Abstract
Dialysis patients have a high risk of cardiovascular disease. In the general population, cardiac rehabilitation is recommended as a standard component of care and is covered by Medicare for patients who have undergone coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG). Previous investigation demonstrated survival benefit of cardiac rehabilitation in dialysis patients. This study investigated its impact on Medicare expenditure and its cost effectiveness. A cohort of 4,324 end-stage renal disease (ESRD) patients who initiated chronic hemodialysis and underwent CABG between 1998 and 2004 was selected from the United States Renal Data System. Cardiac rehabilitation was defined by Current Procedural Terminology codes for monitored and nonmonitored exercise in Medicare claims data. Medicare expenditure included inpatient and outpatient claims with cost adjusted to 1998 dollars. At 42 months of follow-up after a 6-month entry period following CABG hospitalization discharge, cardiac rehabilitation at baseline was associated with higher cumulative Medicare expenditure, incurring a statistically nonsignificant increment of $2,904 (95% CI: −7,028, 11,940). During the same period, cardiac rehabilitation was significantly associated with longer cumulative lifetime, having an incremental benefit of 76 days (95% CI: 22, 129). The incremental cost-effectiveness ratio was $13,887 per year of life saved, suggesting that cardiac rehabilitation is highly cost-effective in ESRD patients following CABG.
In 2005, there were approximately 485,000 end-stage renal disease (ESRD) patients in the United States, for whom total Medicare costs reached 21.3 billion dollars.1 Given this economic burden, cost evaluation of medical therapies, in addition to standard effectiveness and safety assessment, is increasingly important for policy makers and third-party payers.
The leading cause of death among dialysis patients is cardiovascular disease (CVD), with cardiovascular mortality almost 40 times that in the general population.2 For patients having experienced coronary events, cardiac rehabilitation is considered an integral part of the contemporary care.3,4 Medicare covers cardiac rehabilitation for patients who have undergone coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) and for patients who have had an acute myocardial infarction (AMI) in the past 12 months or have stable angina.5 In the general population, cardiac rehabilitation has been shown to reduce coronary heart disease risk factors6 and mortality from coronary heart disease.7–11 Furthermore, a limited number of studies have suggested that it is cost-effective and even cost-saving.12–15
CABG may confer a lowered risk for death in dialysis patients compared with no revascularization. In an earlier report, we investigated the characteristics and long-term survival of dialysis patients who received cardiac rehabilitation after CABG, using United States Renal Data System (USRDS) files linked with Medicare inpatient and outpatient claims.16 We found that patients who received cardiac rehabilitation after CABG, compared to those who did not, had significantly improved survival. The purpose of this study is to assess the impact of dialysis patients’ receipt of cardiac rehabilitation after CABG on Medicare expenditure and cost effectiveness.
RESULTS
Patient characteristics
A total of 6,040 eligible ESRD patients who initiated chronic hemodialysis (HD) and underwent CABG between 1998 and 2004 were identified from USRDS database. Of them, 635 patients were excluded because of being non-ambulatory, having extended hospital stays for the CABG procedure, or incurring excessive Medicare expenditure during a 6-month entry period. Additionally, 1,081 patients were dropped from the study cohort as being in the lowest propensity quintile for receiving cardiac rehabilitation at baseline. See Materials and Methods section for details of these exclusion criteria. The final study cohort consisted of 4,324 patients.
Baseline demographic and clinical characteristics of the 4,324 patients are reported in Table 1. A propensity score (C-index, 0.65) was calculated for receiving cardiac rehabilitation at baseline, and Table 1 is summarized by the cardiac rehabilitation status and the propensity score quartiles. Of the study cohort, 68% were 65 years of age or older, 72% were male, and 81% were white. Approximately 16.4% received cardiac rehabilitation in a period between CABG surgery and 6 months after CABG hospitalization discharge. The cardiac rehabilitation and non-cardiac rehabilitation groups as a whole were fairly different in their baseline characteristics. However, these differences were minimized after stratification by the propensity score quartiles.
