Abstract
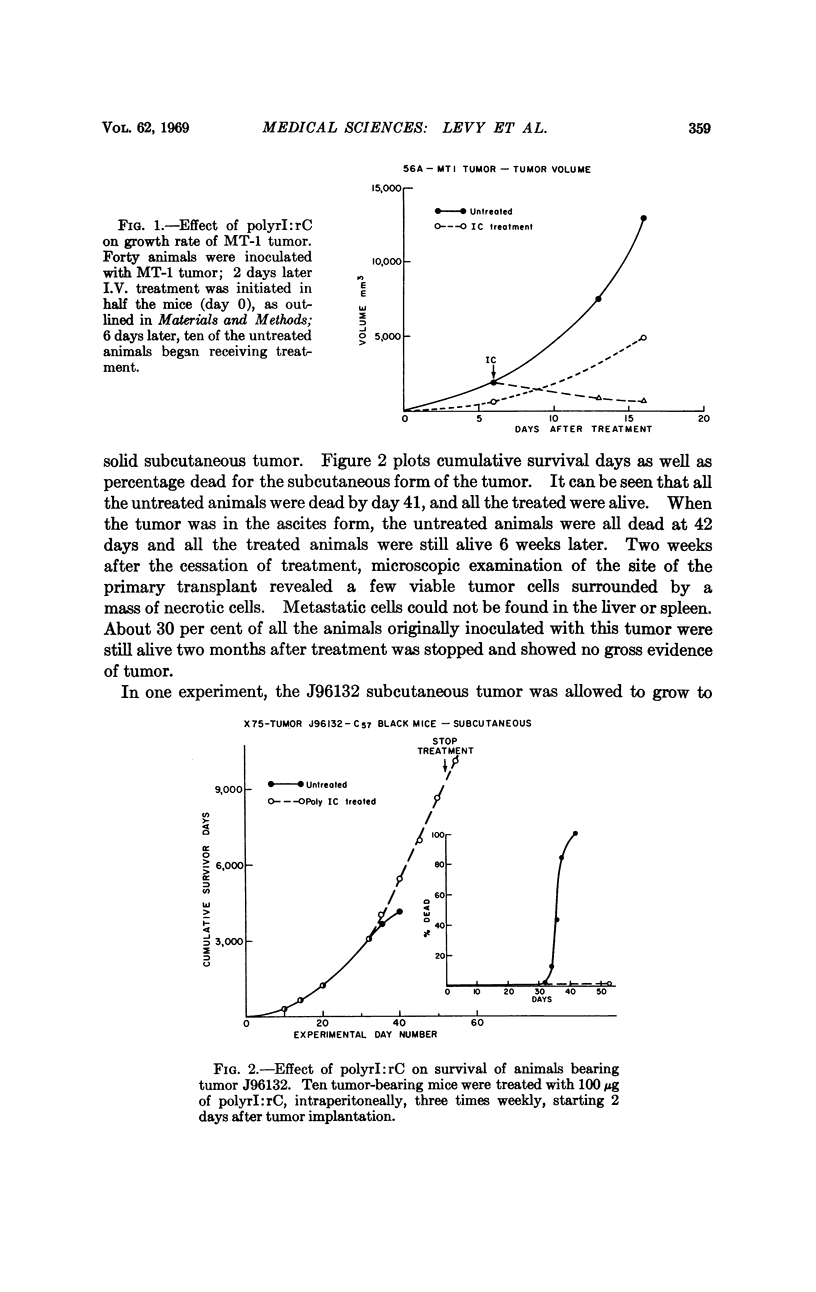
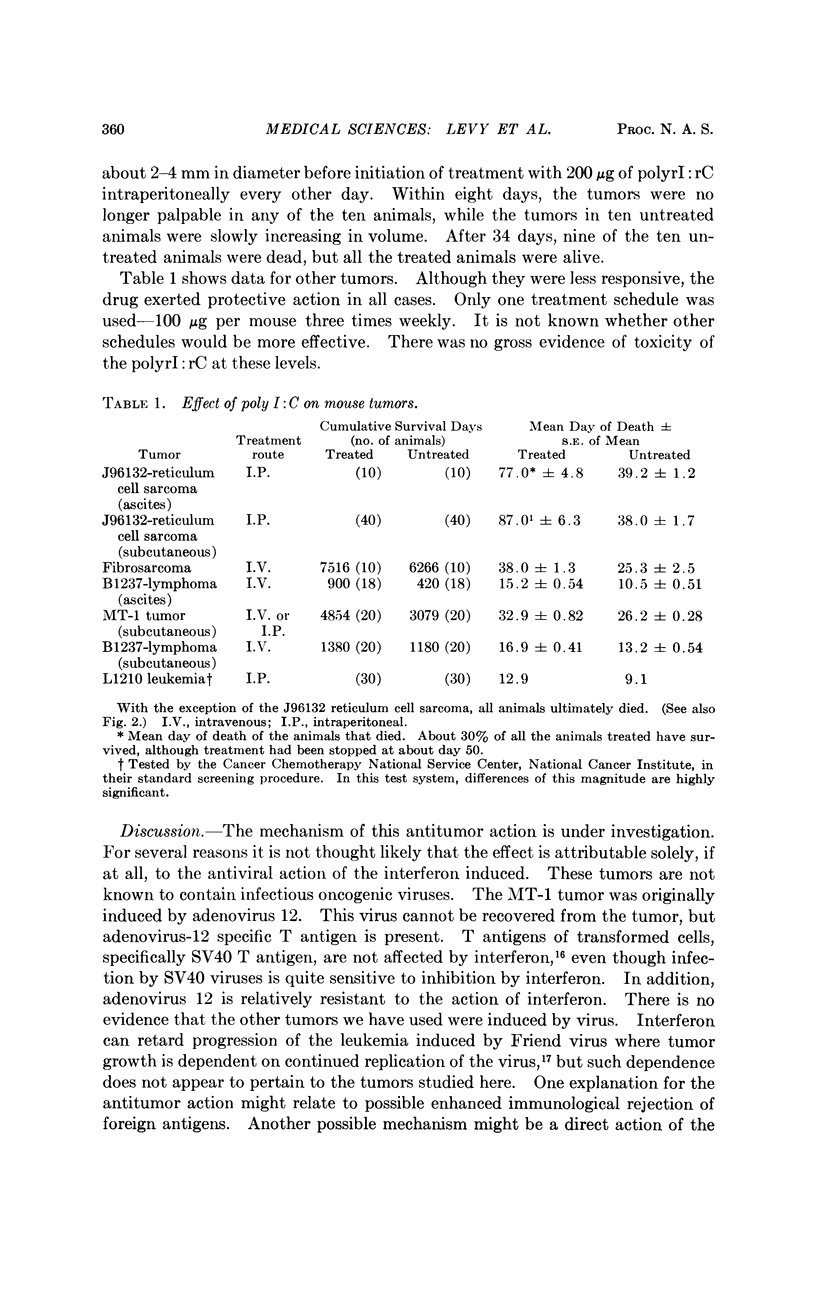
The synthetic double-stranded RNA, polyinosinic-cytidylic acid, inhibits the growth of some tumors in mice. Two days after implantation of a reticulum cell sarcoma, a lymphatic lymphoma, a fibrosarcoma, two leukemias, and a human adenovirus 12-induced tumor, treatment of groups of mice resulted in decreased growth rates of the tumors and increased survival times of the animals. In the two tumors tested (the reticulum cell sarcoma and the adenovirus 12-induced tumor) initiation of treatment after the tumor was grown to moderate size caused a regression of the tumor. In the case of the reticulum cell sarcoma, the tumor had not reappeared in some of the animals two months after cessation of treatment.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carter W. A., Levy H. B. Ribosomes: effect of interferon on their interaction with rapidly labeled cellular and viral RNA's. Science. 1967 Mar 10;155(3767):1254–1257. doi: 10.1126/science.155.3767.1254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUNN T. B. Normal and pathologic anatomy of the reticular tissue in laboratory mice, with a classification and discussion of neoplasms. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1954 Jun;14(6):1281–1433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field A. K., Tytell A. A., Lampson G. P., Hilleman M. R. Inducers of interferon and host resistance. II. Multistranded synthetic polynucleotide complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Sep;58(3):1004–1010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.3.1004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISAACS A. FOREIGN NUCLEIC ACIDS. Sci Am. 1963 Oct;209:46–50. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican1063-46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joklik W. K., Merigan T. C. Concerning the mechanism of action of interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Aug;56(2):558–565. