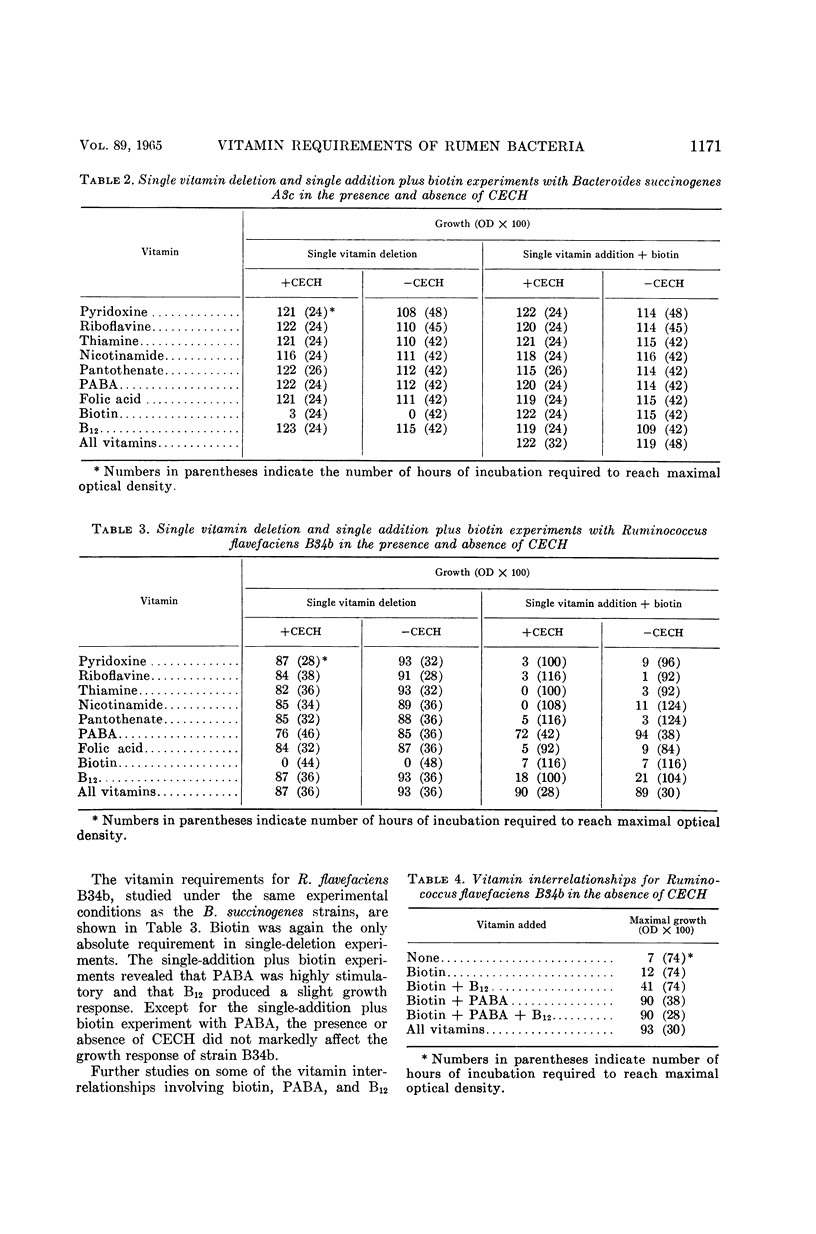
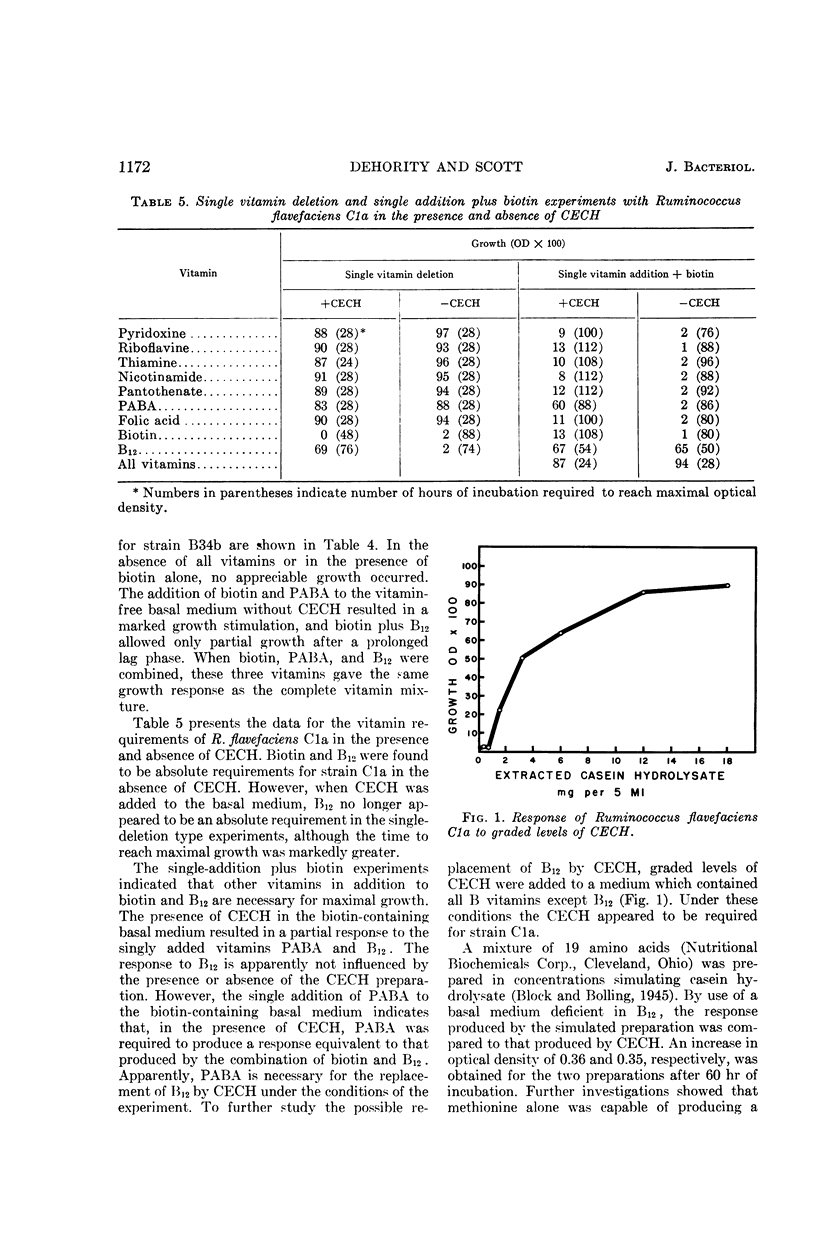
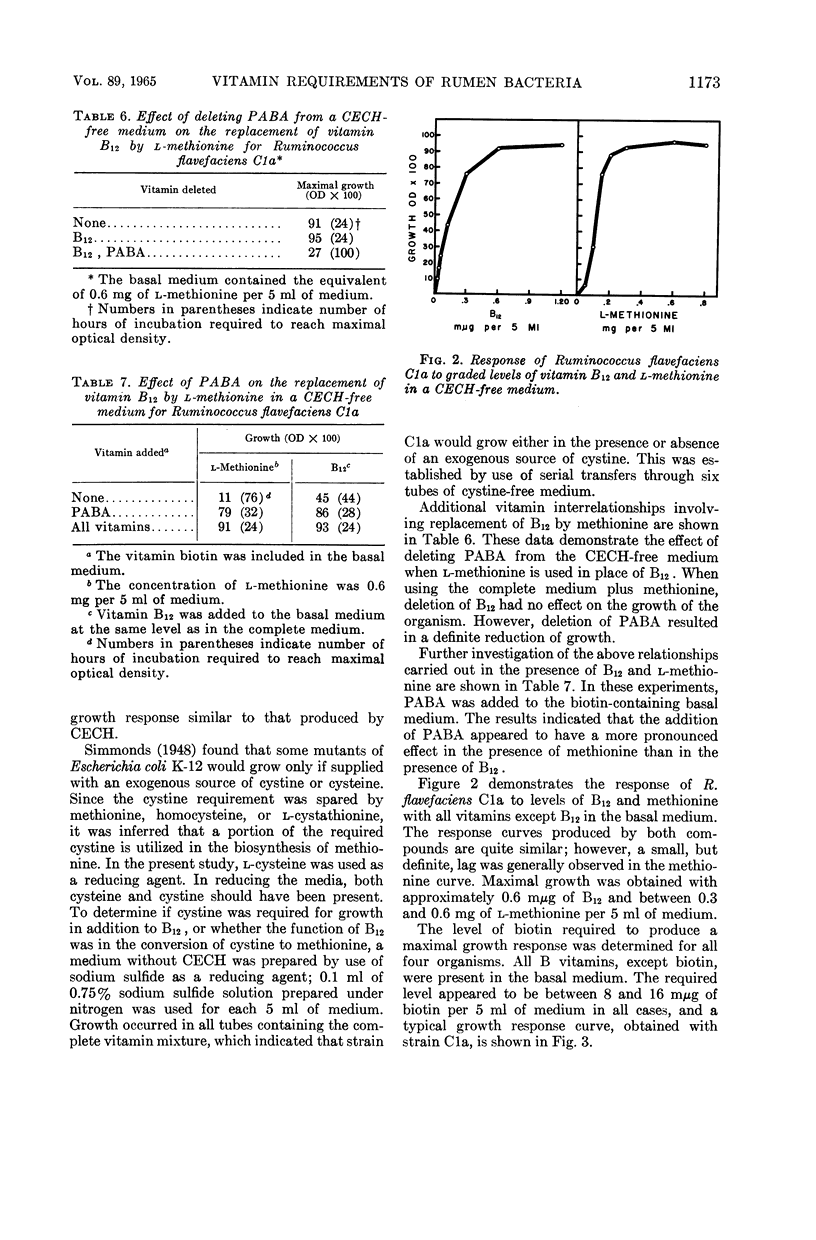
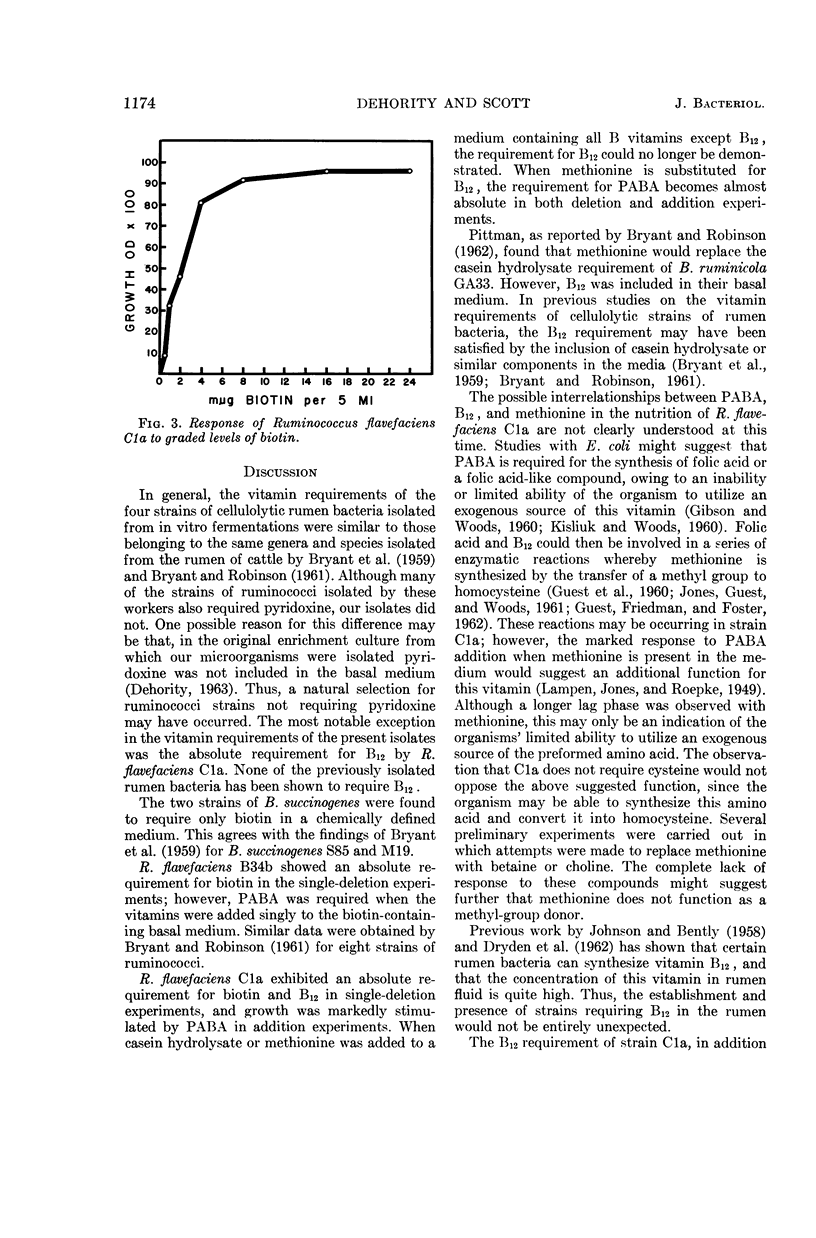
Abstract
Scott, H. W. (Ohio Agricultural Experiment Station, Wooster), and B. A. Dehority. Vitamin requirements of several cellulolytic rumen bacteria. J. Bacteriol. 89:1169–1175. 1965.—Four strains of cellulolytic bacteria recently isolated from in vitro rumen fermentations were used in this study. Nine water-soluble vitamins were tested in single-deletion and single-addition plus biotin experiments, each with and without charcoal-extracted casein hydrolysate. Bacteroides succinogenes A3C and B21a required only biotin under the above experimental conditions. Ruminococcus flavefaciens B34b showed an absolute requirement for biotin and was stimulated by p-aminobenzoic acid (PABA) in the single-deletion experiments. In the single-addition plus biotin experiments, PABA and, to a lesser extent, vitamin B12 appeared to be required for maximal growth. The presence or absence of casein hydrolysate did not affect the