Table 1.
Characteristics of the study cohort: 4,324 HD patients with CABG surgery as selected on the basis of baseline measures
| Propensity score quartile | 1st | 2nd | 3rd | 4th | P value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cardiac rehabilitation (yes/no) | Y | N | Y | N | Y | N | Y | N | |
| size | 79 | 1001 | 147 | 934 | 194 | 888 | 287 | 794 | |
| Age >= 65 yr (%) | 57 | 67 | 68 | 69 | 75 | 68 | 72 | 67 | 0.18 |
| Male (%) | 39 | 50 | 73 | 69 | 82 | 78 | 91 | 93 | 0.90 |
| Race (%) | 1.00 | ||||||||
| Asian | 6 | 5 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | |
| black | 37 | 30 | 16 | 16 | 4 | 7 | 2 | 2 | |
| Native American | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 2 | |
| white | 56 | 63 | 79 | 78 | 91 | 89 | 96 | 96 | |
| Other | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Medicaid coveragea (%) | 33 | 29 | 14 | 15 | 5 | 5 | 0 | 1 | 0.98 |
| No. of cardiovascular conditionsa (mean) | 1.2 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.3 | 1.4 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.2 | 0.45 |
| Hemoglobina (g/dl; mean) | 9.7 | 9.8 | 10.1 | 9.9 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 10.1 | 0.97 |
| Serum albuminaa (g/dl; mean) | 3.1 | 3.1 | 3.1 | 3.1 | 3.2 | 3.2 | 3.3 | 3.3 | 0.73 |
| Diabetic ESRDa (%) | 61 | 57 | 56 | 55 | 49 | 47 | 30 | 35 | 0.86 |
| AMI before CABG (%) | 41 | 50 | 43 | 42 | 35 | 36 | 21 | 20 | 0.69 |
| COPDa (%) | 6 | 8 | 12 | 8 | 5 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 0.88 |
| Vintage (mo; mean) | 17.4 | 13.8 | 13.0 | 14.5 | 12.3 | 14.4 | 14.4 | 15.1 | 0.29 |
| Hospital stays after CABG (d; mean) | 14.4 | 16.7 | 14.0 | 13.8 | 12.9 | 12.6 | 9.7 | 9.5 | 0.83 |
| Discharge to self care / outpatient (%) | 35 | 35 | 46 | 42 | 49 | 52 | 59 | 56 | 0.53 |
| Initial Medicare expenditureb ($; mean) | 26,579 | 27,341 | 24,797 | 24,714 | 18,729 | 19,283 | 14,736 | 14,551 | 0.69 |
Measured at HD start
accumulated during the 6-month entry period.
Abbreviations: ESRD, end-stage renal disease; CABG, coronary artery bypass grafting; HD, hemodialysis; AMI, acute myocardial infarction; COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Long-term cost and effectiveness of receiving cardiac rehabilitation
The follow-up of this study started 6 months after CABG hospitalization discharge. The mean follow-up time of the study cohort was 20.3 months, and 43.6% reached either death or 42 months of follow-up. The censoring was due to either the end of follow-up as of December 31, 2004 or renal transplantation; about 6% of the study cohort had renal transplantation during the 42-month follow-up period. The overall survival rate was 45.0% at 42 months. Cumulative Medicare expenditure and cumulative lifetime at 42 months were used as the primary cost and effectiveness outcomes, respectively. A cumulative measure at a follow-up time is the measure accumulated up to death or the follow-up time, whichever occurs earlier. The estimated mean cumulative Medicare expenditure and lifetime at 42 months for the study cohort were $105,133 and 29.8 months, respectively.
