Abstract
Duncan, Margaret G. (The University of British Columbia, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada) and J. J. R. Campbell. Oxidative assimilation of glucose by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Bacteriol. 84:784–792. 1962—Oxidative assimilation of glucose by washed-cell suspensions of Pseudomonas aeruginosa was studied using C14-labeled substrate. At the time of glucose disappearance, only small amounts of radioactivity were present in the cells, and α-ketoglutaric acid accumulated in the supernatant fluid. Most of the material synthesized by the cells during oxidative assimilation was nitrogenous, the ammonia being supplied by the endogenous respiration. The cold trichloroacetic acid-soluble fraction and the lipid fraction appeared to be important during the early stages of oxidative assimilation, and the largest percentage of the incorporated radioactivity was found in the protein fraction. In the presence of added ammonia, assimilation was greatly increased and no α-ketoglutaric acid was found in the supernatant fluid. Sodium azide partially inhibited incorporation into all major cell fractions, and at higher concentrations depressed the rate of glucose oxidation. During oxidative assimilation, chloramphenicol specifically inhibited the synthesis of protein. Oxidative assimilation of glucose by this organism did not appear to involve the synthesis of a primary product such as is found in the majority of bacteria.
Full text
PDF

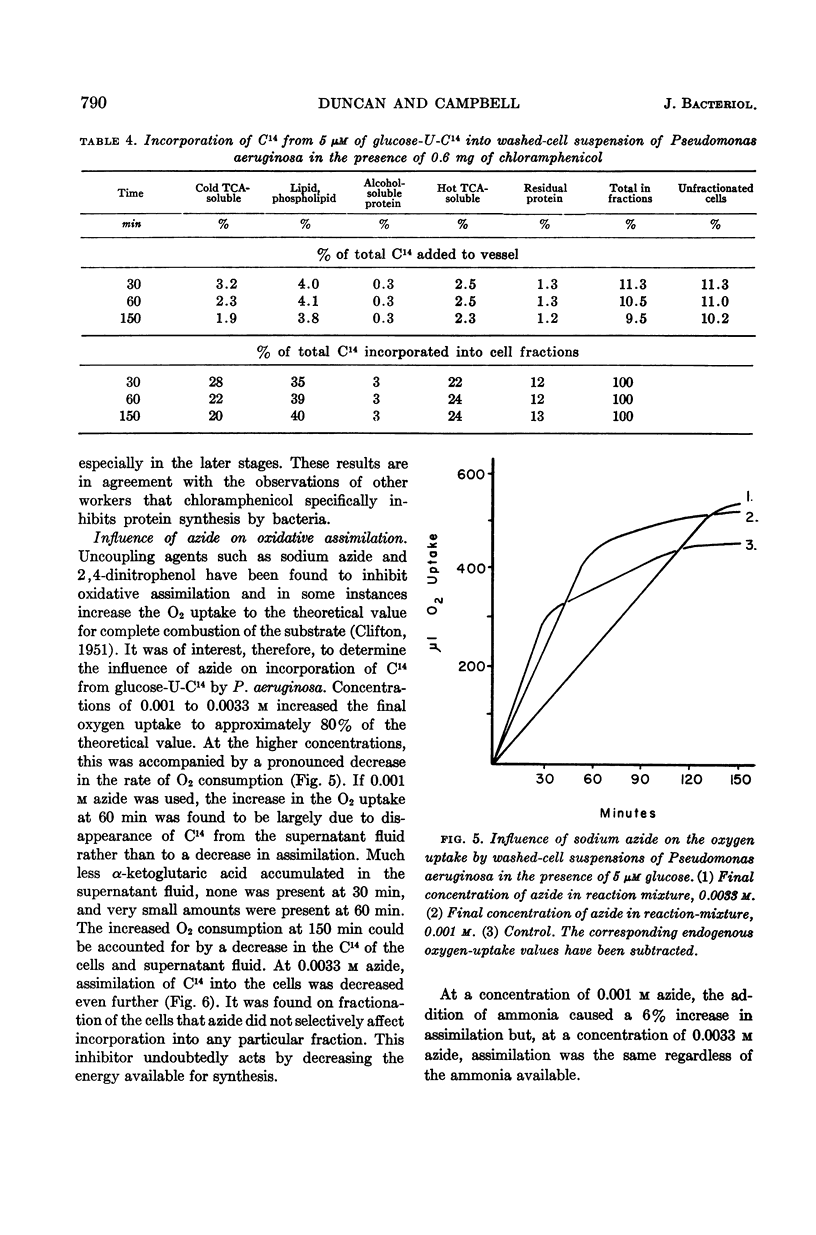
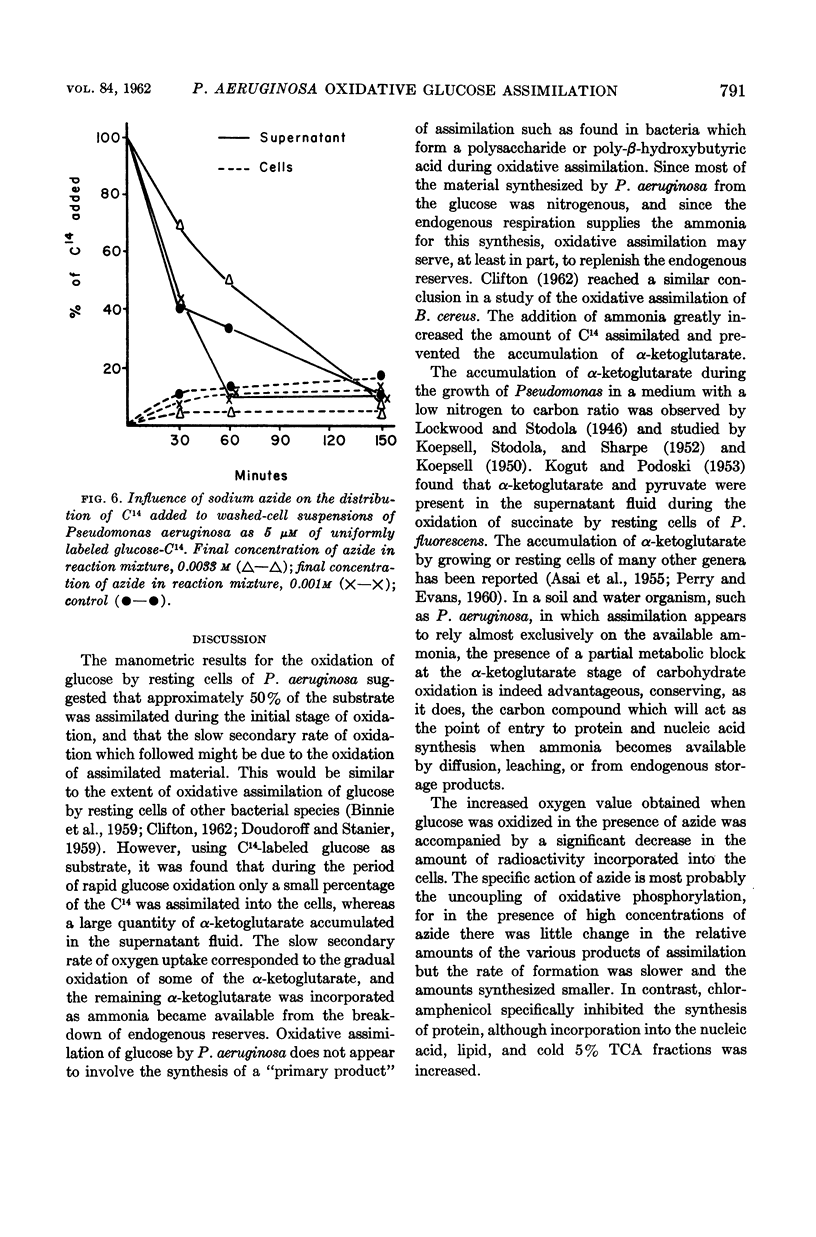

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BINNIE B., DAWES E. A., HOLMS W. H. Metabolism of Sarcina lutea. IV. Patterns of oxidative assimilation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 May 20;40:237–251. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91348-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLIFTON C. E. Oxidative assimilation and distribution of glucose in Bacillus cereus. J Bacteriol. 1962 Jan;83:66–69. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.1.66-69.