Abstract
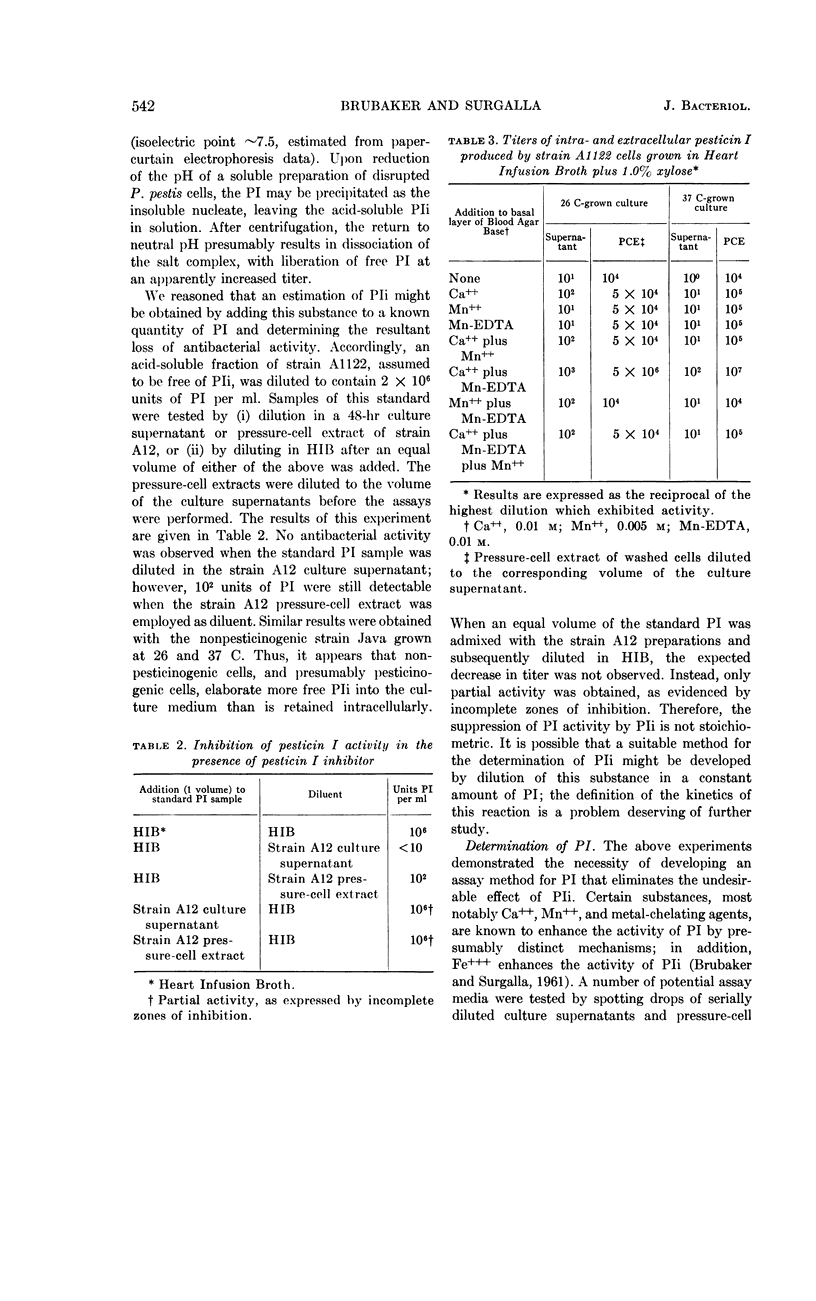
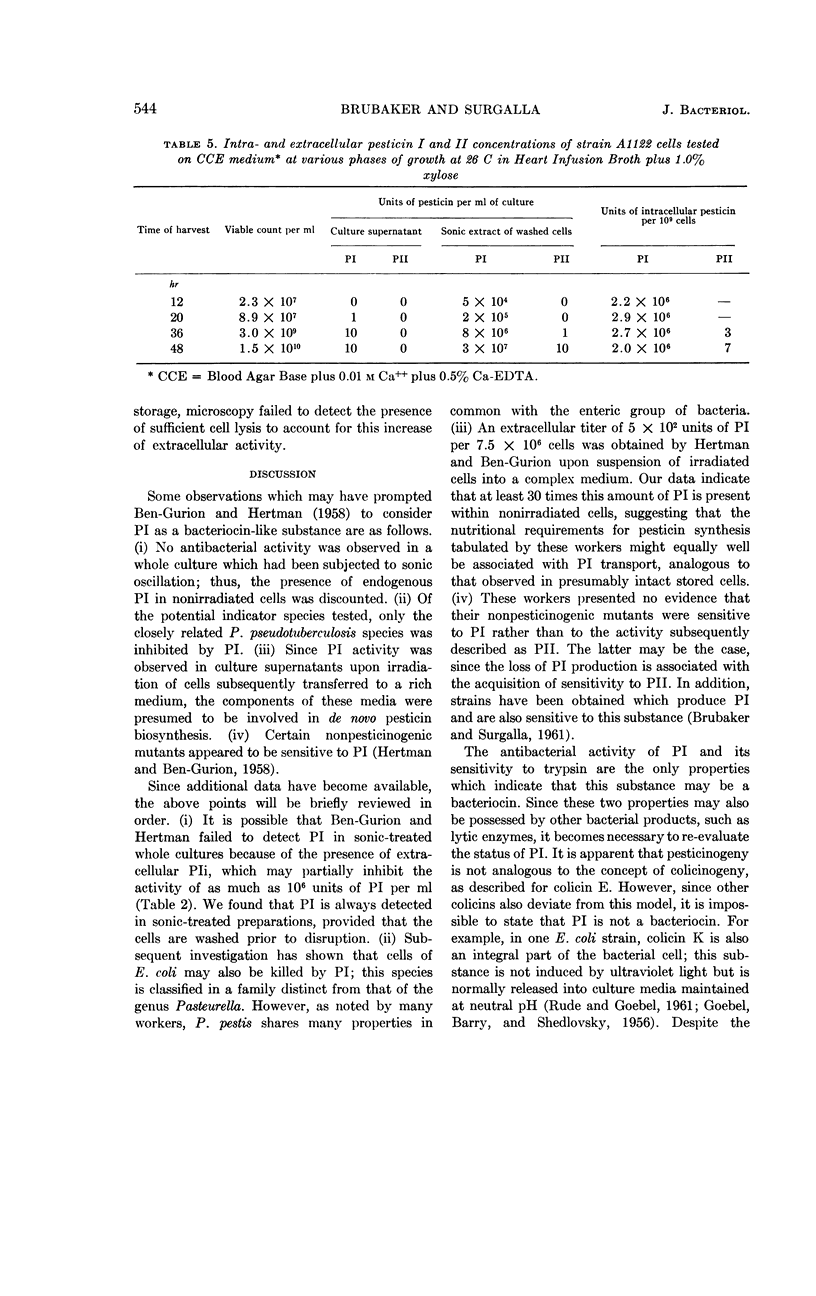
Brubaker, Robert R. (Fort Detrick, Frederick, Md.) and Michael J. Surgalla. Pesticins. II. Production of pesticin I and II. J. Bacteriol. 84:539–545. 1962.—Pesticin I was separated from pesticin I inhibitor by ion-exchange chromatography of cell-free culture supernatant fluids and by acid precipitation of soluble preparations obtained from mechanically disrupted cells. The latter procedure resulted in formation of an insoluble pesticin I complex which, upon removal by centrifugation and subsequent dissolution in neutral buffer, exhibited a 100- to 1,000-fold increase in antibacterial activity over that originally observed. However, activity returned to the former level upon addition of the acid-soluble fraction, which contained pesticin I inhibitor. Since the presence of pesticin I inhibitor leads to serious errors in the determination of pesticin I, an assay medium containing ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid in excess Ca++ was developed; this medium eliminated the effect of the inhibitor. By use of the above medium, sufficient pesticin I was found to be contained within 500 nonirradiated cells to inhibit growth of a suitable indicator strain; at least 107 cells were required to effect a corresponding inhibition by pesticin II. Although both pesticins are located primarily within the cell during growth, pesticin I may arise extracellularly during storage of static cells. Slightly higher activity of pesticin I inhibitor was found in culture supernatant fluids than occurred in corresponding cell extracts of equal volume. The differences and similarities between pesticin I and some known bacteriocins are discussed.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANACKER R. L., ORDAL E. J. Studies on the myxobacterium Chondrococcus columnaris. II. Bacteriocins. J Bacteriol. 1959 Jul;78(1):33–40. doi: 10.1128/jb.78.1.33-40.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEN-GURION R., HERTMAN I. Bacteriocin-like material produced by Pasteurella pestis. J Gen Microbiol. 1958 Oct;19(2):289–297. doi: 10.1099/00221287-19-2-289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRUBAKER R. R., SURGALLA M. J. Pesticins. I. Pesticinbacterium interrelationships, and environmental factors influencing activity. J Bacteriol. 