Table 2 provides estimated covariate effects on cumulative Medicare expenditure and lifetime at 42 months, from multivariate regression models with stratification by the propensity score quartiles. Cardiac rehabilitation at baseline was associated with higher cumulative Medicare expenditure at 42 months, with an increase of $2,904 (95% CI: −7,028, 11,940), but this increase was not statistically significant. At the same time, cardiac rehabilitation at baseline was significantly associated with longer cumulative lifetime with an increase of 76 days (95% CI: 22, 129). The estimated ICER was $13,887 per year of life saved at 42 months. Among other baseline measures included in the models, older patient age (>=65), male gender, and vintage were significantly associated with both shorter survival time and lower Medicare expenditure, whereas initial Medicare expenditure was significantly associated with shorter survival and higher Medicare expenditure. Number of cardiovascular conditions and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) at HD start were significantly associated with shorter survival, whereas Asian race (relative to white) was significantly associated with longer survival. Finally, black race (relative to white), Medicaid coverage, higher serum albumin, primary diagnosis of diabetes, and AMI before CABG were significantly associated with higher Medicare expenditure at 42 months.
Table 2.
Multivariate linear regression models predicting cumulative Medicare expenditure and cumulative lifetime at 42 months of 4,324 HD Patients with CABG surgery
| Risk Factor at baseline | Medicare expenditure ($) | Lifetime (d) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| estimate | 95% CI | estimate | 95% CI | |||
| Age ≥ 65 yr | −22,454 | −32,978 | −12,775 | −98 | −144 | −51 |
| Male gender | −15,498 | −25,345 | −6,636 | −53 | −107 | −5 |
| Race (reference = white) | ||||||
| Asian | 22,908 | −14,968 | 55,130 | 116 | 3 | 214 |
| black | 18,683 | 4,394 | 32,119 | 34 | −38 | 100 |
| Native American | 3,844 | −24,745 | 34,533 | 89 | −45 | 201 |
| Other | 40,574 | −41,705 | 65,778 | 264 | −582 | 491 |
| Medicaid coveragea | 21,564 | 6,100 | 35,780 | 28 | −49 | 100 |
| No. of cardiovascular conditionsa |
−1,406 | −4,274 | 1,052 | −26 | −42 | −11 |
| Hemoglobina | −486 | −2,861 | 1,726 | −6 | −17 | 5 |
| Serum albumina | 6,346 | 390 | 11,698 | 16 | −15 | 48 |
| Diabetic ESRDa | 11,623 | 3,284 | 19,771 | 25 | −19 | 68 |
| AMI before CABG | 9,179 | 607 | 17,198 | 6 | −38 | 47 |
| COPDa | 130 | −10,790 | 11,319 | −76 | −146 | −1 |
| Vintage | −600 | −843 | −327 | −9 | −11 | −7 |
| Hospital stays after CABG | −336 | −1,022 | 283 | −2 | −6 | 2 |
| Percentile of initial Medicare expenditureb |
47,437 | 28,687 | 66,159 | −236 | −336 | −139 |
| Discharge to self care / outpatient |
1,516 | −6,483 | 9,048 | 18 | −18 | 56 |
| Cardiac rehabilitation | 2,904 | −7,028 | 11,940 | 76 | 22 | 129 |
Measured at HD start
accumulated during the 6-month entry period.