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLIFTON C. E., SOBEK J. M. Endogenous respiration of Bacillus cereus. J Bacteriol. 1961 Aug;82:252–256. doi: 10.1128/jb.82.2.252-256.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOUDOROFF M., STANIER R. Y. Role of poly-beta-hydroxybutyric acid in the assimilation of organic carbon by bacteria. Nature. 1959 May 23;183(4673):1440–1442. doi: 10.1038/1831440a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EL HAWARY M. F. S., THOMPSON R. H. S. Separation and estimation of blood keto acids by paper chromatography. Biochem J. 1953 Feb;53(3):340–347. doi: 10.1042/bj0530340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRONLUND A. F., CAMPBELL J. J. Nitrogenous compounds as substrates for endogenous respiration in microorganisms. J Bacteriol. 1961 May;81:721–724. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.5.721-724.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER G. D., GOODSALL R. A. Lipo-amino acid complexes from Bacillus megaterium and their possible role in protein synthesis. Biochem J. 1961 Mar;78:564–570. doi: 10.1042/bj0780564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOEPSELL H. J. Gluconate oxidation by Pseudomonas fluorescens. J Biol Chem. 1950 Oct;186(2):743–751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOGUT M., PODOSKI E. P. Oxidative pathways in a fluorescent Pseudomonas. Biochem J. 1953 Dec;55(5):800–811. doi: 10.1042/bj0550800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACRAE R. M., WILKINSON J. F. Poly-beta-hyroxybutyrate metabolism in washed suspensions of Bacillus cereus and Bacillus megaterium. J Gen Microbiol. 1958 Aug;19(1):210–222. doi: 10.1099/00221287-19-1-210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERRY J. J., EVANS J. B. Oxidative metabolism of lactate and acetate by Micrococcus sodonensis. J Bacteriol. 1960 Jan;79:113–118. doi: 10.1128/jb.79.1.113-118.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN R. A., ELLS A. F., CAMPBELL J. J. Endogenous respiration of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1960 Jun;79:875–879. doi: 10.1128/jb.79.6.875-879.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


