Abstract
Converse, J. L. (U. S. Army Chemical Corps, Frederick, Md.), M. W. Castleberry, A. R. Besemer, and E. M. Snyder. Immunization of mice against coccidioidomycosis. J. Bacteriol. 84:46–52. 1962—The observed lower virulence of Coccidioides immitis arthrospores of the M-11 strain compared with the Cash strain was ascribed to the lower ability of the M-11 spores to invade the lungs and brain. Endospores of strain M-11, grown in synthetic medium, were equally as virulent by the intraperitoneal route as arthrospores of strain Cash. Immunization of mice with viable strain M-11 arthrospores protected approximately 50% of the animals against challenge with strain Cash arthrospores. This was evidenced by lower mortality over a 5-month period and lack of gross pathological lesions in killed animals. Although fewer lesions resulted after the use of a viable vaccine, higher survival was obtained with formaldehyde-killed arthrospores. Either preparation tended to confine the infection to the peritoneal cavity.
Full text
PDF
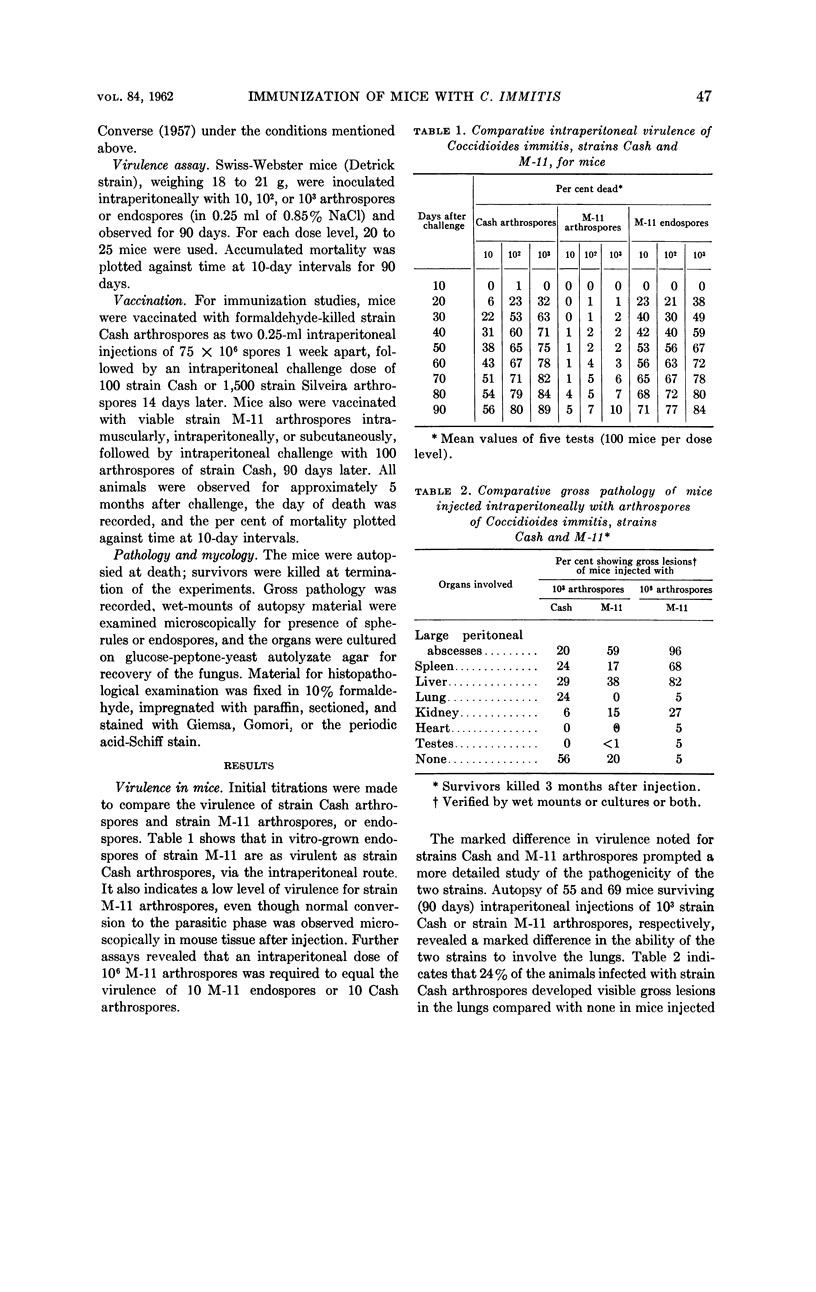
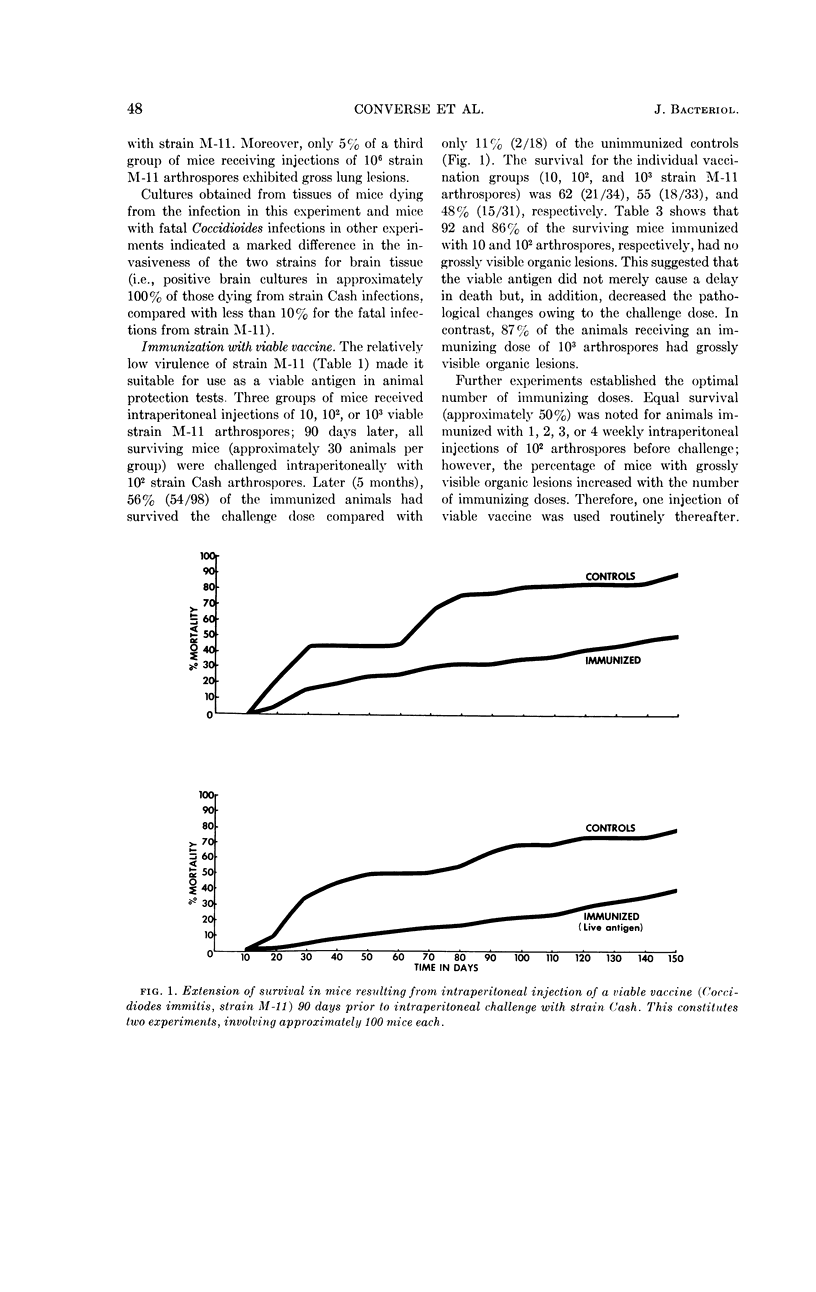


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERMAN R. J., FRIEDMAN L., ROESSLER W. G., SMITH C. E. The virulence and infectivity of twenty-seven strains of Coccidioides immitis. Am J Hyg. 1956 Sep;64(2):198–210. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a119834. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONVERSE J. L. Effect of surface active agents on endosporulation of Coccidioides immitis in a chemically defined medium. J Bacteriol. 