Abbreviations: CABG, coronary artery bypass grafting; HD, hemodialysis; ESRD, end-stage renal disease; AMI, acute myocardial infarction; COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
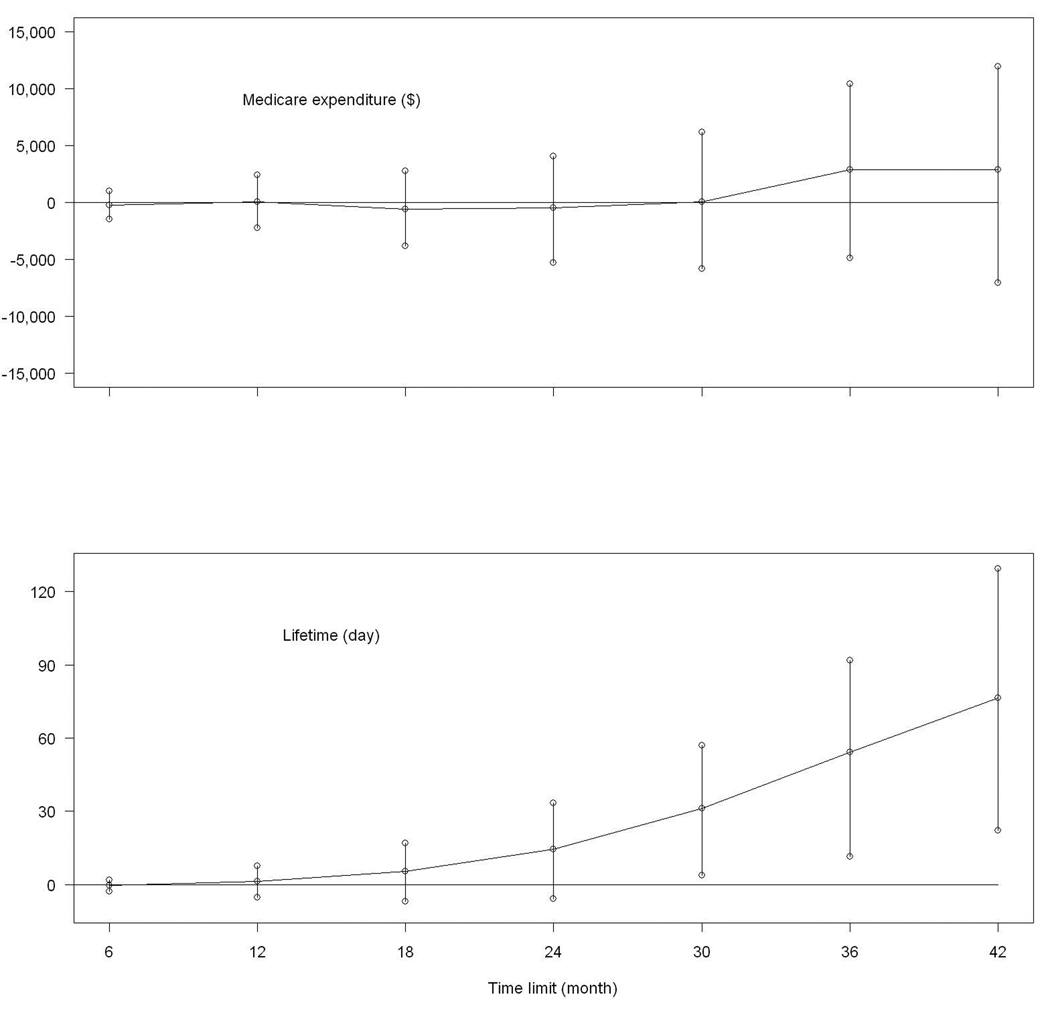
To investigate the temporal trend of differences between the cardiac rehabilitation and non-cardiac rehabilitation groups, the same models were applied to cumulative Medicare expenditure and lifetime at 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, and 36 months. The regression coefficients of cardiac rehabilitation along with their 95% confidence intervals are plotted in Figure 1. The differences in both cumulative Medicare expenditure and lifetime were small during the first year. The survival benefit of cardiac rehabilitation increased steadily over time, reaching statistical significance after month 30. Meanwhile, by month 36, the cardiac rehabilitation group showed a statistically non-significant increase in cumulative Medicare expenditure.
Figure 1.
