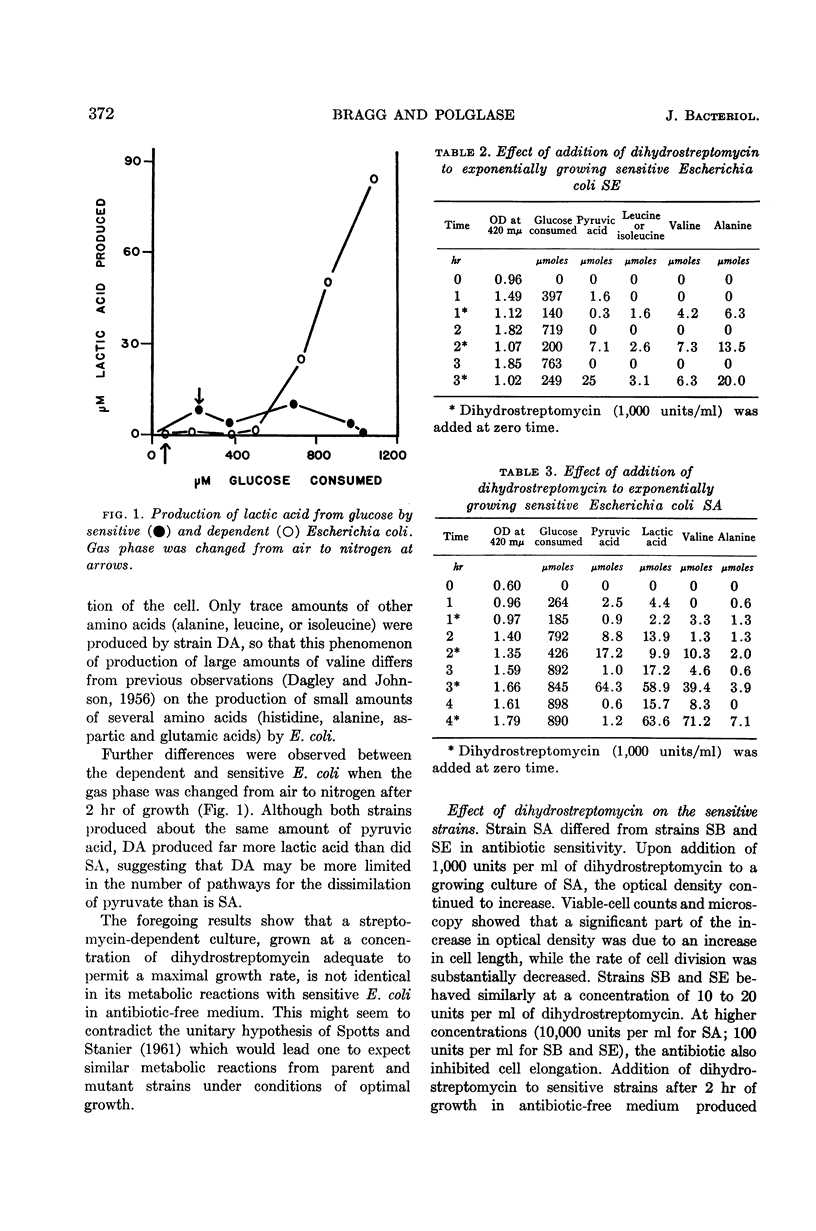
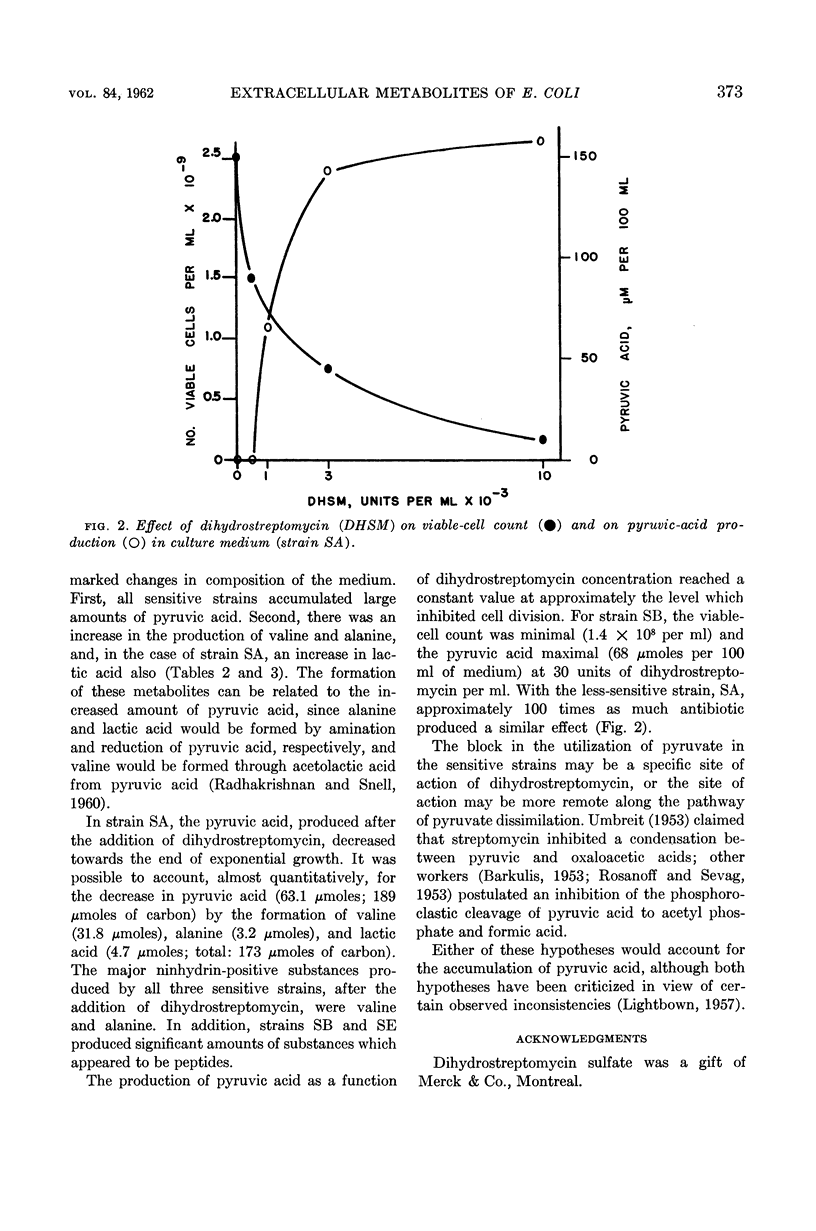
Abstract
Bragg, P. D. (University of British Columbia, Vancouver, Canada) and W. J. Polglase. Extracellular metabolites of streptomycin mutants of Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 84:370–374. 1962.—A comparison of the extracellular products of glucose metabolism during aerobic exponential growth of Escherichia coli showed that a streptomycin-dependent strain produced large amounts of l-valine while only trace amounts of this amino acid were produced by streptomycin-sensitive strains. A further difference between sensitive and dependent mutants was the production by the latter of lactic acid when the gas phase was changed from air to nitrogen. Resistant cultures grown in antibiotic-free medium were similar to sensitive cultures, but when dihydrostreptomycin was added, the resistant organism produced lactic and pyruvic acids. Three strains of streptomycin-sensitive E. coli accumulated pyruvic acid from glucose oxidation in the presence of concentrations of dihydrostreptomycin which inhibited multiplication. Further evidence is thus provided to implicate reactions of pyruvate as being of significance in the mechanism of action of streptomycin.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANAND N., DAVIS B. D. Damage by streptomycin to the cell membrane of Escherichia coli. Nature. 1960 Jan 2;185:22–23. doi: 10.1038/185022a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARKULIS I. L. Inhibition of the anaerobic pyruvate metabolism of Escherichia coli by dihydrostreptomycin. J Bacteriol. 1953 Mar;65(3):337–343. doi: 10.1128/jb.65.3.337-343.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BODE F. Eine Vereinfachung und Verbesserung der Methode zur quantitativen Bestimmung von Aminosäuren und Peptiden mittels des Ninhydrin-Kupferkomplexes. Biochem Z. 1955;326(6):433–435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAGLEY S., JOHNSON A. R. Appearance of amino acids and peptides in culture filtrates of micro-organisms growing in mineral salt media. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1956 Aug;21(2):270–276. