Abstract
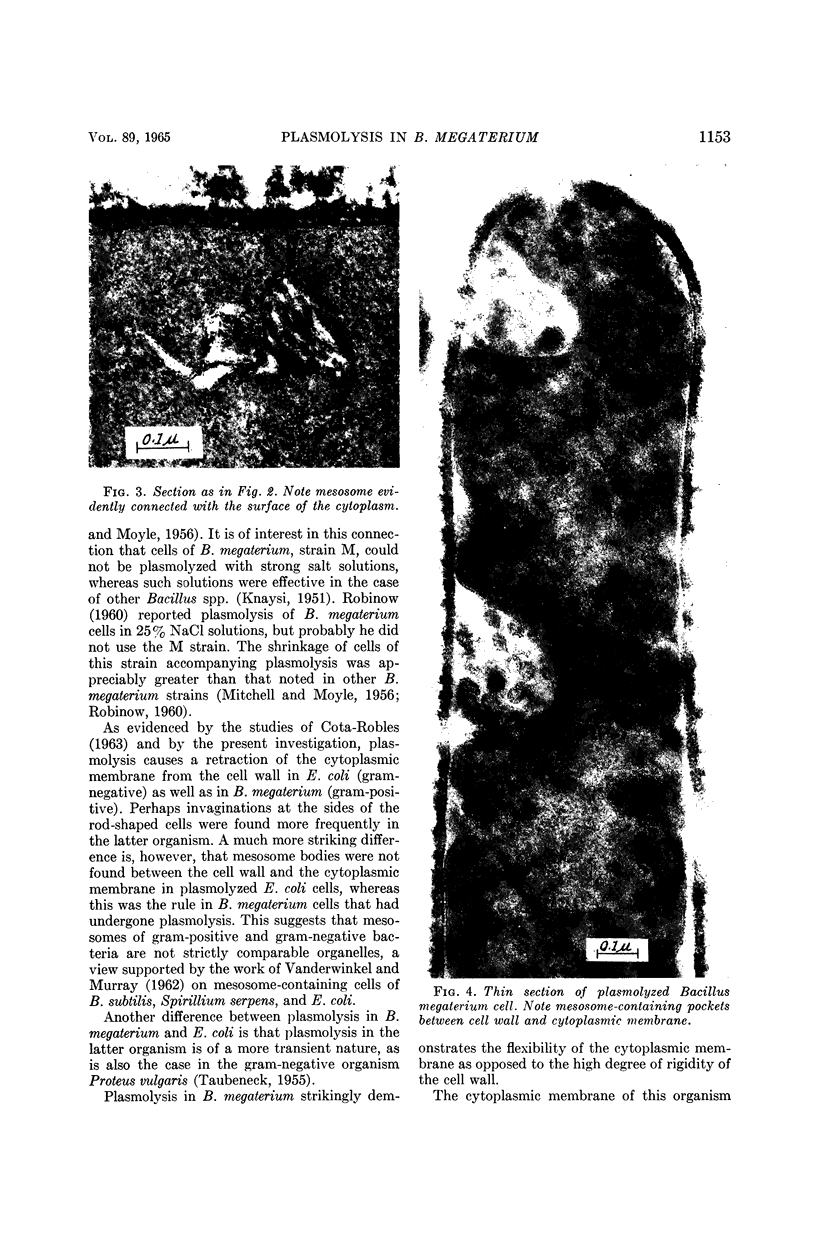
Weibull, Claes (Central Bacteriological Laboratory of Stockholm City, Stockholm, Sweden). Plasmolysis in Bacillus megaterium. J. Bacteriol. 89:1151–1154. 1965.—Sucrose solutions stronger than 1 m caused plasmolysis in Bacillus megaterium strain M, whereas concentrated NaCl and KNO3 solutions were ineffective. In plasmolyzed cells, mesosome bodies were found in pockets between the cytoplasmic membrane and the cell wall. After plasmolysis, the cytoplasmic membrane appeared as a triple-layered structure, a “unit membrane.” Plasmolysis did not markedly influence the viability of the cells.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BAUMANN-GRACE J. B., TOMCSIK J. The surface structure and serological typing of Bacillus megaterium. J Gen Microbiol. 1957 Aug;17(1):227–237. doi: 10.1099/00221287-17-1-227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FITZ-JAMES P. FATE OF THE MESOSOMES OF BACILLUS MEGATERIUM DURING PROTOPLASTING. J Bacteriol. 1964 Jun;87:1483–1491. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.6.1483-1491.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUFT J. H. Improvements in epoxy resin embedding methods. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Feb;9:409–414. doi: 10.1083/jcb.9.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RYTER A., JACOB F. ETUDE AU MICROSCOPE 'ELECTRONIQUE DES RELATIONS ENTRE M'ESOSOMES ET NOYAUX CHEZ BACILLUS SUBTILIS. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1963 Nov 13;257:3060–3063. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RYTER A., KELLENBERGER E. L'inclusion au polyester pour l'ultramicrotomie. J Ultrastruct Res. 1958 Dec;2(2):200–214. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(58)90018-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RYTER A., LANDMAN O. E. ELECTRON MICROSCOPE STUDY OF THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN MESOSOME LOSS AND THE STABLE L STATE (OR PROTOPLAST STATE) IN BACILLUS SUBTILIS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Aug;88:457–467. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.2.457-467.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAUBENECK U. Uber Plasmolyseversuche mit penicillininduzierten Umbildungsformen von Proteus vulgaris. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1955 Oct;163(7-8):477–483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAN ITERSON W. Some features of a remarkable organelle in Bacillus subtilis. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Jan;9:183–192. doi: 10.1083/jcb.9.1.183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZAMORA A., BOJALIL L. F., BASTARRACHEA F. IMMUNOLOGICALLY ACTIVE POLYSACCHARIDES FROM NOCARDIA ASTEROIDES AND NOCARDIA BRASILIENSIS. J Bacteriol. 1963 Mar;85:549–555. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.3.549-555.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]