Estimated differences and their 95% confidence intervals between the cardiac rehabilitation group and non-cardiac rehabilitation group in cumulative Medicare expenditure and cumulative lifetime
DISCUSSION
The estimated ICER value for receiving cardiac rehabilitation at baseline was $13,887 per year of life saved among dialysis patients over a time horizon of 42 months. Although there is no universally accepted benchmark for the ‘cost-effective’ ICER value, a familiar categorization scheme designates a value of $20,000 or less as highly cost-effective, a value of $20,000 to $40,000 as cost-effective, a value of $40,000 to $60,000 as borderline cost-effective, and a value of $60,000 or more as expensive.17–19 In this realm, cardiac rehabilitation is regarded as highly cost-effective in our dialysis population under investigation.
In order to perform cost-effectiveness analysis, we adopted an approach to the analysis of survival time different from that in our previous investigation.16 The propensity score was used in the current analysis to define the study cohort and to conduct stratified analysis. In addition, the main survival time outcome was cumulative lifetime at 42 months and the multivariate linear regression model was adopted here, whereas the Cox proportional hazards model was employed in the previous investigation. Nevertheless, both analyses were highly consistent in showing that receiving cardiac rehabilitation was significantly associated with longer survival time in dialysis patients after CABG.
Our study suggested a moderate increment in cumulative Medicare expenditure at 42 months associated with receiving cardiac rehabilitation. However, this increment was not likely due to the cardiac rehabilitation cost. By the start of follow-up, most baseline cardiac rehabilitation sessions were complete. Also, Figure 1 shows that the difference in cumulative Medicare expenditure between the cardiac rehabilitation and non-cardiac rehabilitation groups was small during the first year. Repeating our analysis by considering hospitalization expenditure only (data not shown), we found that the increment of cumulative hospitalization expenditure was similar to that of cumulative Medicare expenditure in the cardiac rehabilitation group.
Economic evaluations of cardiac rehabilitation have been limited even in the general population.20,21 Data have supported cost-effectiveness of cardiac rehabilitation, with increased cost per year of life saved comparing favorably with other currently funded interventions. The majority of these investigations focused on patients who have had myocardial infarction. The strength of our study lies in the large population-based sample of dialysis patients who were followed for an extended period of time after CABG. Nevertheless, it is also important to recognize several potential limitations of this investigation. First, large differences in baseline characteristics were observed between patients who received cardiac rehabilitation and those who did not. We made extensive efforts to address this imbalance by adopting propensity score and multivariate regression analysis. Nevertheless, as with any observational studies, imbalance could still exist in unobserved patient characteristics which might account for the expenditure and survival differences.
Second, our results were based on and therefore applied to healthier patients in the chronic HD population who underwent CABG. The observed rate of receiving cardiac rehabilitation among dialysis patients, approximately 13%, was lower than the estimated rate of approximately 23% in the general population after CABG.16 The cardiac rehabilitation rate for less healthy subgroups of chronic HD patients was even lower, and these subgroups were excluded from this investigation.
Third, the time horizon for this study was 42 months after the 6-month entry period following CAGB hospitalization discharge. As in any study with limited follow-up, the increments of cumulative Medicare expenditure and lifetime might not be the same when the time horizon is extended.
At the same time, the findings of our study are consistent with literature in the general population that supports the efficacy and cost effectiveness of cardiac rehabilitation. It is likely that core aspects of cardiac rehabilitation services would be beneficial for virtually all patients with CVD. In conclusion, this observational study suggests that cardiac rehabilitation is highly cost-effective in ESRD patients following CABG.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Study population
The data used in this analysis came from linking USRDS files to Medicare inpatient and outpatient claims. The former contained demographic and clinical information of dialysis patients. Medicare primary-pay ESRD patients who initiated chronic HD and underwent CABG while on chronic dialysis during the period between January 1, 1998 and December 31, 2004 were identified retrospectively from the USRDS database. For patients who were younger than 65 years, only those with CABG procedure dates that occurred day 90 or later of ESRD were included, because many of these patients did not become eligible for Medicare for up to 90 days after initiating dialysis and therefore might not have complete claims data. In addition, we did not include patients who, after the CABG procedure, left the hospital against medical advice or were discharged to home under care of an IV therapy provider or to hospice care.