vitamin requirements for the aforementioned three strains. In the single-deletion experiments, R. flavefaciens Cla showed an absolute requirement for biotin and, when casein hydrolysate was omitted, for B12. When casein hydrolysate was present, no requirement for B12 could be observed. In the single-addition experiments where the basal medium contained biotin and casein hydrolysate or B12, PABA was required for maximal growth; however, the single deletion of PABA caused only slight retardation of growth. Investigation of the B12 or casein hydrolysate requirement of Cla revealed that a mixture of purified amino acids simulating casein hydrolysate satisfied this requirement. Subsequent work indicated that this requirement could be satisfied by the amino acid methionine.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BENTLEY O. G., JOHNSON R. R., HERSHBERGER T. V., CLINE J. H., MOXON A. L. Cellulolytic-factor activity of certain short-chain fatty acids for rumen microorganisms in vitro. J Nutr. 1955 Nov 10;57(3):389–400. doi: 10.1093/jn/57.3.389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRYANT M. P., ROBINSON I. M. Some nutritional characteristics of predominant culturable ruminal bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1962 Oct;84:605–614. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.4.605-614.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant M. P., Robinson I. M. Some Nutritional Requirements of the Genus Ruminococcus. Appl Microbiol. 1961 Mar;9(2):91–95. doi: 10.1128/am.9.2.91-95.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DRYDEN L. P., HARTMAN A. M., BRYANT M. P., ROBINSON I. M., MOORE L. A. Production of vitamin B12 and vitamin B12 analogues by pure cultures of ruminal bacteria. Nature. 1962 Jul 14;195:201–202. doi: 10.1038/195201b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIBSON F., WOODS D. D. The synthesis of methionine by suspensions of Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1960 Jan;74:160–172. doi: 10.1042/bj0740160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILL J. W., KING K. W. Nutritional characteristics of a Butyrivibrio. J Bacteriol. 1958 Jun;75(6):666–673. doi: 10.1128/jb.75.6.666-673.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUEST J. R., HELLEINER C. W., CROSS M. J., WOODS D. D. Cobalamin and the synthesis of methionine by ultrasonic extracts of Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1960 Aug;76:396–405. doi: 10.1042/bj0760396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNGATE R. E. The anaerobic mesophilic cellulolytic bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1950 Mar;14(1):1–49. doi: 10.1128/br.14.1.1-49.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JONES K. M., GUEST J. R., WOODS D. D. Folic acid and the synthesis of methionine by extracts of Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1961 Jun;79:566–574. doi: 10.1042/bj0790566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KISLIUK R. L., WOODS D. D. Interrelationships between folic acid and cobalamin in the synthesis of methionine by extracts of Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1960 Jun;75:467–477. doi: 10.1042/bj0750467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


