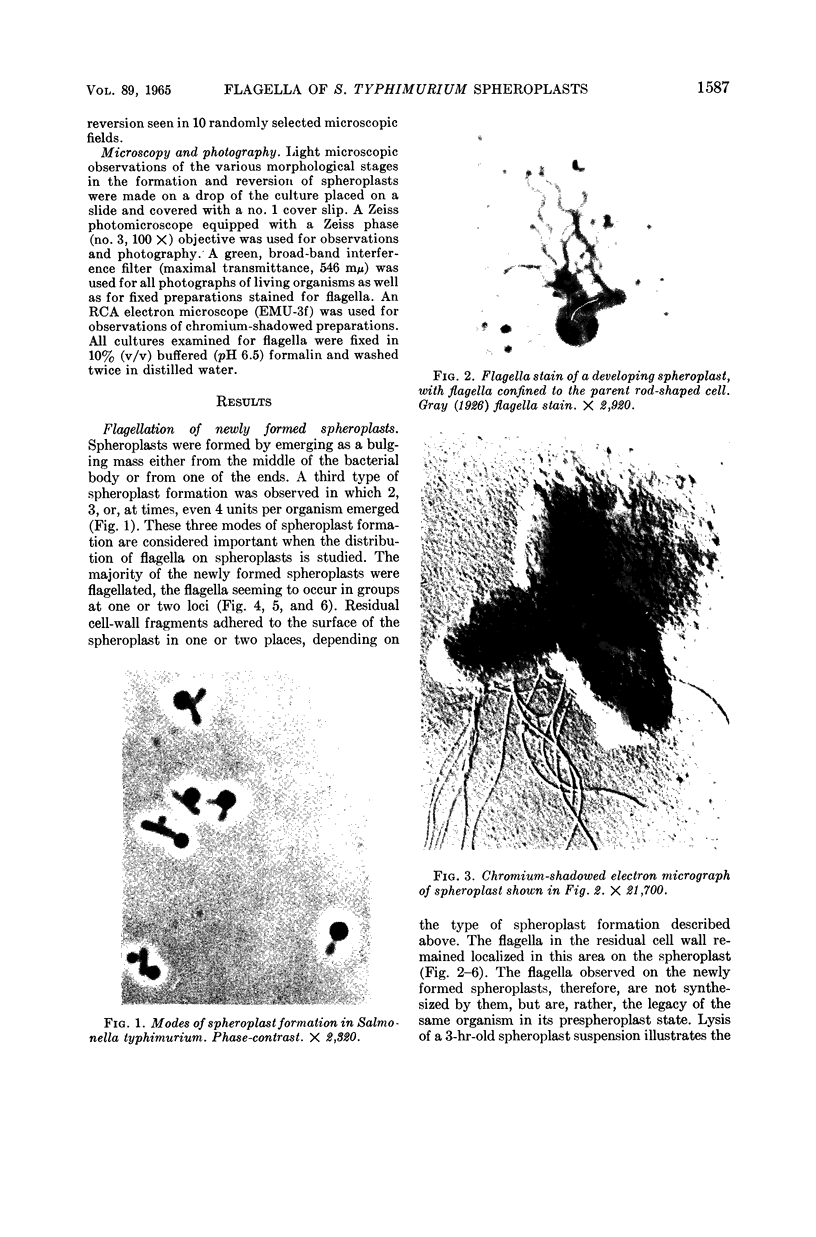
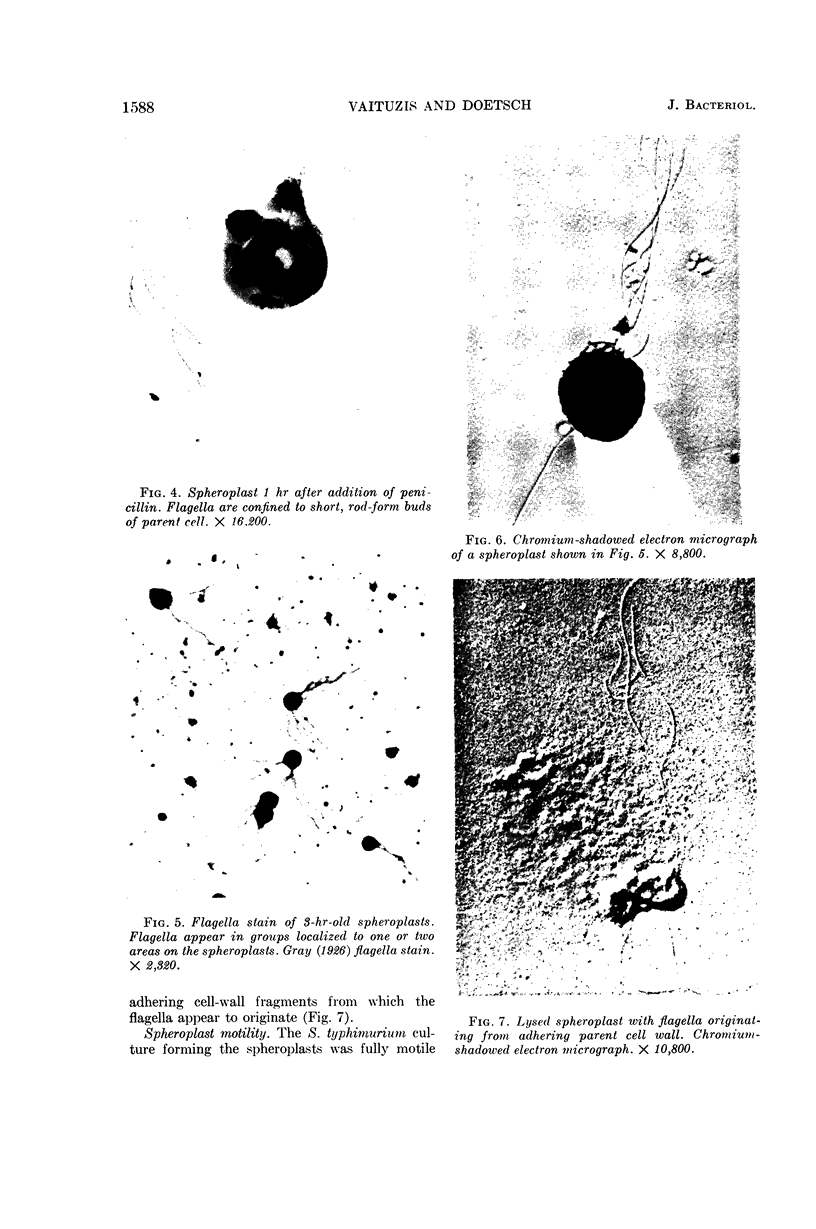
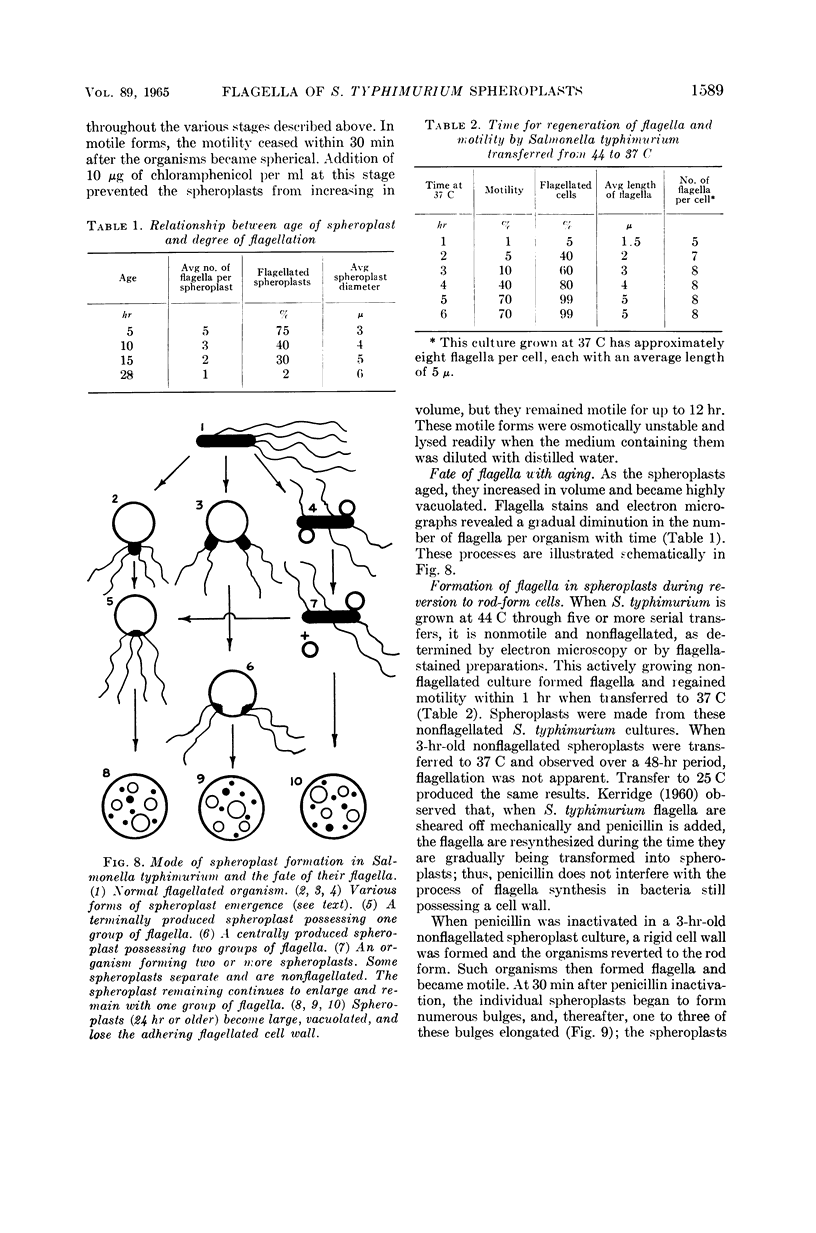
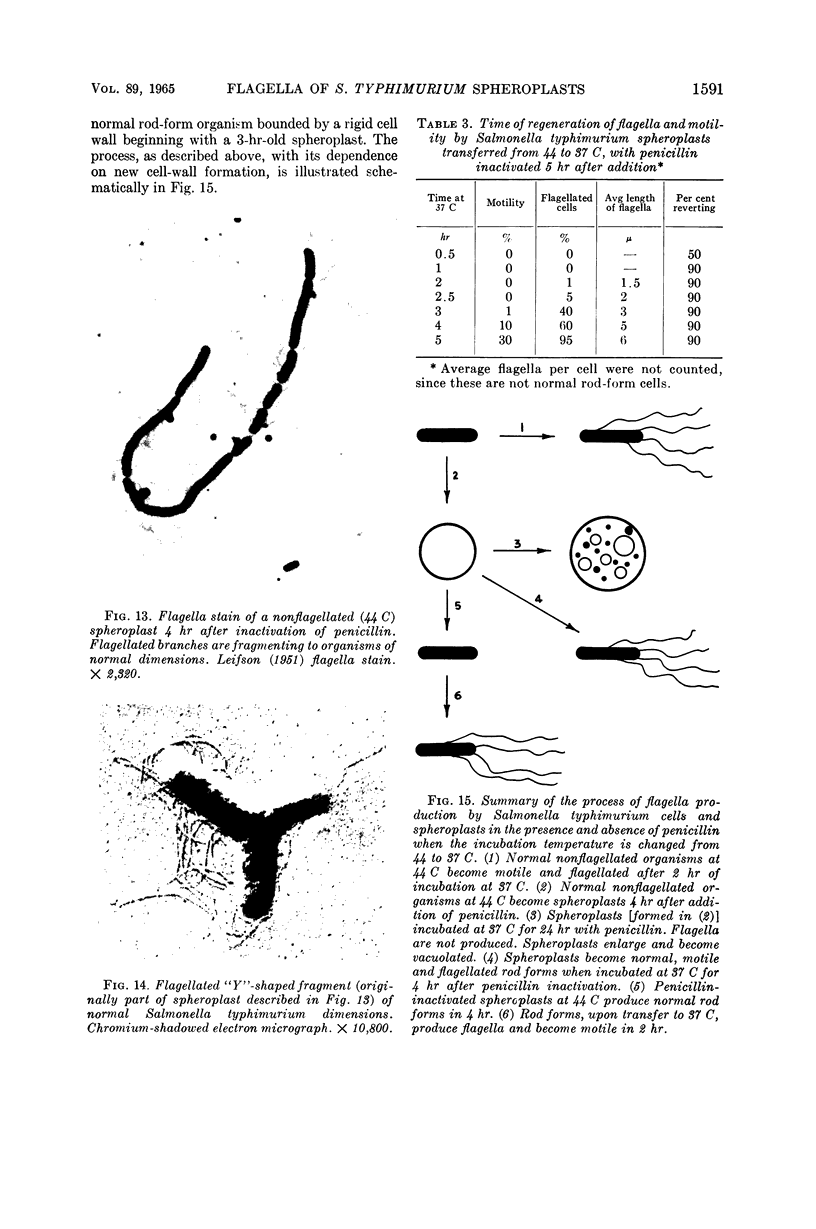
Abstract
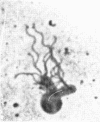
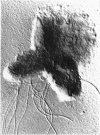
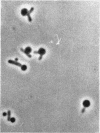
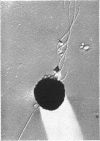
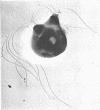
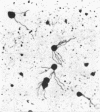
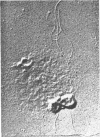
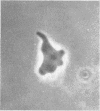
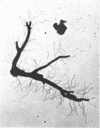
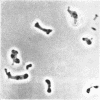
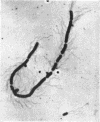
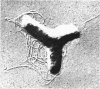
Vaituzis, Z. (University of Maryland, College Park), and R. N. Doetsch. Flagella of Salmonella typhimurium spheroplasts. J. Bacteriol. 89:1586–1593. 1965.