A preliminary investigation of this study cohort showed that less than 13% of CABG survivors received cardiac rehabilitation, and the rate varied substantially across subgroups. Those subgroups with minimal rate would provide little information on the association of cardiac rehabilitation with Medicare expenditure and survival. For this reason, we excluded the following patients: (1) patients who were non-ambulatory at dialysis initiation, (2) patients whose CABG hospitalization exceeded 44 days following the surgery, or (3) patients who incurred Medicare expenditure of over $66,244 during the 6-month entry period. The cut-off points for the hospital stays and initial Medicare expenditure were determined as the 99th percentiles among patients who received cardiac rehabilitation at baseline. Physical limitation might be the main reason for the observed low rehabilitation rate among non-ambulatory patients. Patients with longer hospital stays for the CABG procedure or with higher initial Medicare expenditure were more likely to experience serious complications post surgery; they were overly represented among those who did not receive cardiac rehabilitation. After applying these exclusion criteria, a propensity score for receiving cardiac rehabilitation was calculated, and the patients in the lowest quintile of the propensity score distribution were excluded as well.
Study design
The objective of this study was to assess the association between receiving cardiac rehabilitation at baseline and cumulative Medicare expenditure and survival time during a follow-up period of up to 42 months. The follow-up started after a 6-month entry period following the discharge from CABG hospitalization to allow for the determination of receiving cardiac rehabilitation at baseline. By design, all patients included in the analysis survived at least six months after discharge from CABG hospitalization. Medicare expenditure and survival time were followed up to December 31, 2004. A patient undergoing renal transplantation was treated as being censored at the time of transplantation.
Measures
Cardiac rehabilitation was defined as outpatient cardiac rehabilitation without or with continuous electrocardiogram monitoring (Current Procedural Terminology codes 93797 and 93798). Medicare covers participation by eligible patients in a cardiac rehabilitation exercise program for up to 36 sessions, with three sessions a week in a single 12-week period of therapy. For this analysis, cardiac rehabilitation received after CABG and before the end of the 6-month entry period was regarded as cardiac rehabilitation at baseline. This time period included about 90% of the patients in our study population who ever received cardiac rehabilitation.
Demographic characteristics of the patients included age, gender, and race. Medicaid coverage at dialysis initiation (yes/no) was used as an indicator of socioeconomic status (Medicaid is a federal / state health insurance entitlement program for low-income people). Clinical characteristics documented at dialysis initiation included primary diagnosis of diabetes, number of existing cardiovascular conditions (congestive heart failure, coronary artery disease, history of AMI, cardiac arrest, dysrhythmia, cerebral vascular disease, peripheral vascular disease), COPD, serum albumin (g/dl), and hemoglobin (g/dl). After dialysis initiation, AMI that occurred before CABG was also determined.
Medicare expenditures included claims from institutional and physician/supplier data files. All costs were adjusted to 1998 dollars, using the Medical Care component of the Consumer Price Index (CPI) for inflation. In addition, all cost value was discounted at an annual rate of 3%.
Statistical analyses
The receipt of cardiac rehabilitation was not randomly determined in this investigation, as with any observational study. In fact, substantial clinical and socioeconomic differences between patients who received cardiac rehabilitation at baseline and those who did not were observed. Inadequately accounting for these differences could lead to biased assessment of the effect of cardiac rehabilitation. We employed the propensity score method22,23 to exclude subgroups of patients with minimal propensity for receiving cardiac rehabilitation and to carry out propensity score-stratified analyses. Stepwise logistic regression was used to compute the propensity score for receiving cardiac rehabilitation. Baseline measures used as candidate covariates included demographic characteristics (age, gender, race, and Medicaid coverage), clinical characteristics at the dialysis initiation (number of cardiovascular conditions, hemoglobin, serum albumin, primary diagnosis of diabetes, COPD) and before CABG (AMI), as well as measures associated with the CABG procedure (vintage defined as the dialysis duration at the time of CABG, hospital stays after CABG, discharge destination of the CABG hospitalization), and the decile ranking of Medicare expenditure during the 6-month entry period. After the patients in the lowest quintile of the estimated propensity score were excluded, the same stepwise logistic regression was re-run to refine the propensity scores for the study cohort. The refined propensity score was used in the subsequent stratified analyses.
