Abstract
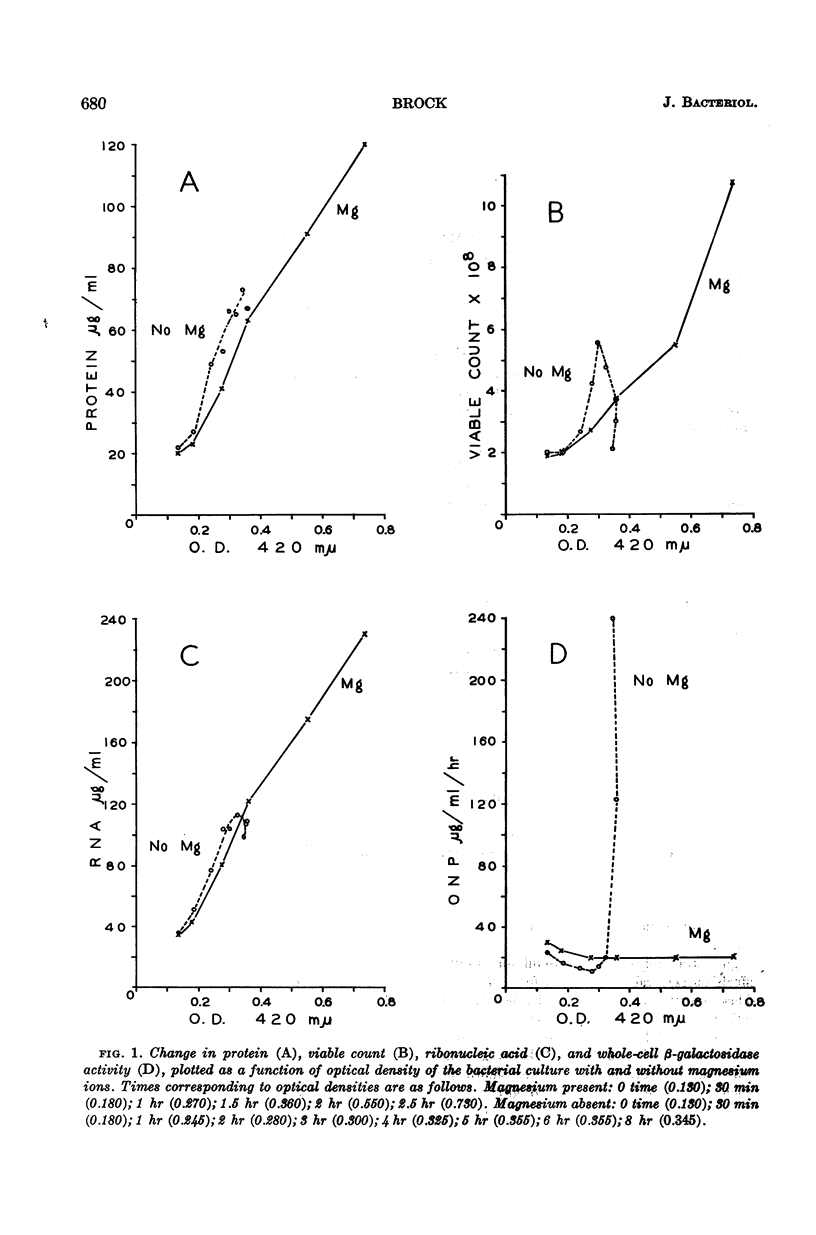
Brock, Thomas D. (Indiana University, Bloomington). Effects of magnesium ion deficiency on Escherichia coli and possible relation to the mode of action of novobiocin. J. Bacteriol. 84:679–682. 1962.—Cells of Escherichia coli ML35 grew in magnesium-deficient medium at an arithmetic rate for 4 to 5 hr. In the later stages of this period, the viability of the cells decreased, ribonucleic acid was lost, and the cells became able to hydrolyze o-nitro-phenyl-β-d-galactoside at a much increased rate. Further, the cells became filamentous and stained less intensely with methylene blue. Since magnesium ions are known to stabilize cell membranes, the changes are interpreted as due to alterations in membrane integrity. Novobiocin induced the same changes as magnesium ion deficiency, providing further support for the hypothesis that novobiocin acts by inducing a magnesium ion deficiency.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BROCK T. D., BROCK M. L. Effect of novobiocin on permeability of Escherichia coli. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1959 Nov;85:176–185. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(59)90461-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROCK T. D. Magnesium binding as an explanation of the mode of action of novobiocin. Science. 1962 Apr 27;136(3513):316–317. doi: 10.1126/science.136.3513.316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROCK T. D. Studies on the mode of action of novobiocin. J Bacteriol. 1956 Sep;72(3):320–323. doi: 10.1128/jb.72.3.320-323.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUTTIN G., COHEN G. N., MONOD J., RICKENBERG H. V. La galactoside-perméase d'Escherichia coli. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1956 Dec;91(6):829–857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEBB M. Effects of magnesium on cellular division in bacteria. Science. 1953 Nov 20;118(3073):607–611. doi: 10.1126/science.118.3073.607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