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.2.558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIRSCHSTEIN R. L., RABSON A. S., PETERS E. A. ONCOGENIC ACTIVITY OF ADENOVIRUS 12 IN THYMECTOMIZED BALB/C AND C3H/HEN MICE. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Oct;117:198–200. doi: 10.3181/00379727-117-29535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVY H. B., AXELROD D., BARON S. EFFECT OF FUDR ON INTERFERON PRODUCTION. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Apr;118:1013–1014. doi: 10.3181/00379727-118-30032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy H. B., Carter W. A. Molecular basis of the action of interferon. J Mol Biol. 1968 Feb 14;31(3):561–577. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90428-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy H. B., Merigan T. C. Interferon and uninfected cells. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Jan;121(1):53–55. doi: 10.3181/00379727-121-30695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus P. I., Salb J. M. Molecular basis of interferon action: inhibition of viral RNA translation. Virology. 1966 Nov;30(3):502–516. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90126-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxman M. N., Baron S., Black P. H., Takemoto K. K., Habel K., Rowe W. P. The effect of interferon on SV-40 T antigen production in SV-40-transformed cells. Virology. 1967 May;32(1):122–127. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90260-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. Inhibition of interferon action by actinomycin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1964;14:447–451. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(64)90084-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WAGNER R. R., LEVY A. H. Interferon as a chemical intermediary in viral interference. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1960 Nov 21;88:1308–1318. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1960.tb20122.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