Demographic and baseline clinical characteristics were summarized using means for continuous variables and percentages for discrete variables, by the status of receiving cardiac rehabilitation at baseline and by the propensity score quartiles. Comparisons, as stratified by the propensity score quartiles, were made between cardiac rehabilitation and non-cardiac rehabilitation groups, using linear regression for continuous variables and the Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel test for discrete variables.
A multivariate linear regression model was used to examine the association between receiving cardiac rehabilitation at baseline and cumulative Medicare expenditure during the follow-up. Other dependent variables incorporated for adjustment included demographic characteristics and baseline clinical characteristics as well as percentiles of the entry-period Medicare expenditure. The analysis was stratified by the propensity score quartiles, i.e., stratum-specific intercepts being incorporated in the model. To accommodate censoring due to either renal transplantation or the end of follow-up, we used a Horvitz-Thompson-type approach to missing data.24,25 An important component of this approach was to estimate the probability of being censored for every uncensored observation in the sample. A proportional hazards model was employed for the censoring time with all the aforementioned dependent variables. Subsequently, the uncensored observations, each weighted inversely by its associated probability, formed a pseudo-sample of complete cases to which the linear regression model could be applied. To carry out further cost-effectiveness analysis, a similar multivariate linear regression model coupled with the Horvitz-Thompson approach was employed for cumulative lifetime. For inference with these models, bootstrap of size 1000 was used to construct 95% percentile confidence intervals. The incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER) was calculated for the cost-effectiveness assessment of receiving cardiac rehabilitation at baseline after CABG.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This study was supported by National Institutes of Health contracts N01-DK-1-2471 and HHSN267200715004C, ADB No. N01-DK-7-5004 and by National Institutes of Health grant R01 CA090747.
Footnotes
DISCLOSURE
The authors state no conflict of interest.
REFERENCES
- 1.U.S. Renal Data System. Bethesda, MD: National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; USRDS 2007 Annual Data Report: Atlas of End-Stage Renal Disease in the United States. 2007
- 2.Collins AJ. Cardiovascular mortality in end-stage renal disease. Am J Med Sci. 2003;325:163–167. doi: 10.1097/00000441-200304000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Leon AS, Franklin BA, Costa F, et al. Cardiac rehabilitation and secondary prevention of coronary heart disease: an American Heart Association scientific statement from the Council on Clinical Cardiology (Subcommittee on Exercise, Cardiac Rehabilitation, and Prevention) and the Council on Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Metabolism (Subcommittee on Physical Activity), in collaboration with the American Association of Cardiovascular and Pulmonary Rehabilitation. Circulation. 2005;111:369–376. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000151788.08740.5C. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Giannuzzi P, Saner H, Bjornstad H, et al. Secondary prevention through cardiac rehabilitation: position paper of the Working Group on Cardiac Rehabilitation and Exercise Physiology of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur Heart J. 2003;24:1273–1278. doi: 10.1016/s0195-668x(03)00198-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) [Accessed July 11,2007];Medicare National Coverage Determinations Manual. Available: http://www.cms.hhs.gov/manuals/downloads/ncd103c1_Part1.pdf.
