indicating quite different activation energies for the reactions above and below this critical point. The degradation of interfering power exhibits a similar discontinuity, although less in magnitude, but none has been found in the antibody-reactive power of the virus, which is much more heat resistant.
Full text
PDF

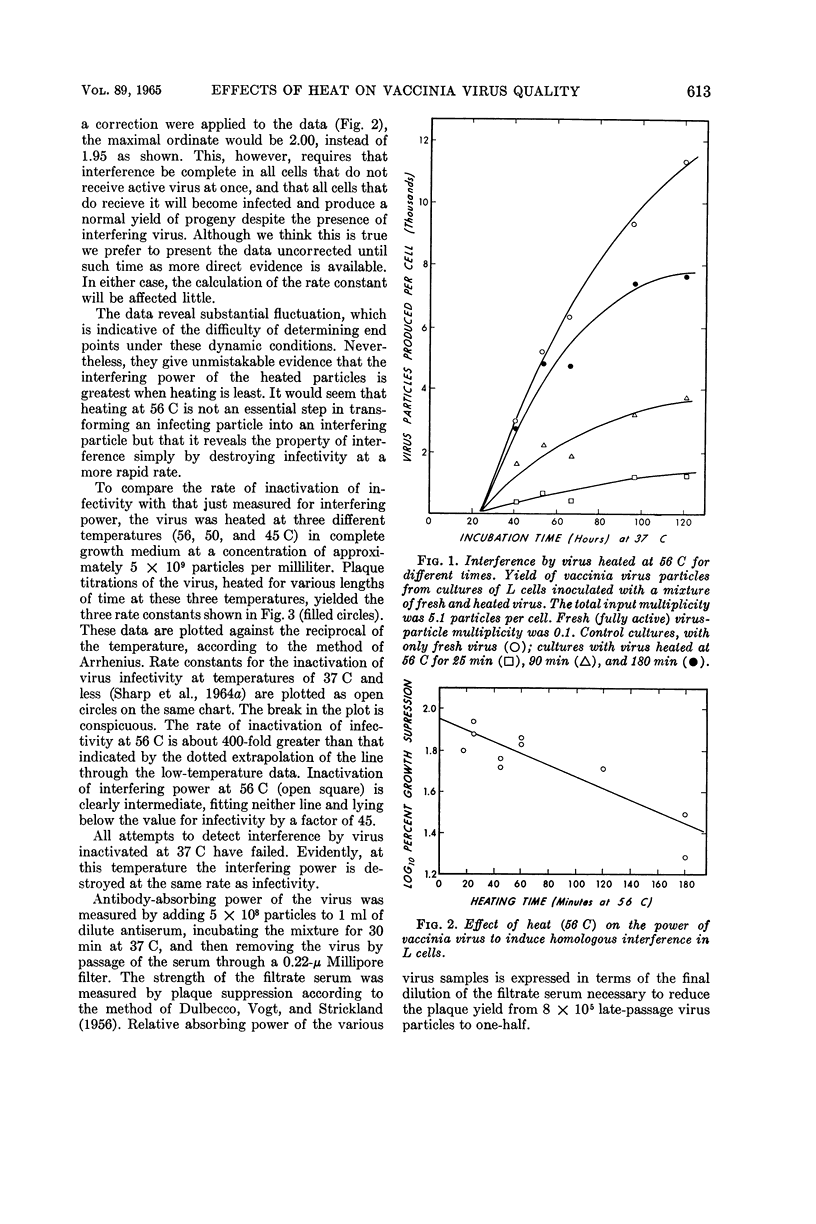
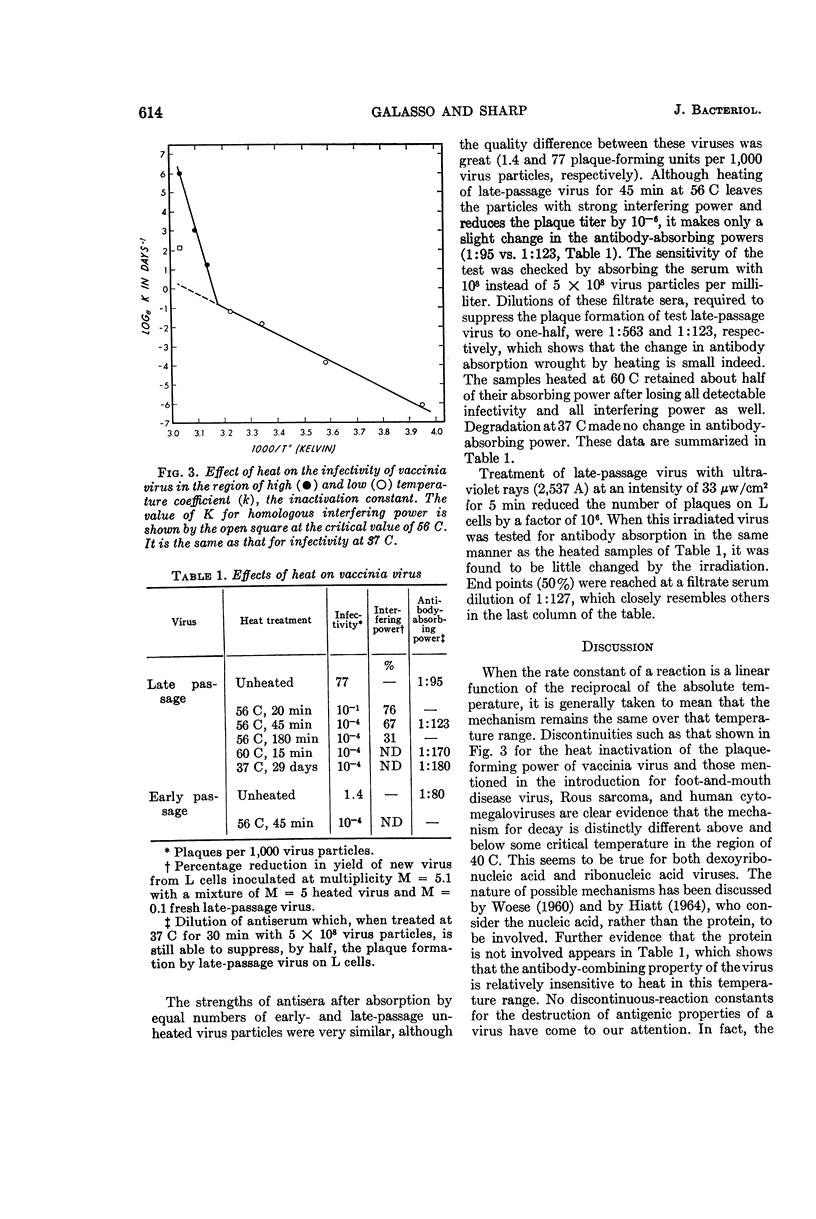


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BACHRACH H. L., BREESE S. S., Jr, CALLIS J. J., HESS W. R., PATTY R. E. Inactivation of foot-and-mouth disease virus by pH and temperature changes and by formaldehyde. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1957 May;95(1):147–152. doi: 10.3181/00379727-95-23148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOUGHERTY R. M. Heat inactivation of Rous sarcoma virus. Virology. 1961 Jul;14:371–372. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90321-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DULBECCO R., VOGT M., STRICKLAND A. G. A study of the basic aspects of neutralization of two animal viruses, western equine encephalitis virus and poliomyelitis virus. Virology. 1956 Apr;2(2):162–205. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(56)90017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GALASSO G. J., SHARP D. G. HOMOLOGOUS INHIBITION, TOXICITY, AND MULTIPLICITY REACTIVATION WITH ULTRAVIOLET-IRRADIATED VACCINIA VIRUS. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jun;85:1309–1314. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.6.1309-1314.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GALASSO G. J., SHARP D. G. Homologous inhibition with heated and ultraviolet-treated vaccinia virus in cultures of L cells. Virology. 