1961 Dec;82:940–949. doi: 10.1128/jb.82.6.940-949.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURROWS T. W., BACON G. A. The effects of loss of different virulence determinants on the virulence and immunogenicity of strains of Pasteurella pestis. Br J Exp Pathol. 1958 Jun;39(3):278–291. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREDERICQ P. Colicins and colicinogenic factors. Symp Soc Exp Biol. 1958;12:104–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOEBEL W. F., BARRY G. T., SHEDLOVSKY T. Colicine K. I. The production of colicine K in media maintained at constant pH. J Exp Med. 1956 May 1;103(5):577–588. doi: 10.1084/jem.103.5.577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERTMAN I., BEN-GURION R. A study on pesticin biosynthesis. J Gen Microbiol. 1959 Aug;21:135–143. doi: 10.1099/00221287-21-1-135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IVANOVICS G., ALFOLDI L. A new antibacterial principle: megacine. Nature. 1954 Sep 4;174(4427):465–465. doi: 10.1038/174465a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOB F. Biosynthèse induite et mode d'action d'une pyocine, antibiotique de Pseudomonas pyocyanea. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1954 Feb;86(2):149–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOB F., LWOFF A., SIMINOVITCH A., WOLLMAN E. Définition de quelques termes relatifs a la lysogénie. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1953 Jan;84(1):222–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOB F., SIMINOVITCH L., WOLLMAN E. Sur la biosynthèse d'une colicine et sur son mode d'action. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1952 Sep;83(3):295–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOB F., WOLLMAN E. L. Les épisomes, éléments génétiques ajoutés. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1958 Jul 7;247(1):154–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUKAI F. H. Interrelationship between colicin sensitivity and phage resistance. J Gen Microbiol. 1960 Dec;23:539–551. doi: 10.1099/00221287-23-3-539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH D. A., BURROWS T. W. Phage and bacteriocin investigations with Pasteurella pestis and other bacteria. Nature. 1962 Jan 27;193:397–398. doi: 10.1038/193397a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


