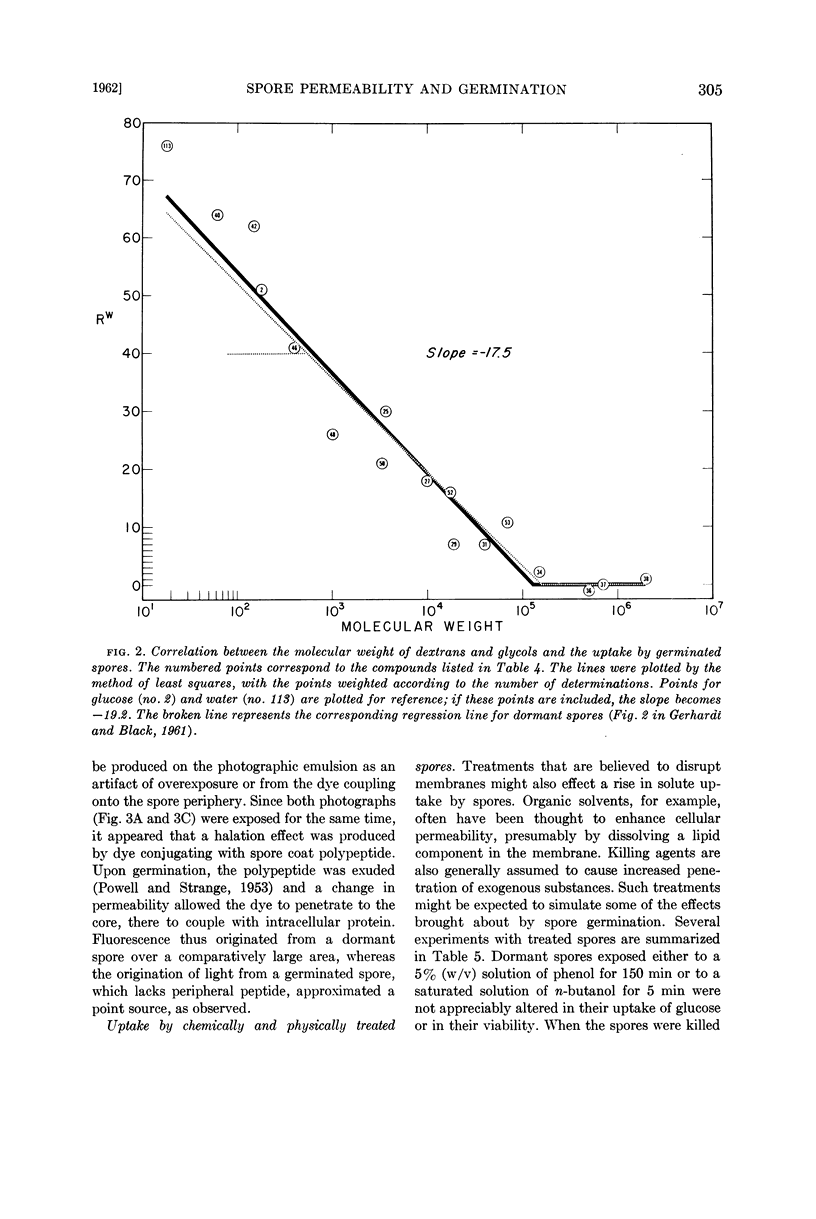
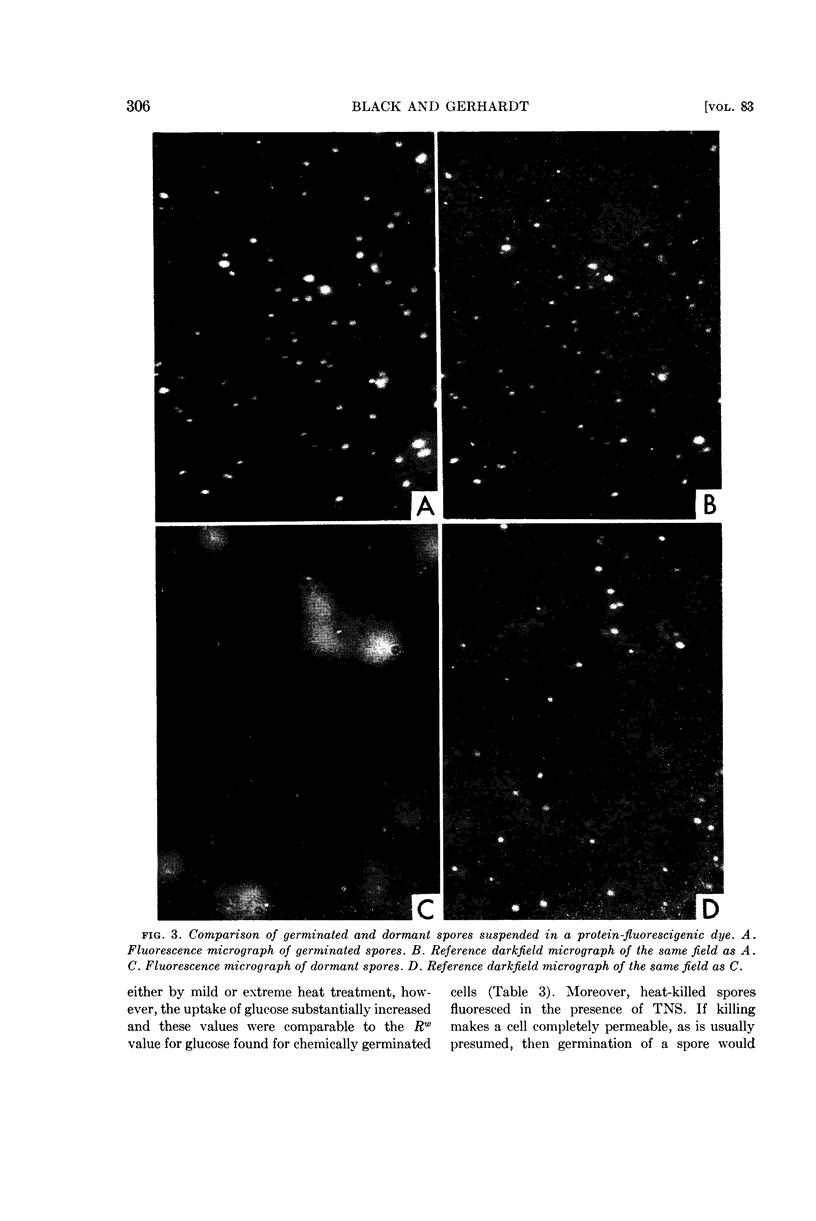
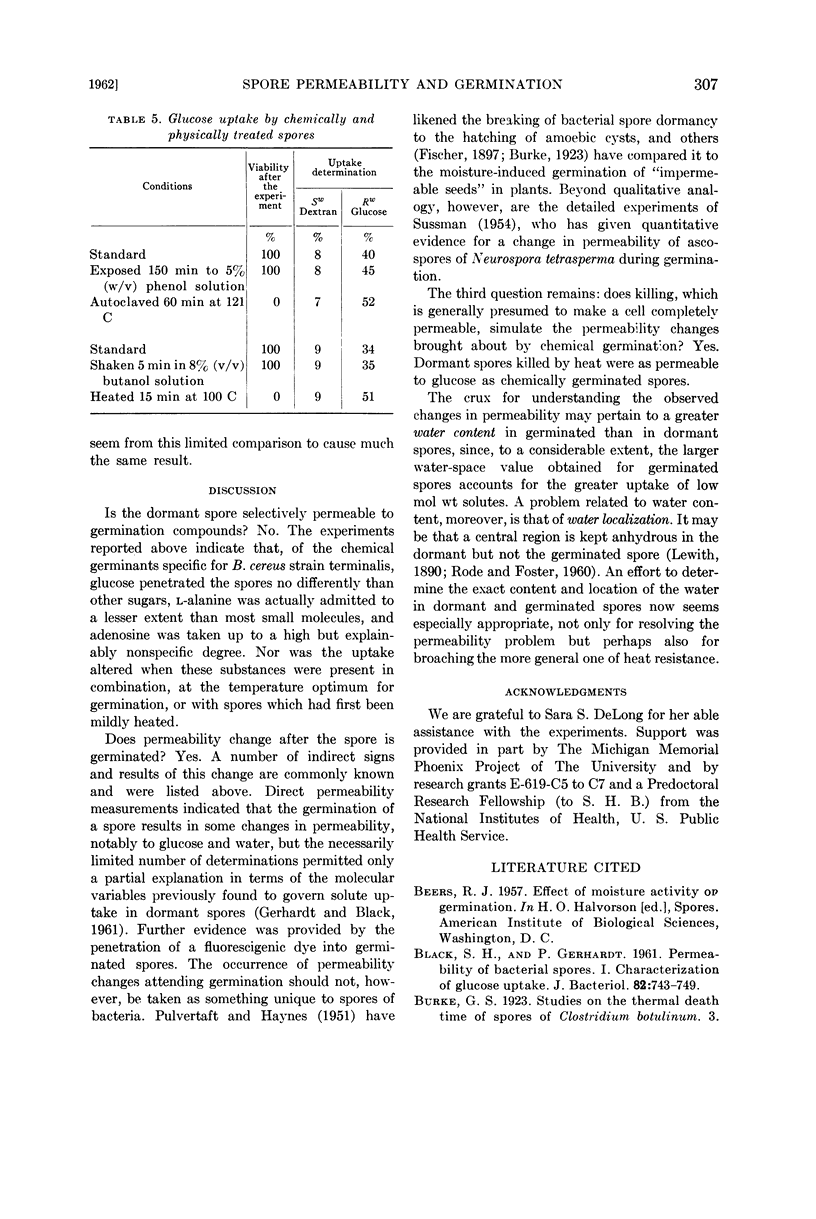
Abstract
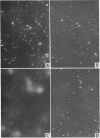
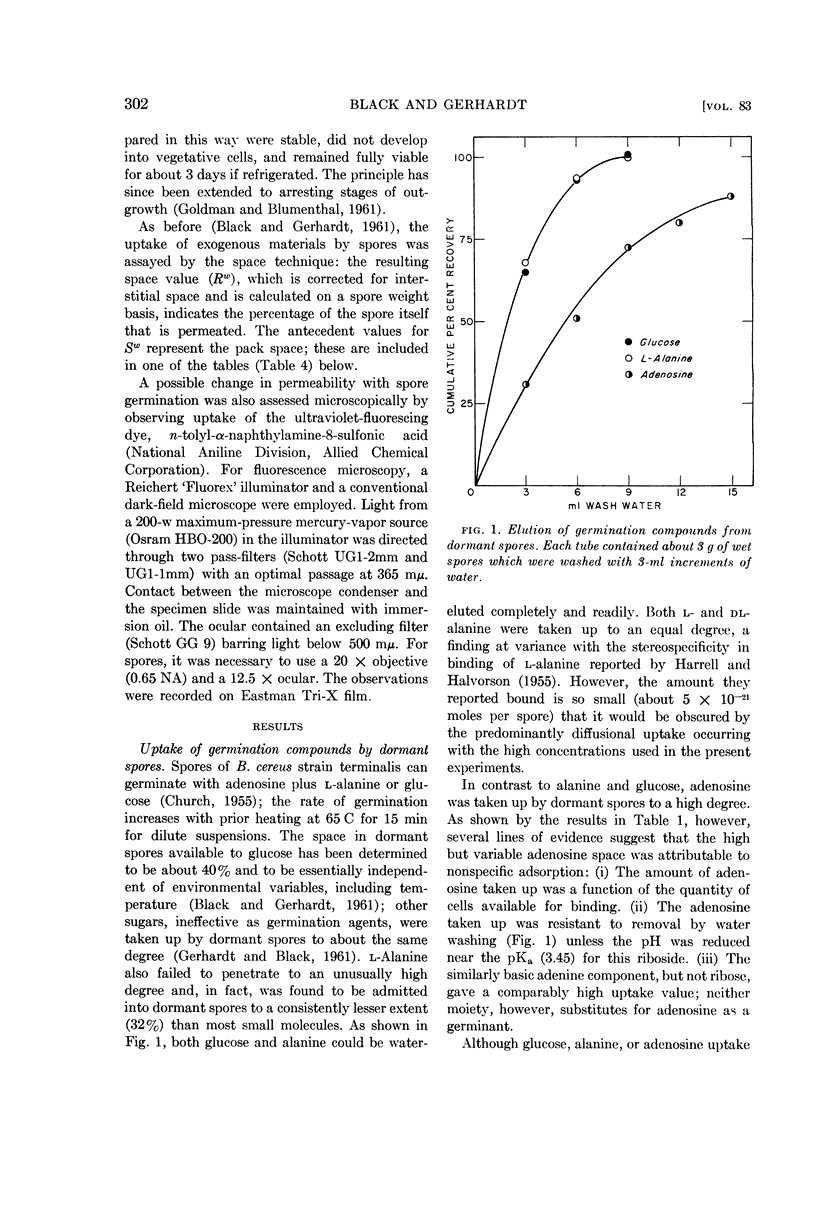
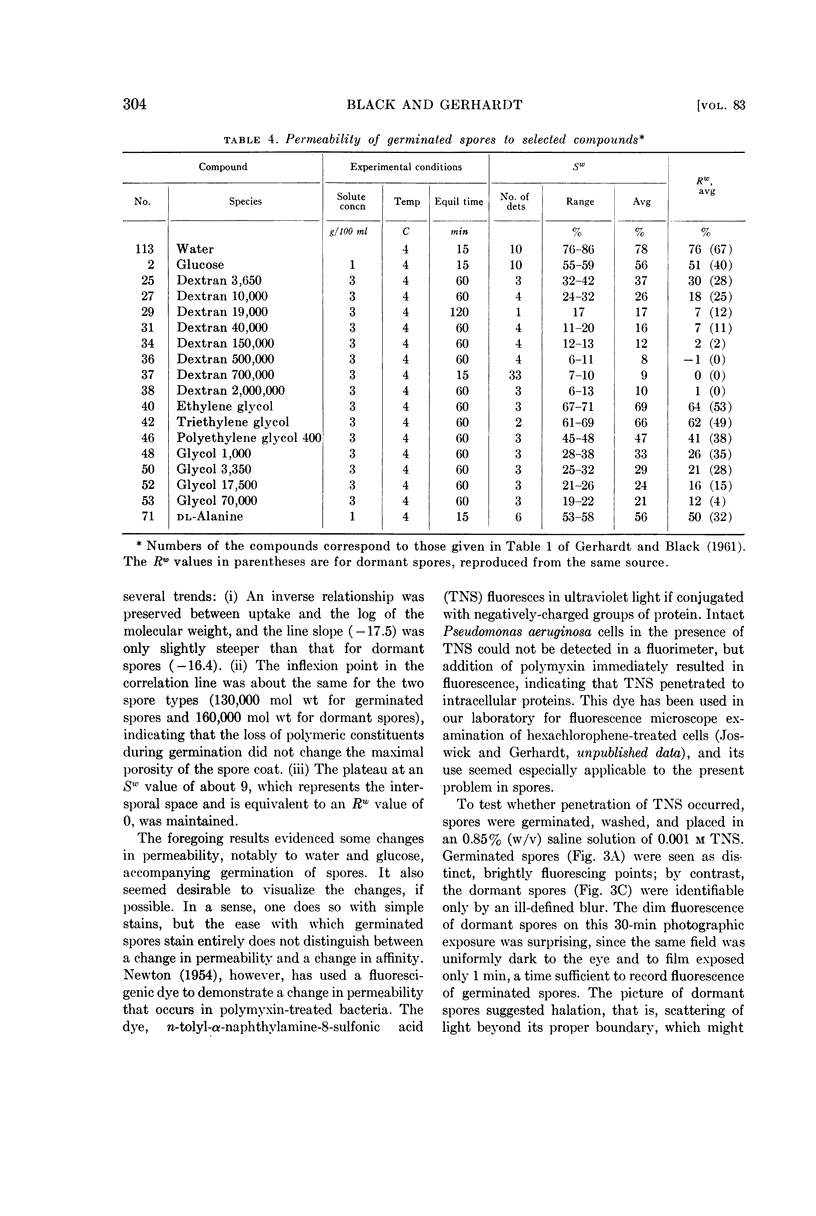
Black, S. H. (The University of Michigan, Ann Arbor) and Philipp Gerhardt. Permeability of bacterial spores. III. Permeation relative to germination. J. Bacteriol. 83:301–308. 1962.—The passive diffusion of solutes into dormant spores, characterized previously with the test organism Bacillus cereus strain terminalis, has now been examined in relation to germination. Dormant spores did not take up specific germinants differently