1963 May;20:1–13. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90135-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GALASSO G. J., SHARP D. G. RELATIVE PLAQUE-FORMING, CELL-INFECTING, AND INTERFERING QUALITIES OF VACCINIA VIRUS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Aug;88:433–439. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.2.433-439.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GALASSO G. J., SHARP D. G. Virus particle aggregation and the plaque-forming unit. J Immunol. 1962 Mar;88:339–347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIATT C. W. KINETICS OF THE INACTIVATION OF VIRUSES. Bacteriol Rev. 1964 Jun;28:150–163. doi: 10.1128/br.28.2.150-163.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPLAN C. The heat inactivation of vaccinia virus. J Gen Microbiol. 1958 Feb;18(1):58–63. doi: 10.1099/00221287-18-1-58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHARP D. G., SADHUKHAN P., GALASSO G. J. QUALITY CHANGES IN VACCINIA VIRUS DURING ADAPTATION TO GROWTH IN CULTURES OF EARLE'S L CELLS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Aug;88:309–312. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.2.309-312.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHARP D. G., SMITH K. O. Rapid adsorption of vaccinia virus on tissue culture cells by centrifugal force. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1960 May;104:167–169. doi: 10.3181/00379727-104-25767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOESE C. Thermal inactivation of animal viruses. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1960 Jan 13;83:741–751. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1960.tb40943.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


