Abstract
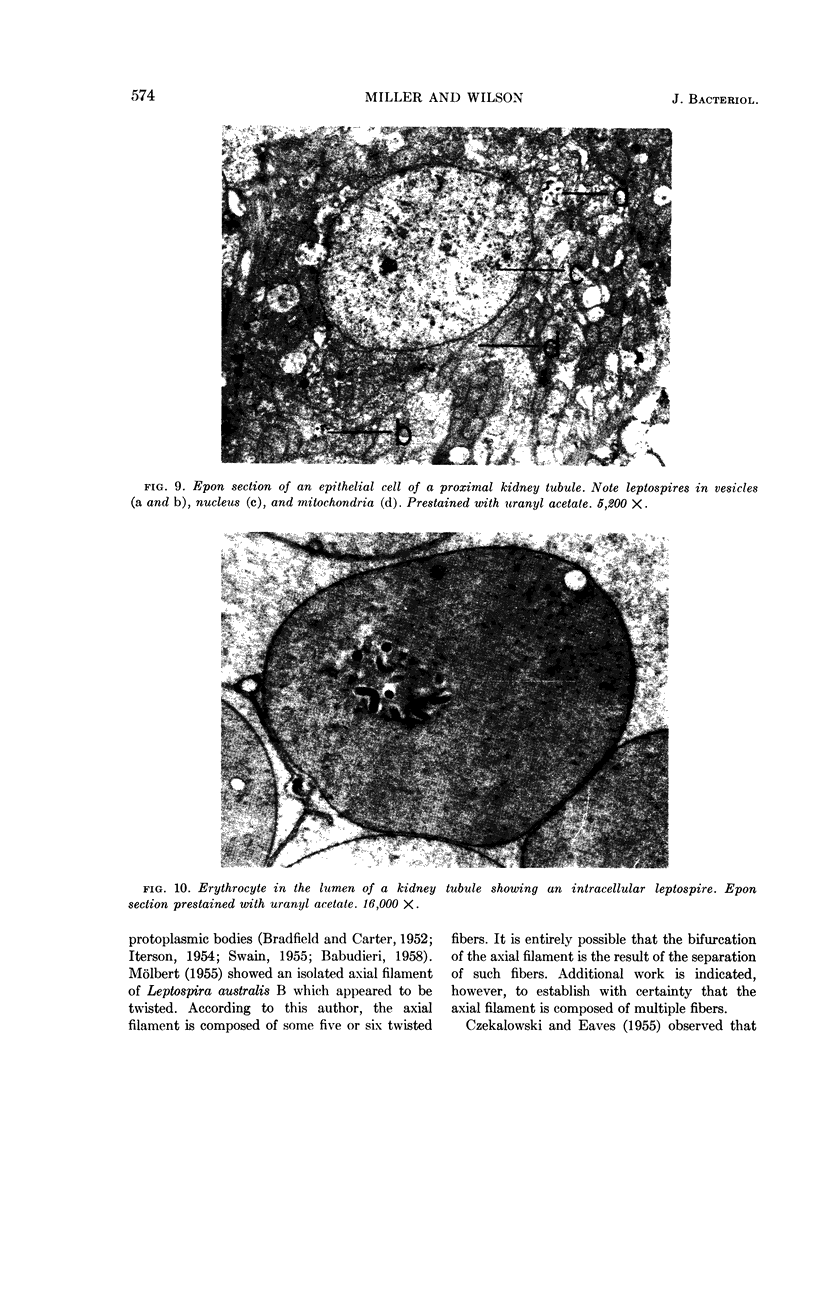
Miller, Norman G. (University of Nebraska College of Medicine, Omaha) and Richard B. Wilson. In vivo and in vitro observations of Leptospira pomona by electron microscopy. J. Bacteriol. 84:569–576. 1962.—Leptospira pomona 3341 was observed by electron microscopy, after the preparation of thin sections from culture material and from infected hamster tissue. The external membrane of low electron density envelops the entire leptospire and appears to be quite flexible, as suggested by its many folds. The spiral protoplasmic body is tubular in structure with a relatively dense wall and a central area of low electron density. Occasionally, very dark circumscribed bodies were seen imbedded in the protoplasmic wall. Detailed morphology is presented of a knoblike structure located at the end of the axial filament. Bifurcation of the axial filament could be demonstrated in leptospires from cultures. Leptospires were observed free or enclosed in vesicles within the cytoplasm of liver parenchymal and renal tubule cells. Erythrocytes located in kidney tissue also contained leptospires within the cytoplasm. The appearance of intracellular leptospires is much the same as those seen extracellularly or from culture.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BABUDIERI B. [The cell structure and serology of Leptospira]. Ergeb Mikrobiol Immunitatsforsch Exp Ther. 1960;33:259–306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRADFIELD J. R. G., CATER D. B. Electron-microscopic evidence on the structure of spirochaetes. Nature. 1952 Jun 7;169(4310):944–946. doi: 10.1038/169944a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BREESE S. S., Jr, GOCHENOUR W. S., Jr, YAGER R. H. Electron microscopy of Leptospiral strains. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1952 Jun;80(2):185–188. doi: 10.3181/00379727-80-19564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAULFIELD J. B. Effects of varying the vehicle for OsO4 in tissue fixation. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1957 Sep 25;3(5):827–830. doi: 10.1083/jcb.3.5.827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COX C. D. Hemolysis of sheep erythrocytes sensitized with leptospiral extracts. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1955 Dec;90(3):610–615. doi: 10.3181/00379727-90-22113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CZEKALOWSKI J. W., EAVES G. The structure of leptospirae as revealed by electron microscopy. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1955 Jan-Apr;69(1-2):129–132. doi: 10.1002/path.1700690118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLAMATER E. D., WIGGALL R. H., HAANES M. Studies on the life cycle of spirochetes; the life cycle of the Nichols pathogenic Treponema pallidum in the rabbit testis as seen by phase contrast microscopy. J Exp Med. 1950 Sep;92(3):239–246. doi: 10.1084/jem.92.3.239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARQUHAR M. G. Preparation of ultrathin tissue sections for electron microscopy; review and compilation of procedures. Lab Invest. 1956 Jul-Aug;5(4):317–337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUFT J. H. Improvements in epoxy resin embedding methods. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Feb;9:409–414. doi: 10.1083/jcb.9.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOLBERT E. Elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen zur Morphologie von Leptospiren. Z Hyg Infektionskr. 1955;141(1):82–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton H. E., Anderson T. F. The Morphology of Leptospira icterohemorrhagiae and L. canicola as Revealed by the Electron Microscope. J Bacteriol. 1943 Feb;45(2):143–146. doi: 10.1128/jb.45.2.143-146.1943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIMPSON C. F., WHITE F. H. Electron microscope studies and staining reactions of leptospires. J Infect Dis. 1961 Nov-Dec;109:243–250. doi: 10.1093/infdis/109.3.243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SWAIN R. H. Electron microscopic studies of the morphology of pathogenic spirochaetes. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1955 Jan-Apr;69(1-2):117–128. doi: 10.1002/path.1700690117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKEYA K., MORI R., TODA T. Studies on the structure of Leptospira as revealed by the electron microscope. Jpn J Microbiol. 1957 Apr;1(2):99–104. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1957.tb00014.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VARPHOLOMEEVA A. A., STANISLAVSKY E. S. Recherches sur la morphologie des Leptospires à l'aide du microscope électronique. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1958 Mar;94(3):361–366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]