1957 Jul;74(1):106–107. doi: 10.1128/jb.74.1.106-107.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONVERSE J. L., LOWE E. P., CASTLEBERRY M. W., BLUNDELL G. P., BESEMER A. R. Pathogenesis of Coccidioides immitis in monkeys. J Bacteriol. 1962 Apr;83:871–878. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.4.871-878.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLEY J. M., BERMAN R. J., SMITH C. E. X-ray irradiation of Coccidioides immitis arthrospores: survival curves and avirulent mutants isolated. J Bacteriol. 1960 Apr;79:480–487. doi: 10.1128/jb.79.4.480-487.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIEDMAN L., SMITH C. E. Vaccination of mice against Coccidoides immitis. Am Rev Tuberc. 1956 Aug;74(2 Pt 1):245–248. doi: 10.1164/artpd.1956.74.2-1.245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAPPAGIANIS D., SMITH C. E., BERMAN R. J., KOBAYASHI G. S. Experimental subcutaneous coccidioidal infection in the mouse. J Invest Dermatol. 1959 May;32(5):589–598. doi: 10.1038/jid.1959.98. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAPPAGIANIS D., SMITH C. E., KOBAYASHI G. S. Relationship of the in vivo form of Coccidioides immitis to virulence. J Infect Dis. 1956 May-Jun;98(3):312–319. doi: 10.1093/infdis/98.3.312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGEL R. A., FETTER B. F., CONANT N. F., LOWE E. P. Preliminary studies on artificial active immunization of guinea pigs against respiratory challenge with Coccidioides immitis. Am Rev Tuberc. 1954 Sep;70(3):498–503. doi: 10.1164/art.1954.70.3.498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]