than they did other compounds, under conditions optimal for germination. Germinated spores, viable but prevented from growing out, displayed some changes in permeability, evidenced by increased total uptake of glucose and water and by observable penetration of a fluorescigenic dye. Heat-killed spores were as permeable to glucose and the dye as germinated ones.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLACK S. H., GERHARDT P. Permeability of bacterial spores. I. Characterization of glucose uptake. J Bacteriol. 1961 Nov;82:743–749. doi: 10.1128/jb.82.5.743-749.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GERHARDT P., BLACK S. H. Permeability of bacterial spores. II. Molecular variables affecting solute permeation. J Bacteriol. 1961 Nov;82:750–760. doi: 10.1128/jb.82.5.750-760.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDMAN M., BLUMENTHAL H. J. Arrest of bacterial spores in stages of postgerminative development. Can J Microbiol. 1961 Aug;7:677–679. doi: 10.1139/m61-080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRELL W. K., HALVORSON H. Studies on the role of L-alanine in the germination of spores of Bacillus terminalis. J Bacteriol. 1955 Mar;69(3):275–279. doi: 10.1128/jb.69.3.275-279.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knaysi G. OPTICAL DENSITY OF THE ENDOSPORE OF BACILLUS CEREUS AND ITS RELATION TO GERMINATION AND RESISTANCE. J Bacteriol. 1959 Aug;78(2):206–216. doi: 10.1128/jb.78.2.206-216.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leifson E. Bacterial Spores. J Bacteriol. 1931 May;21(5):331–356. doi: 10.1128/jb.21.5.331-356.1931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEWTON B. A. Site of action of polymyxin on Pseudomonas aeruginosa: antagonism by cations. J Gen Microbiol. 1954 Jun;10(3):491–499. doi: 10.1099/00221287-10-3-491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POWELL J. F., STRANGE R. E. Biochemical changes occurring during the germination of bacterial spores. Biochem J. 1953 May;54(2):205–209. doi: 10.1042/bj0540205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PULVERTAFT R. J. V., HAYNES J. A. Adenosine and spore germination; phase-contrast studies. J Gen Microbiol. 1951 Oct;5(4):657–663. doi: 10.1099/00221287-5-4-657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rode L. J., Foster J. W. MECHANICAL GERMINATION OF BACTERIAL SPORES. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1960 Jan;46(1):118–128. doi: 10.1073/pnas.46.1.118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUSSMAN A. S. Changes in the permeability of ascospores of Neurospora tetra-sperma during germination. J Gen Physiol. 1954 Sep 20;38(1):59–77. doi: 10.1085/jgp.38.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]