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(56)90007-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EL HAWARY M. F. S., THOMPSON R. H. S. Separation and estimation of blood keto acids by paper chromatography. Biochem J. 1953 Feb;53(3):340–347. doi: 10.1042/bj0530340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ERDOS T., ULLMANN A. Effect of streptomycin on the incorporation of amino-acids labelled with carbon-14 into ribonucleic acid and protein in a cell-free system of a Mycobacterium. Nature. 1959 Feb 28;183(4661):618–619. doi: 10.1038/183618a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANDMAN O. E., BURCHARD W. The mechanism of action of streptomycin as revealed by normal and abnormal division in streptomycin-dependent Salmonellae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Feb;48:219–228. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.2.219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIGHTBOWN J. W. Metabolic processes underlying streptomycin resistance. G Ital Chemioter. 1957 Jan-Jun;4(1-2):22–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MONTGOMERY R. Determination glycogen. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1957 Apr;67(2):378–386. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(57)90292-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POLGLASE W. J., PERETZ S., ROOTE S. M. Adaptive enzyme formation by dihydrostreptomycine-dependent Escherichia coli. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1956 May;34(3):558–562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RADHAKRISHANAN A. N., SNELL E. E. Biosynthesis of valine and isoleucine. 2. Formation of alpha-acetolactate and alpha-aceto-alpha-hydroxybutyrate in Neurospora crassa and Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1960 Aug;235:2316–2321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROOTE S. M., POLGLASE W. J. The effect of dihydrostreptomycin on the formation of adaptive enzymes by a strain of Escherichia coli. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1955 Sep;33(5):792–796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPOTTS C. R., STANIER R. Y. Mechanism of streptomycin action on bacteria: a unitary hypothesis. Nature. 1961 Nov 18;192:633–637. doi: 10.1038/192633a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UMBREIT W. W. The action of streptomycin. VI. A new metabolic intermediate. J Bacteriol. 1953 Jul;66(1):74–81. doi: 10.1128/jb.66.1.74-81.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