—The flagella of penicillin-induced spheroplasts of Salmonella typhimurium were examined by electron and light microscopy. The process of spheroplast formation was followed for a period of 20 hr from its inception. Flagella were found to be confined to those areas of the spheroplast where cell-wall fragments remained. Flagella disappeared as the spheroplasts aged. Spheroplasts produced from nonflagellated organisms were found incapable of synthesizing flagella. Upon inactivation of the penicillin, however, flagella again were synthesized by spheroplasts during reversion to their original rod form. Flagella formation, it is suggested, is dependent on prior synthesis of the normal cell wall. The morphology of the microorganisms at the time of appearance of new flagella is described.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABRAM D., KOFFLER H. IN VITRO FORMATION OF FLAGELLA-LIKE FILAMENTS AND OTHER STRUCTURES FROM FLAGELLIN. J Mol Biol. 1964 Jul;9:168–185. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80098-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ASAKURA S., EGUCHI G., IINO T. RECONSTITUTION OF BACTERIAL FLAGELLA IN VITRO. J Mol Biol. 1964 Oct;10:42–56. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80026-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHATTERJEE B. R., WILLIAMS R. P. PREPARATION OF SPHEROPLASTS FROM VIBRIO COMMA. J Bacteriol. 1963 Apr;85:838–841. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.4.838-841.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray P. H. A METHOD OF STAINING BACTERIAL FLAGELLA. J Bacteriol. 1926 Oct;12(4):273–274. doi: 10.1128/jb.12.4.273-274.1926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KERRIDGE D. The effect of inhibitors on the formation of flagella by Salmonella typhimurium. J Gen Microbiol. 1960 Dec;23:519–538. doi: 10.1099/00221287-23-3-519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEDERBERG J., ST CLAIR J. Protoplasts and L-type growth of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1958 Feb;75(2):143–160. doi: 10.1128/jb.75.2.143-160.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEIFSON E. Staining, shape and arrangement of bacterial flagella. J Bacteriol. 1951 Oct;62(4):377–389. doi: 10.1128/jb.62.4.377-389.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederberg J. BACTERIAL PROTOPLASTS INDUCED BY PENICILLIN. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1956 Sep;42(9):574–577. doi: 10.1073/pnas.42.9.574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin H. H. Bacterial protoplasts--a review. J Theor Biol. 1963 Jul;5(1):1–34. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(63)90034-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIBULL C. The isolation of protoplasts from Bacillus megaterium by controlled treatment with lysozyme. J Bacteriol. 1953 Dec;66(6):688–695. doi: 10.1128/jb.66.6.688-695.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]