- 6.Thomas RJ, Miller NH, Lamendola C, et al. National survey on gender differences in cardiac rehabilitation programs: Patient characteristics and enrollment patterns. J Cardiopulm Rehabil. 1996;16:402–412. doi: 10.1097/00008483-199611000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Dalal H, Evans PH, Campbell JL. Recent developments in secondary prevention and cardiac rehabilitation after acute myocardial infarction. BMJ. 2004;328:693–697. doi: 10.1136/bmj.328.7441.693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Belardinelli R, Georgiou D, Cianci G, et al. Randomized, controlled trial of long-term moderate exercise training in chronic heart failure: Effects on functional capacity, quality of life, and clinical outcome. Circulation. 1999;99:1173–1182. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.99.9.1173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Hedback B, Perk J, Wodlin P. Long-term reduction of cardiac mortality after myocardial infarction: 10-year results of a comprehensive rehabilitation programme. Eur Heart J. 1993;14:831–835. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/14.6.831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Lau A, Antman EM, Jimenez-Silva J, et al. Cumulative meta-analysis of therapeutic trials for myocardial infarction. N Eng J Med. 1992;327:248–254. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199207233270406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Oldridge NB, Guyatt GH, Fischer ME, et al. Cardiac rehabilitation after myocardial infarction: Combined experience of randomized clinical trials. JAMA. 1988;260:945–950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Yu C, Lau C, Chau J, McGhee S, et al. A short course of cardiac rehabilitation program is highly cost effective in improving long-term quality of life in patients with recent myocardial infarction or percutaneous coronary intervention. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2004;85:1915–1922. doi: 10.1016/j.apmr.2004.05.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Georgiou D, Chen Y, Appadoo S, et al. Cost-effectiveness analysis of long-term moderate exercise training in chronic heart failure. Am J Cardiol. 2003;87:984–988. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9149(01)01434-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Ades P, Pashkow F, Nestor J. Cost-effectiveness of cardiac rehabilitation after myocardial infarction. J Cardiopulm Rehabil. 1997;17:222–231. doi: 10.1097/00008483-199707000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Ades P, Huang D, Weaver S. Cardiac rehabilitation participation redicts lower rehospitalization costs. Am Heart J. 1992;123:916–921. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(92)90696-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Kutner NG, Zhang R, Huang Y, et al. Cardiac rehabilitation and survival of dialysis patients after coronary bypass. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006;17:1175–1180. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2005101027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kupersmith J, Holmes-Rovner M, Hogan A, et al. Cost-effectiveness analysis in heart disease, Part I: General principles. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 1994;37:161–184. doi: 10.1016/s0033-0620(05)80041-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kupersmith J, Holmes-Rovner M, Hogan A, et al. Cost-effectiveness analysis in heart disease, Part II: Preventive therapies. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 1995;37:243–271. doi: 10.1016/s0033-0620(05)80009-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kupersmith J, Holmes-Rovner M, Hogan A, et al. Cost-effectiveness analysis in heart disease, Part III: Ischemia, congestive heart failure, and arrhythmias. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 1995;37:307–346. doi: 10.1016/s0033-0620(05)80017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Papadakis S, Oldridge NB, Coyle D, et al. Economic evaluation of cardiac rehabilitation: a systematic review. Eur J Cardiovasc Prev Rehabil. 2005;12:513–520. doi: 10.1097/01.hjr.0000186624.60486.e8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Oldridge NB. Comprehensive cardiac rehabilitation: is it cost-effective? Eur Heart J. 1998;19 Suppl O:O42–O49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Rosenbaum PR, Rubin DB. The central role of the propensity score in observational studies for causal effects. Biometrika. 1983;70:41–55. [Google Scholar]
- 23.D’Agostino R., Jr Propensity score methods for bias reduction in the comparison of a treatment to a non-randomized control group. Statist Med. 1998;17:2265–2281. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-0258(19981015)17:19<2265::aid-sim918>3.0.co;2-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Little RJA, Rubin DB. Statistical Analysis with Missing Data. 2nd ed. New Jersey: John Wiley &Sons; 2002. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Lin DY. Linear regression analysis of censored medical costs. Biostatistics. 2000;1:35–47. doi: 10.1093/biostatistics/1.1.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]